Abstract
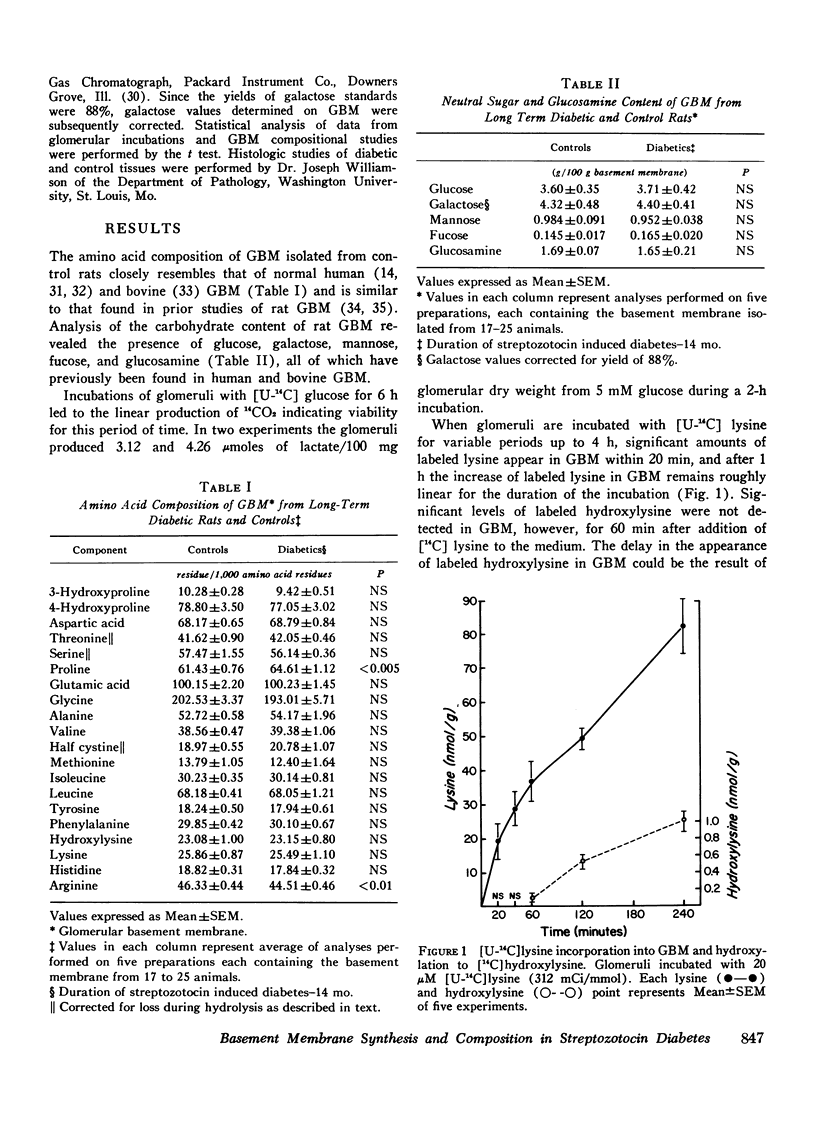
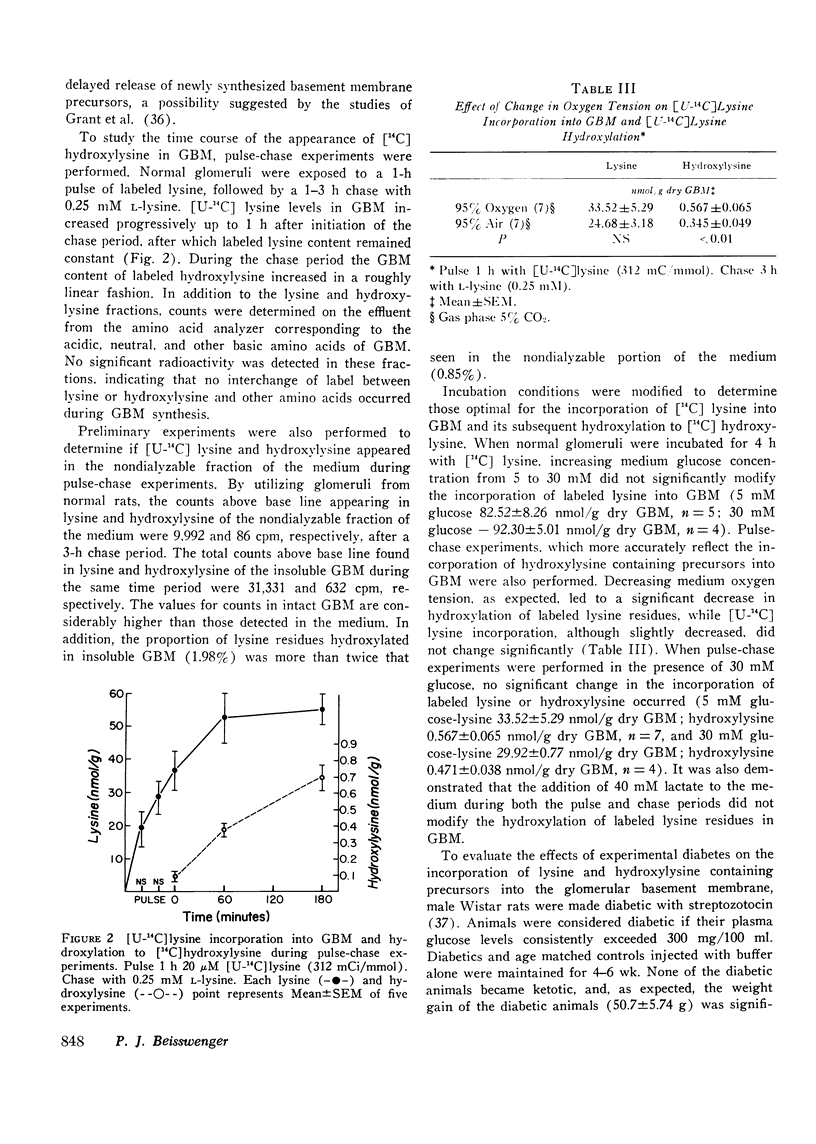
To study the effect of streptozotocin induced diabetes on glomerular basement membrane (GBM) synthesis, an isolated rat glomerular preparation has been developed, and its metabolic properties have been defined. The chemical composition of normal rat GBM isolated from this preparation closely resembles human GBM. Incubation with [U-14C] lysine leads to prompt incorporation of label into GBM and the subsequent appearance of labeled hydroxylysine. A 1-h lag before detection of labeled hydroxylysine in GBM suggests a delay in the release of GBM precursors. Significantly lower counts appeared in the nondialyzable fraction of the medium than in insoluble GBM during pulse-chase experiments, and labeled hydroxylysine accounted for a lower portion of the total counts in the medium (0.85%) than in the GBM (1.98%). Isolated glomeruli were prepared from streptozotocin diabetic rats of 4-6 wks duration. After incubation with [ U-14C] lysine recovery of label in diabetic GBM (88.98+/-8.26 nmol/g GBM) did not differ from age matched controls (82.52 +/- 8.26 nmol/g GBM). In pulse-chase experiments recovery of label in hydroxylysine of diabetic GBM (o.473 +/- 0.082 nmol/g GBM) did not differ from age matched controls (0567+/-0.065 nmol/g GBM). These findings indicate normal rates of GBM synthesis and hydroxylation of lysine residues in animals with streptozotocin diabetes.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERGSTRAND A., BUCHT H. Electron microscopic investigations on the glomerular lesions in diabetes mellitus (diabetic glomerulosclerosis). Lab Invest. 1957 Jul-Aug;6(4):293–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOODWORTH J. M., Jr Diabetic microangiopathy. Diabetes. 1963 Mar-Apr;12:99–114. doi: 10.2337/diab.12.2.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisswenger P. G., Spiro R. G. Human glomerular basement membrane: chemical alteration in diabetes mellitus. Science. 1970 May 1;168(3931):596–598. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3931.596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisswenger P. J. Specificity of the chemical alteration in the diabetic glomerular basement membrane. Diabetes. 1973 Oct;22(10):744–750. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.10.744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisswenger P. J., Spiro R. G. Studies on the human glomerular basement membrane. Composition, nature of the carbohydrate units and chemical changes in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1973 Mar;22(3):180–193. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.3.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau E., Michael A. F. Rat glomerular basement membrane composition and metabolism in aminonucleoside nephrosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Jan;77(1):97–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloodworth J. M., Jr, Engerman R. L., Powers K. L. Experimental diabetic microangiopathy. I. Basement membrane statistics in the dog. Diabetes. 1969 Jul;18(7):455–458. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.7.455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. P., Vogt C. Evidence for enhanced basement membrane synthesis and lysine hydroxylation in renal glomerulus in experimental diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Dec 18;49(6):1542–1546. