Abstract
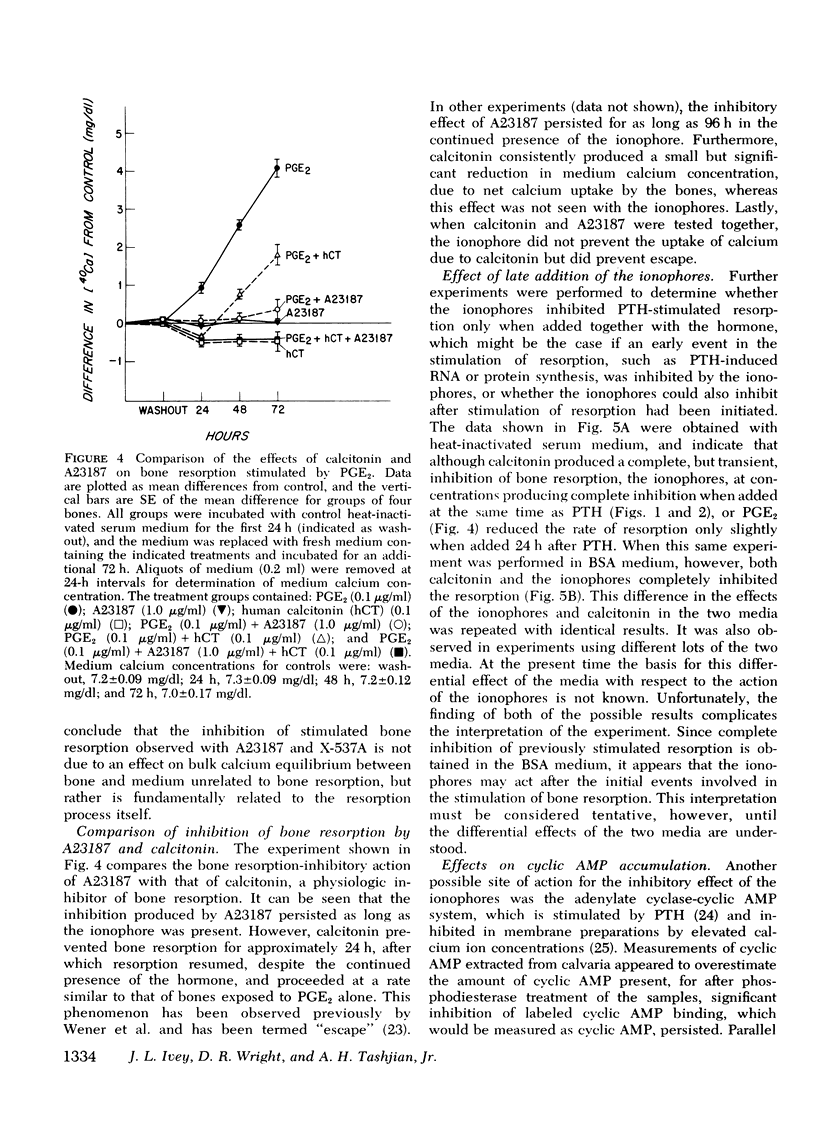
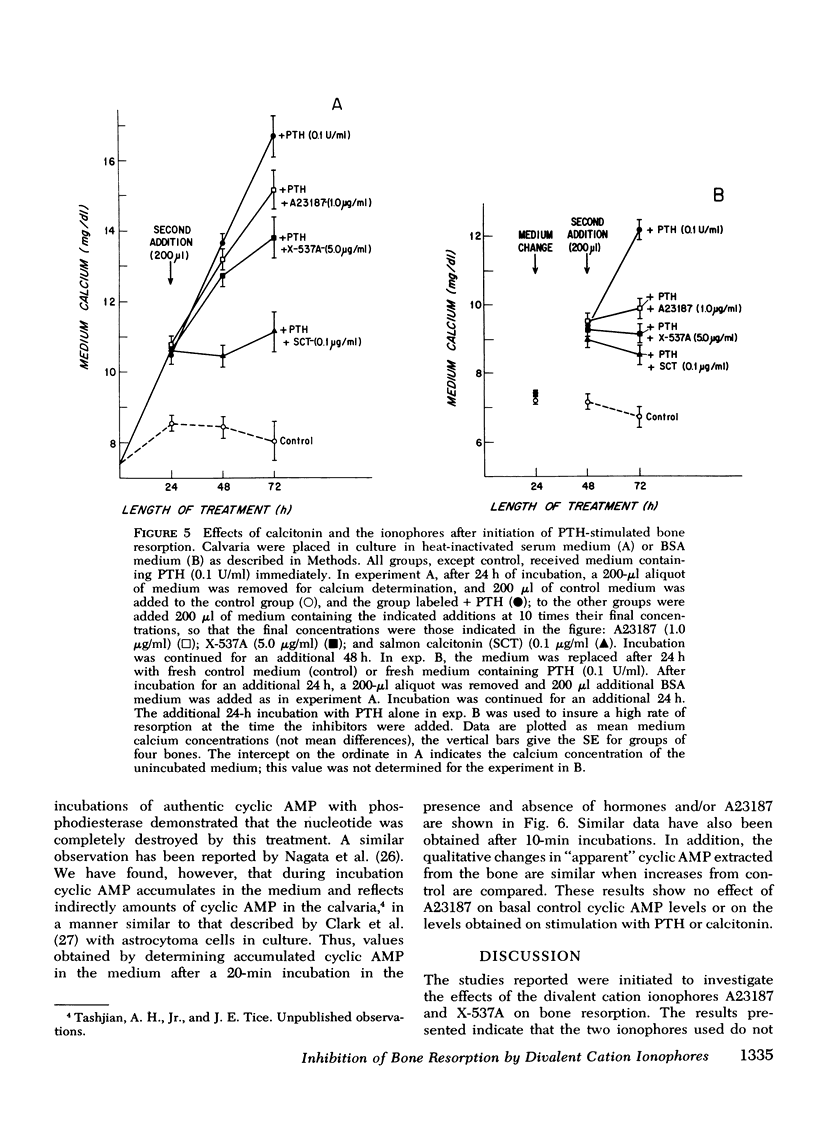
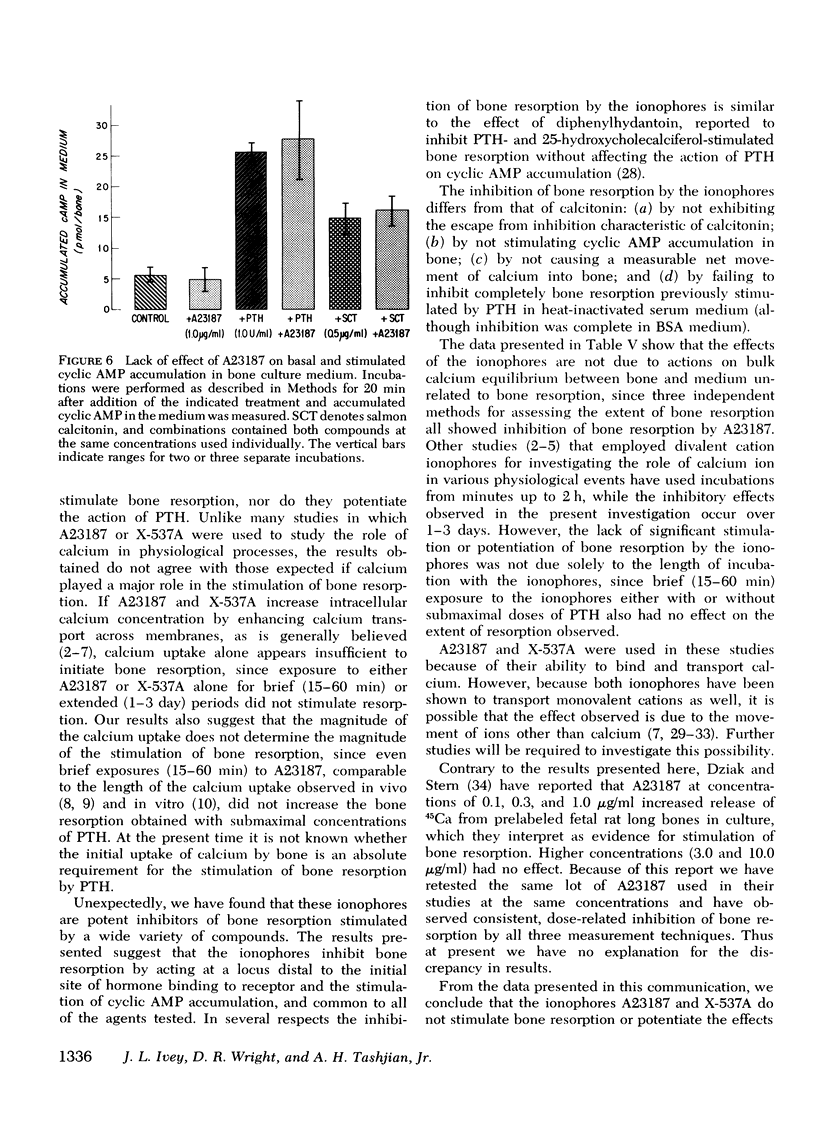
The ionophores A23187 and X-537A were used as probes to investigate the possible role of calcium uptake by bone as a mediator for the stimulation of bone resorption induced by parathyroid hormone (PTH) and other agents in cultured mouse calvaria. The ionophores alone at concentrations from 1 nM to 20 muM did not stimulate bone resorption, nor did they potentiate bone resorption stimulated by submaximal concentrations of PTH after either brief (15-60 min) or extended (1-3 day) exposure to the ionophores. Unexpectedly, we found that the ionophores inhibit in a dose-dependent manner bone resorption stimulated by PTH and a wide variety of other compounds (prostaglandin E2, 1alpha-hydroxycholecalciferol, 3-isobutyl-1-methyl-xanthine, and phorbol myristate acetate). This inhibition was not due to irreversible damage to the bones by the ionophores, because the inhibition was reversible even after 24 h of treatment. Inhibition of bone resorption by the ionophores was observed in media of both high and low calcium concentration, indicating that the inhibition was not due to a critical extracellular calcium concentration. Inhibition by the ionophores differs qualitatively in several ways from that produced by calcitonin, a natural inhibitor of bone resorption. Furthermore, A23187 at 1.0 mug/ml had no effect on the accumulation of cyclic AMP in the medium of either control, PTH- or calcitonin treated calvaria. We conclude that the ionophores A23187 or X537A do not stimulate bone resorption nor potentiate the effects of stimulators of bone resorption; instead they are inhibitors of bone resorption stimulated by a wide variety of compounds.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Case G. D., Vanderkooi J. M., Scarpa A. Physical properties of biological membranes determined by the fluorescence of the calcium ionophore A23187. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 May;162(1):174–185. