Abstract
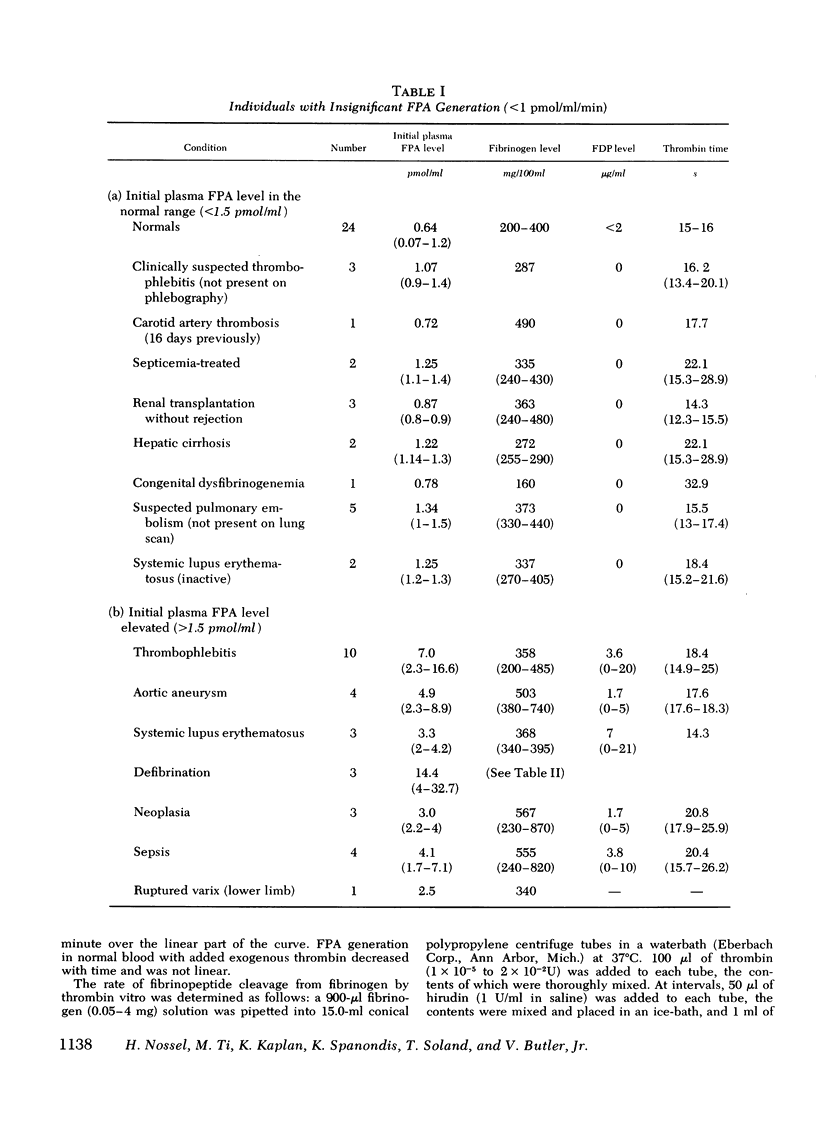
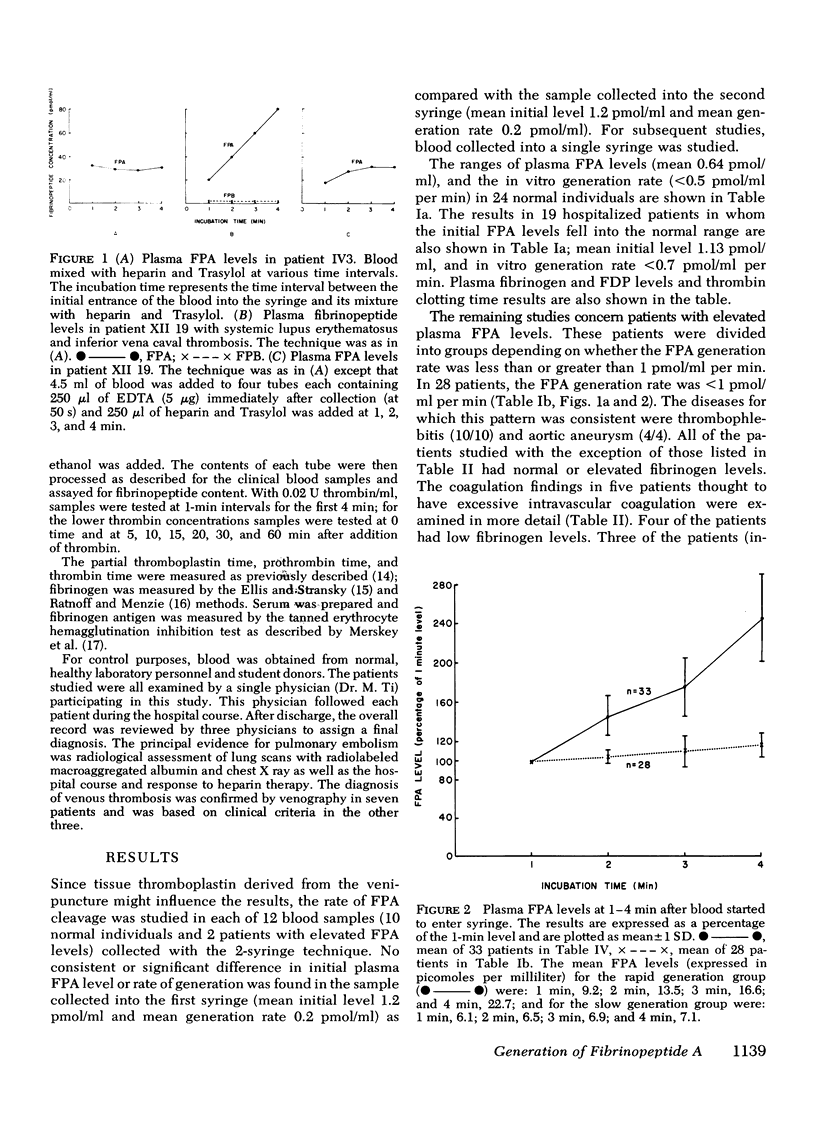
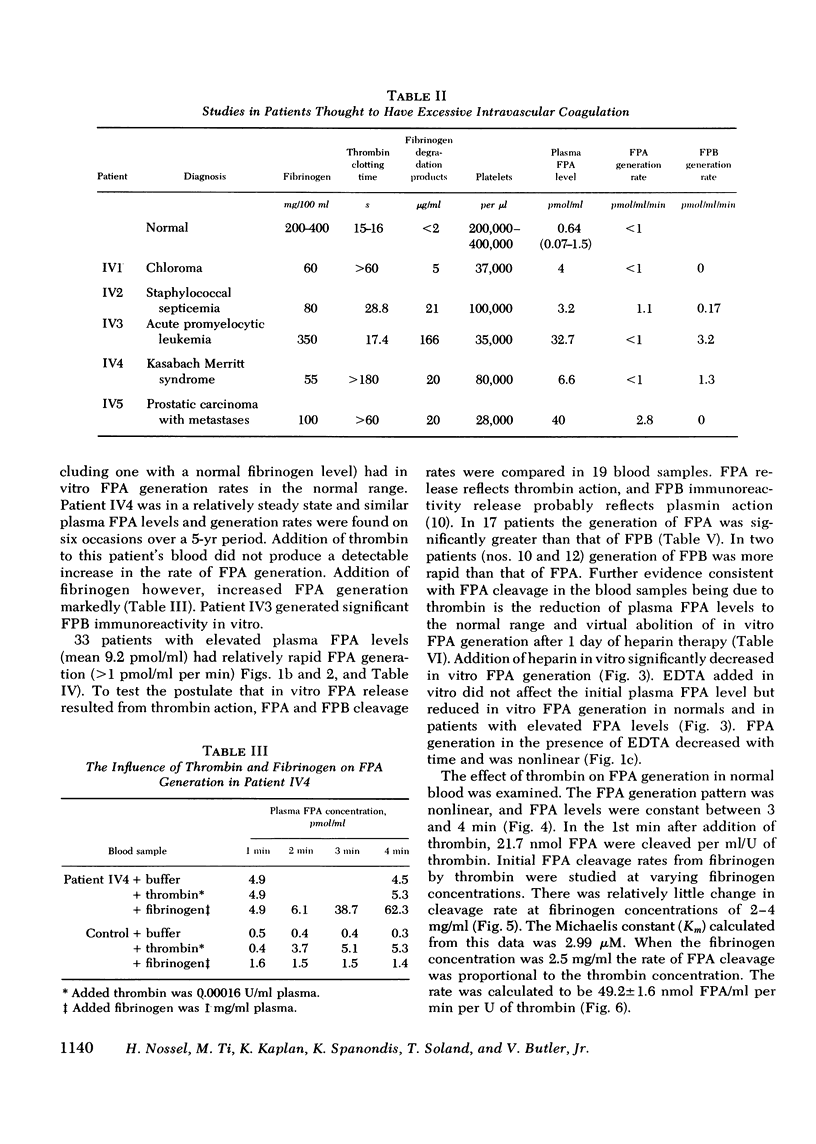
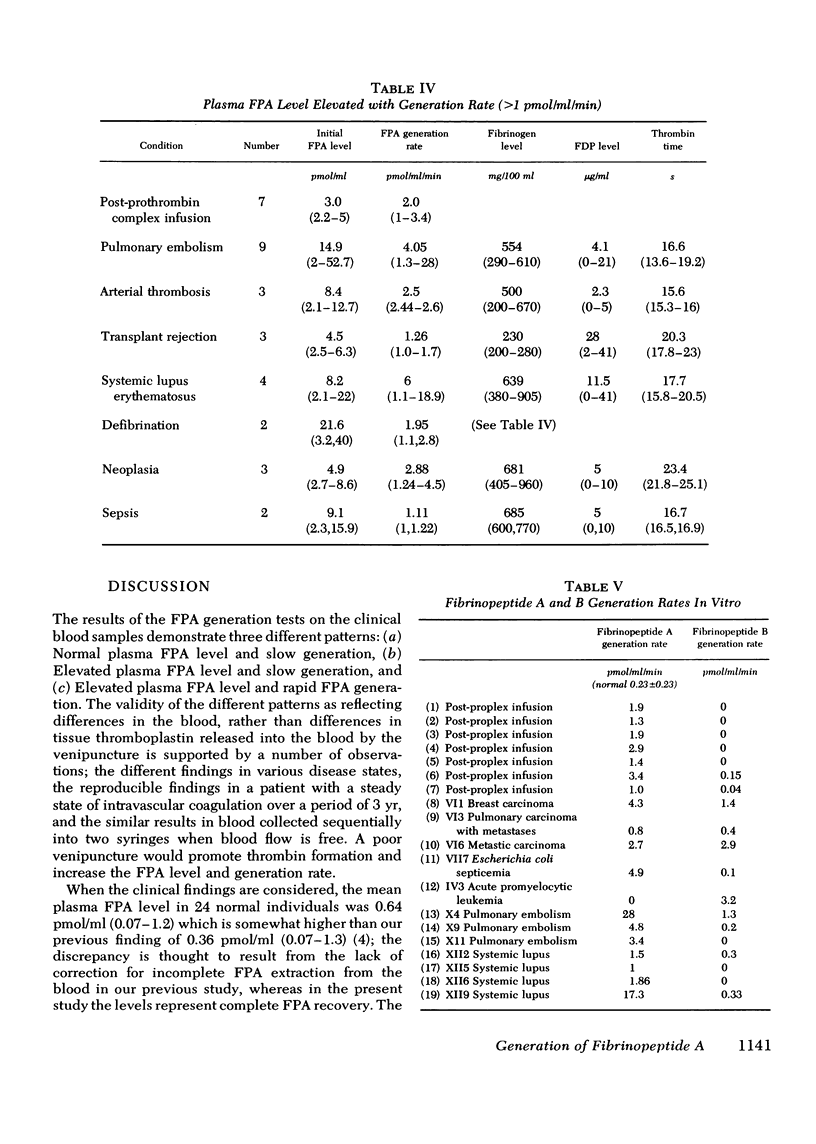
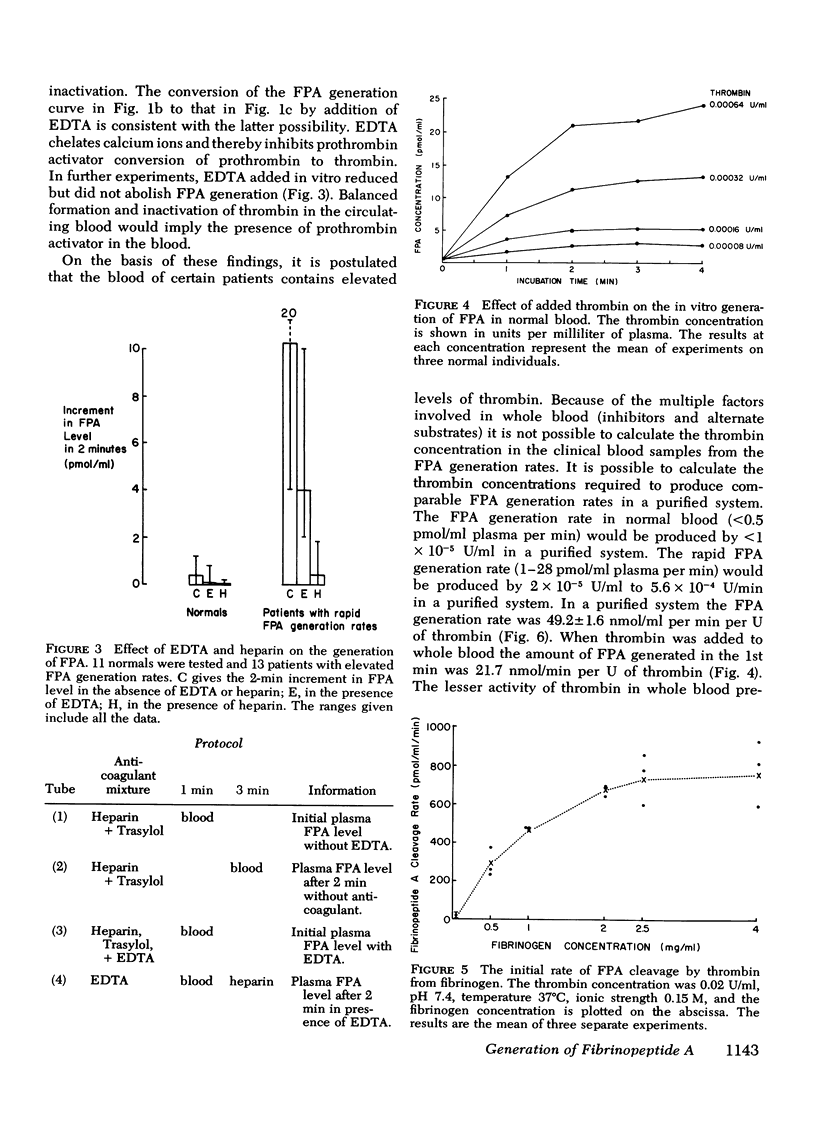
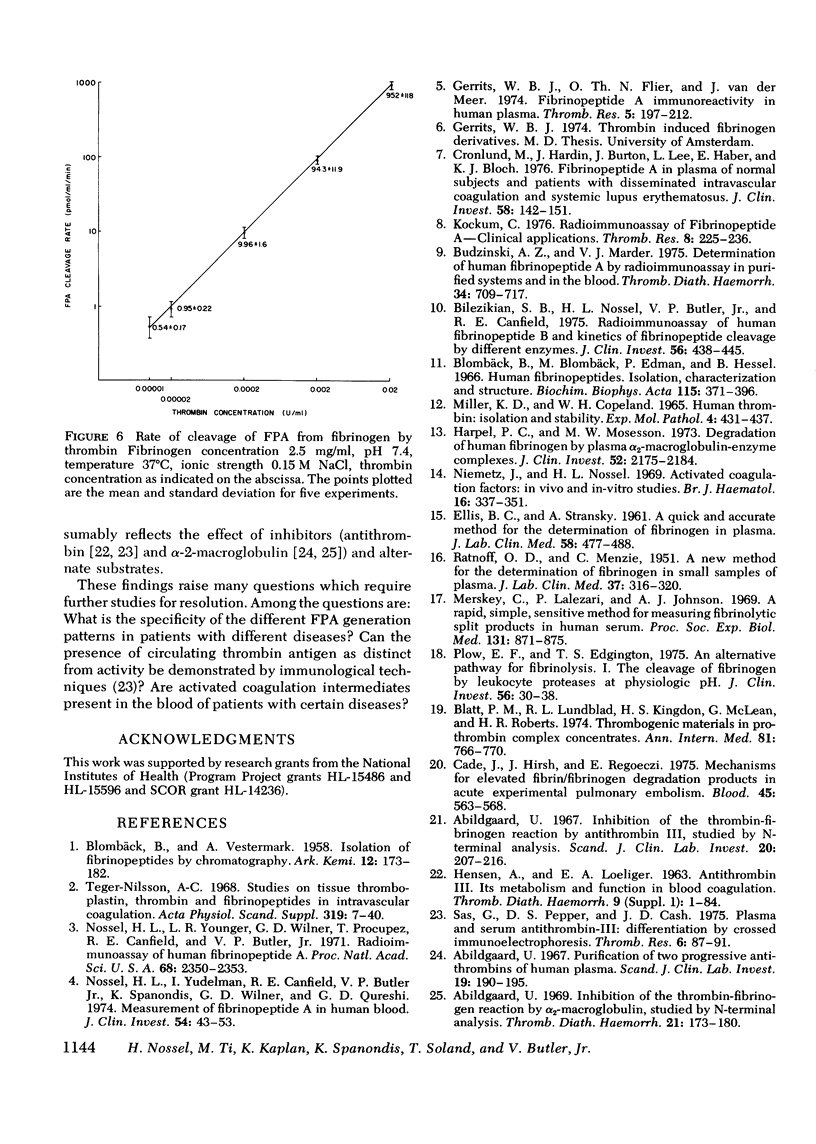
Plasma fibrinopeptide A (FPA) concentrations were measured in clinical blood samples incubated in the collecting syringe for different time periods before addition to heparin and Trasylol, and the rate of in vitro generation of FPA was calculated as the mean increment in FPA concentration per minute over the linear portion of the generation curve. 36 normal individuals had a mean plasma FPA level of 0.64 +/- 0.56 pmol/ml and an FPA generation rate of less than 0.5 pmol/ml per min. Clinical samples with elevated plasma FPA levels manifested slow (less than 1 pmol/ml per min) (28 patients) or rapid FPA generation (greater than 1 pmol/ml per min) (33 patients). Slow FPA generation was found in 10/10 patients with venous thrombosis, in 4/4 with aortic aneurysm, and in several patients with acquired hypofibrinogenemia. In one such patient, addition of fibrinogen resulted in rapid FPA generation whereas thrombin addition was without effect. Rapid FPA generation was generally linear, was usually associated with slower fibrinopeptide B