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90516-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deckert T., Poulsen J. E. Prognosis for juvenile diabetics with late diabetic manifestations. Acta Med Scand. 1968 Apr;183(4):351–356. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1968.tb10490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENTMACHER P. S., ROOT H. F., MARKS H. H. LONGEVITY OF DIABETIC PATIENTS IN RECENT YEARS. Diabetes. 1964 Jul-Aug;13:373–377. doi: 10.2337/diab.13.4.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARQUHAR M. G., HOPPER J., Jr, MOON H. D. Diabetic glomerulosclerosis: electron and light microscopic studies. Am J Pathol. 1959 Jul-Aug;35(4):721–753. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong J. S., Drummond K. N. Method for preparation of glomeruli for metabolic studies. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Jun;71(6):1034–1039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDENBERG S., ALEX M., JOSHI R. A., BLUMENTHAL H. T. Nonatheromatous peripheral vascular disease of the lower extremity in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1959 Jul-Aug;8(4):261–273. doi: 10.2337/diab.8.4.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant M. E., Harwood R., Williams I. F. The biosynthesis of basement-membrane collagen by isolated rat glomeruli. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):531–540. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant M. E., Kefalides N. A., Prockop D. J. The biosynthesis of basement membrane collagen in embryonic chick lens. I. Delay between the synthesis of polypeptide chains and the secretion of collagen by matrix-free cells. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 10;247(11):3539–3544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson B. G., Spiro R. G. Fractionation of glycoprotein components of the reduced alkylated renal glomerular basement membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 10;247(13):4239–4247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hägg E. Glomerular basement membrane thickening in rats with long-term alloxan diabetes. A quantitative electron microscopic study. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1974 Mar;82(2):211–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb03845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junod A., Lambert A. E., Stauffacher W., Renold A. E. Diabetogenic action of streptozotocin: relationship of dose to metabolic response. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):2129–2139. doi: 10.1172/JCI106180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURTZ S. M., MCMANUS J. F. A reconsideration of the development, structure, and disease of the human renal glomerulus. Am Heart J. 1959 Sep;58:357–371. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(59)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefalides N. A. Biochemical properties of human glomerular basement membrane in normal and diabetic kidneys. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):403–407. doi: 10.1172/JCI107573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalifa A., Cohen M. P. Glomerular protocollagen lysyl-hydroxylase activity in streptozotocin diabetes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 28;386(1):332–339. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90275-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Like A. A., Lavine R. L., Poffenbarger P. L., Chick W. L. Studies in the diabetic mutant mouse. VI. Evolution of glomerular lesions and associated proteinuria. Am J Pathol. 