Abstract
Lead intoxication is accompanied by an acquired deficiency of erythrocyte pryimidine-specific, 5'-nucleotidase. Genetically determined deficiency of this enzyme is associated with chronic hemolysis, marked basophilic stippling of erythrocytes on stained blood films, and unique intraerythrocytic accumulations of pyrimidine-containing nucleotides. The present report documents that lead-induced deficiency when sufficiently severe gives rise to findings similar to the hereditary disorder. Whereas pyrimidine-containing nucleotides are virutally absent in the erythrocytes of normal and reticulocyte-rich blood, 12% of erythrocyte nucloetides in the blood of a patient with lead intoxication contained cytidine. Nucleotidase activity was about 25% that in normal erythrocytes and 15% or less of that expected in comparable reticulocyte-rich blood. The distribution of nucleotidase activity in patient erythrocytes is unknown, and much more severe deficiency could have been present in subsets of the cell populations analyzed. The findings indicate that the hemolytic anemia and increased basophilic stippling characteristic of certain cases of lead intoxication may share a common etiology with essentially identical features of the genetically determined disorder.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albahary C. Lead and hemopoiesis. The mechanism and consequences of the erythropathy of occupational lead poisoning. Am J Med. 1972 Mar;52(3):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90025-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angle C. R., McIntire M. S. Red cell lead, whole blood lead, and red cell enzymes. Environ Health Perspect. 1974 May;7:133–137. doi: 10.1289/ehp.747133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Human red cell glycolytic intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):449–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEUTLER E., DURON O., KELLY B. M. Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 May;61:882–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BISHOP C. Changes in the nucleotides of stored or incubated human blood. Transfusion. 1961 Nov-Dec;1:349–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.1961.tb00073.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BISHOP C., RANKINE D. M., TALBOTT J. H. The nucleotides in normal human blood. J Biol Chem. 1959 May;234(5):1233–1237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baughan M. A., Valentine W. N., Paglia D. E., Ways P. O., Simons E. R., DeMarsh Q. B. Hereditary hemolytic anemia associated with glucosephosphate isomerase (GPI) deficiency--a new enzyme defect of human erythrocytes. Blood. 1968 Aug;32(2):236–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonsignore D. L'attività ala-deidratasica eritrocitaria quale test diagnostico nel saturnismo professionale. Med Lav. 1966 Nov;57(11):647–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE LUCA C., STEVENSON J. H., Jr, KAPLAN E. Simultaneous multiple-column chromatography: its application to the separation of the adenine nucleotides of human erythrocytes. Anal Biochem. 1962 Jul;4:39–45. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink K., Adams W. S. Paper chromatographic data for purines, pyrimidines and derivatives in a variety of solvents. J Chromatogr. 1966 Apr;22(1):118–129. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)97077-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. Lead poisoning and haem biosynthesis. Br J Haematol. 1972 Nov;23(5):521–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb07087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. Lead poisoning as a disorder of heme synthesis. Semin Hematol. 1968 Oct;5(4):424–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasan J., Vihko V., Hernberg S. Deficient red cell membrane /Na++K+/-ATPase in lead poisoning. Arch Environ Health. 1967 Feb;14(2):313–318. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1967.10664738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Mills D. C. The adenylate kinase of human plasma, erythrocytes and platelets in relation to the degradation of adenosine diphosphate in plasma. Biochem J. 1967 Jun;103(3):773–784. doi: 10.1042/bj1030773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
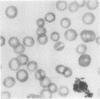
- JENSEN W. N., MORENO G. D., BESSIS M. C. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION OF BASOPHILIC STIPPLING IN RED CELLS. Blood. 1965 Jun;25:933–943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOUTRAS G. A., HATTORI M., SCHNEIDER A. S., EBAUGH F. G., Jr, VALENTINE W. N. STUDIES ON CHROMATED ERYTHROCYTES. EFFECT OF SODIUM CHROMATE ON ERYTHROCYTE GLUTATHIONE REDUCTASE. J Clin Invest. 1964 Feb;43:323–331. doi: 10.1172/JCI104917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDEL P., CHAMBON P., KARON H., KULIC I., SERTER M. [Free nucleotides in red blood cells and reticulocytes]. Folia Haematol Int Mag Klin Morphol Blutforsch. 1962;78:525–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLS G. C., SUMMERS L. B. The metabolism of nucleotides and other phosphate esters in erythrocytes during in vitro incubation at 37 degrees. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Sep;84:7–14. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90548-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minakami S., Suzuki C., Saito T., Yoshikawa H. Studies on erythrocyte glycolysis. I. Determination of the glycolytic intermediates in human erythrocytes. J Biochem. 1965 Dec;58(6):543–550. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paglia D. E., Valentine W. N. Characteristics of a pyrimidine-specific 5'-nucleotidase in human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 25;250(20):7973–7979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paglia D. E., Valentine W. N., Dahlgren J. G. Effects of low-level lead exposure on pyrimidine 5'-nucleotidase and other erythrocyte enzymes. Possible role of pyrimidine 5'-nucleotidase in the pathogenesis of lead-induced anemia. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1164–1169. doi: 10.1172/JCI108192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paglia D. E., Valentine W. N. Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Jul;70(1):158–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers L. E., Battles N. D., Reimold E. W., Sartain P. Erythrocyte enzymes in experimental lead poisoning. Arch Toxikol. 1971;28(3):202–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00330249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNEIDER A. S., VALENTINE W. N., HATTORI M., HEINS H. L., Jr HEREDITARY HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA WITH TRIOSEPHOSPHATE ISOMERASE DEFICIENCY. N Engl J Med. 1965 Feb 4;272:229–235. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196502042720503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholar E. M., Brown P. R., Parks R. E., Jr, Calabresi P. Nucleotide profiles of the formed elements of human blood determined by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Blood. 1973 Jun;41(6):927–936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Secchi G. C., Ambrosi L., Rezzonico A. Ricerche sulla Na+-K+-ATPasi e sulla acetilcolinesterasi delle membrane eritrocitarie nell'anemia saturnina. Med Lav. 1968 Oct;59(10):593–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine W. N., Fink K., Paglia D. E., Harris S. R., Adams W. S. Hereditary hemolytic anemia with human erythrocyte pyrimidine 5'-nucleotidase deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1974 Oct;54(4):866–879. doi: 10.1172/JCI107826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine W. N., Kürschner K. K. Studies on human erythrocyte nucleotide metabolism. I. Monisotopic methodologies. Blood. 1972 May;39(5):666–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine W. N., Oski F. A., Paglia D. E., Baughan M. A., Schneider A. S., Naiman J. L. Hereditary hemolytic anemia with hexokinase deficiency. Role of hexokinase in erythrocyte aging. N Engl J Med. 1967 Jan 5;276(1):1–11. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196701052760101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine W. N., Paglia D. E., Neerhout R. C., Konrad P. N. Erythrocyte glyoxalase II deficiency with coincidental hereditary elliptocytosis. Blood. 1970 Dec;36(6):797–808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldron H. A. The anaemia of lead poisoning: a review. Br J Ind Med. 1966 Apr;23(2):83–100. doi: 10.1136/oem.23.2.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. M., Harvey D. R. Defective synthesis of and globin chains in lead poisoning. Nature. 1972 Mar 10;236(5341):71–73. doi: 10.1038/236071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]