generation and was inhibited by parenteral or in vitro heparin. It is thought to reflect increased thrombin activity and was seen in patients with pulmonary embolism, active systemic lupus erythematosus, renal transplant rejection, and after infusion of prothrombin concentrates. The initial rate of FPA cleavage by thrombin at fibrinogen concentrations from 0.05 to 4 mg/ml showed little change between 2 and 4 mg/ml with a Km of 2.99 muM. At a fibrinogen concentration of 2.5 mg/ml the FPA cleavage rate was 49.2 +/- 1.6 nmol/ml per min per U of thrombin. Exogenous thrombin added to normal blood generated 21.7 nmol/ml per U of thrombin FPA in the first minute with a nonlinear pattern reflecting inactivation of thrombin and the presence of alternative substrates. Hence, the thrombin concentration in the blood cannot be calculated from the FPA generation rate. The FPA generation rates in clinical samples with rapid generation (1-28 pmol/ml per min) could be produced by 2 X 10(-5) to 5.6 X 10(-4) thrombin U/ml acting on purified fibrinogen at physiological conditions of pH, ionic strength, and temperature.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abildgaard U. Inhibition of the thrombin-fibrinogen reaction by alpha2-macroglobulin, studied by N-terminal analysis. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1969 Apr 30;21(2):173–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilezikian S. B., Nossel H. L., Butler V. P., Jr, Canfield R. E. Radioimmunoassay of human fibrinopeptide B and kinetics of fibrinopeptide cleavage by different enzymes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Aug;56(2):438–445. doi: 10.1172/JCI108110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt P. M., Lundblad R. L., Kingdon H. S., McLean G., Roberts H. R. Thrombogenic materials in prothrombin complex concentrates. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Dec;81(6):766–770. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-81-6-766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blombäck B., Blombäck M., Edman P., Hessel B. Human fibrinopeptides. Isolation, characterization and structure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 28;115(2):371–396. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90437-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budzynski A. Z., Marder V. J. Determination of human fibrinopeptide A by radioimmunoassay in purified systems and in the blood. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1975 Dec 15;34(3):709–717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cade J., Hirsh J., Regoeczi E. Mechanisms for elevated fibrin/fibrinogen degradation products in acute experimental pulmonary embolism. Blood. 