1972 Feb;66(2):193–224. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahieu P., Winand R. J. Chemical structure of tubular and glomerular basement membranes of human kidney. Isolation, purification, carbohydrate and amino acid composition. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Feb;12(3):410–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meezan E., Brendel K., Ulreich J., Carlson E. C. Properties of a pure metabolically active glomerular preparation from rat kidneys. I. Isolation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Nov;187(2):332–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterby R. Morphometric studies of the peripheral glomerular basement membrane in early juvenile diabetes. I. Development of initial basement membrane thickening. Diabetologia. 1972 Apr;8(2):84–92. doi: 10.1007/BF01235631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterby R. Morphometric studies of the peripheral glomerular basement membrane. II. Topography of the initial lesions. Diabetologia. 1973 Apr;9(2):108–114. doi: 10.1007/BF01230689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G. Glycoproteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1970;39:599–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.39.070170.003123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G., Spiro M. J. Effect of diabetes on the biosynthesis of the renal glomerular basement membrane. Studies on the glucosyltransferase. Diabetes. 1971 Oct;20(10):641–648. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.10.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G. Studies on the renal glomerular basement membrane. Nature of the carbohydrate units and their attachment to the peptide portion. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1923–1932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G. Studies on the renal glomerular basement membrane. Preparation and chemical composition. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1915–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treser G., Oppermann W., Ehrenreich T., Lange K., Levine R., Camerini-Davalos R. A. Glomerular lesions in a strain of genetically diabetic mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Dec;129(3):820–823. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. The origin, turnover and removal of glomerular basement-membrane. J Pathol. 1973 Jul;110(3):233–244. doi: 10.1002/path.1711100306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. G., Hulter H. N. Some observations of the metabolic activity of glomeruli. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 1970;81:174–183. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westberg N. G., Michael A. F. Human glomerular basement membrane. Preparation and composition. Biochemistry. 1970 Sep 15;9(19):3837–3846. doi: 10.1021/bi00821a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westberg N. G., Michael A. F. Human glomerular basement membrane: chemical composition in diabetes mellitus. Acta Med Scand. 1973 Jul-Aug;1-2(1):39–47. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1973.tb19411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bruchhausen F. Zur Biosynthese der Basalmembran. Die Verwertung von Prolin nd Glucose zum Aufbau von Bestandteilen der glomerulären Basalmembran in vitro. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmakol. 1971;268(1):83–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