1975 Apr;45(4):563–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronlund M., Hardin J., Burton J., Lee L., Haber E., Bloch K. J. Fibrinopeptide A in plasma of normal subjects and patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation and systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):142–151. doi: 10.1172/JCI108443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIS B. C., STRANSKY A. A quick and accurate method for the determination of fibronogen in plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1961 Sep;58:477–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrits W. B., Flier O. T., van der Meer J. Fibrinopeptide A immunoreactivity in human plasma. Thromb Res. 1974 Aug;5(2):197–212. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(74)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C., Mosesson M. W. Degradation of human fibrinogen by plasms alpha2-macroglobulin-enzyme complexes. J Clin Invest. 1973 Sep;52(9):2175–2184. doi: 10.1172/JCI107402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEAN G., RACINE L., MARX R., GAUTIER A. [On the presence of neutral fats in normal and pathological human thrombocytes]. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1963 Apr 15;9:1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kockum C. Radioimmunoassay of fibrinopeptide A-clinical applications. Thromb Res. 1976 Feb;8(2):225–236. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90265-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER K. D., COPELAND W. H. HUMAN THROMBIN: ISOLATION AND STABILITY. Exp Mol Pathol. 1965 Aug;26:431–437. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(65)90051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merskey C., Lalezari P., Johnson A. J. A rapid, simple, sensitive method for measuring fibrinolytic split products in human serum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jul;131(3):871–875. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemetz J., Nossel H. L. Activated coagulation factors: in-vivo and in-vitro studies. Br J Haematol. 1969 Apr;16(4):337–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb00411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossel H. L., Younger L. R., Wilner G. D., Procupez T., Canfield R. E., Butler V. P., Jr Radioimmunoassay of human fibrinopeptide A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2350–2353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossel H. L., Yudelman I., Canfield R. E., Butler V. P., Jr, Spanondis K., Wilner G. D., Qureshi G. D. Measurement of fibrinopeptide A in human blood. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jul;54(1):43–53. doi: 10.1172/JCI107749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Edgington T. S. An alternative pathway for fibrinolysis. I. The cleavage of fibrinogen by leukocyte proteases at physiologic pH. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jul;56(1):30–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI108076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., MENZIE C. A new method for the determination of fibrinogen in small samples of plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Feb;37(2):316–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sas G., Pepper D. S., Cash J. D. Plasma and serum antithrombin - III: differentiation by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Thromb Res. 1975 Jan;6(1):87–91. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(75)90153-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiger-Nilsson A. C. Studies on tissue thromboplastin, thrombin and fibrinopeptides in intravascular coagulation. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1968;319:1–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