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caswell A. H., Pressman B. C. Kinetics of transport of divalent cations across sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles induced by ionophores. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Oct 6;49(1):292–298. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase L. R., Aurbach G. D. The effect of parathyroid hormone on the concentration of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in skeletal tissue in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 10;245(7):1520–1526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase L. R., Fedak S. A., Aurbach G. D. Activation of skeletal adenyl cyclase by parathyroid hormone in vitro. Endocrinology. 1969 Apr;84(4):761–768. doi: 10.1210/endo-84-4-761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. B., Gross R., Su Y. F., Perkins J. P. Regulation of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate content in human astrocytoma cells by adenosine and the adenine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5296–5303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane D. E., Douglas W. W. Calcium-induced extrusion of secretory granules (exocytosis) in mast cells exposed to 48-80 or the ionophores A-23187 and X-537A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):408–412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziak R., Stern P. Parathyromimetic effects of the ionophore, A23187, on bone cells and organ cultures. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Aug 18;65(4):1343–1349. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80377-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson P. J., McGivan J. D., Chappell J. B. The action of certain antibiotics on mitochondrial, erythrocyte and artificial phospholipid membranes. The role of induced proton permeability. Biochem J. 1969 Feb;111(4):521–535. doi: 10.1042/bj1110521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins M. V., Harris M., Wills M. R. The effect of phenytoin on parathyroid extract and 25-hydroxycholecalciferol-induced bone resorption: adenosine 3, 5 cyclic monophosphate production. Calcif Tissue Res. 1974;16(2):163–167. doi: 10.1007/BF02008223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsky S. C. Antibiotic interaction with model membranes. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1970;10:119–142. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.10.040170.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata N., Sasaki M., Kimura N., Nakane K. The hypercalcemic effect of parathyroid hormone and skeletal cyclic AMP. Endocrinology. 1975 Mar;96(3):725–731. doi: 10.1210/endo-96-3-725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons J. A., Neer R. M., Potts J. T., Jr Initial fall of plasma calcium after intravenous injection of parathyroid hormone. Endocrinology. 1971 Sep;89(3):735–740. doi: 10.1210/endo-89-3-735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons J. A., Robinson C. J. Calcium shift into bone causing transient hypocalcaemia after injection of parathyroid hormone. Nature. 1971 Apr 30;230(5296):581–582. doi: 10.1038/230581a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer D. R., Lardy H. A. Ionophore A23187: the effect of H+ concentration on complex formation with divalent and monovalent cations and the demonstration of K+ transport in mitochondria mediated by A23187. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 9;15(5):935–943. doi: 10.1021/bi00650a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Properties of ionophores with broad range cation selectivity. Fed Proc. 1973 Jun;32(6):1698–1703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince W. T., Rasmussen H., Berridge M. J. The role of calcium in fly salivary gland secretion analyzed with the ionophore A-23187. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 2;329(1):98–107. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAISZ L. G. BONE RESORPTION IN TISSUE CULTURE. FACTORS INFLUENCING THE RESPONSE TO PARATHYROID HORMONE. J Clin Invest. 1965 Jan;44:103–116. doi: 10.1172/JCI105117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H., Jensen P., Lake W., Friedmann N., Goodman D. B. Cyclic nucleotides and cellular calcium metabolism. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;5:375–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed P. W., Lardy H. A. A23187: a divalent cation ionophore. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6970–6977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson W. G., Peacock M., Atkins D., Webster L. A. The effect of parathyroid hormone on the uptake and release of calcium by bone in tissue culture. Clin Sci. 1972 Nov;43(5):714–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. R., Tashjian A. H., Jr, Levine L. Prostaglandin-stimulated bone resorption by rheumatoid synovia. A possible mechanism for bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1181–1188. doi: 10.1172/JCI108195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinger Z., Eimerl S., Schramm M. A calcium ionophore simulating the action of epinephrine on the alpha-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):128–131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susi F. R., Goldhaber P., Jennings J. M. Histochemical and biochemical study of acid phosphatase in resorbing bone in culture. Am J Physiol. 1966 Oct;211(4):959–962. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.4.959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian A. H., Jr, Voelkel E. F., Goldhaber P., Levine L. Prostaglandins, calcium metabolism and cancer. Fed Proc. 1974 Jan;33(1):81–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian A. H., Jr, Voelkel E. F., Levine L., Goldhaber P. Evidence that the bone resorption-stimulating factor produced by mouse fibrosarcoma cells is prostaglandin E 2 . A new model for the hypercalcemia of cancer. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1329–1343. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Duuren B. L. Tumor-promoting agents in two-stage carcinogenesis. Prog Exp Tumor Res. 1969;11:31–68. doi: 10.1159/000391388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voelkel E. F., Tashjian A. H., Jr, Franklin R., Wasserman E., Levine L. Hypercalcemia and tumor-prostaglandins: the VX2 carcinoma model in the rabbit. Metabolism. 1975 Aug;24(8):973–986. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90089-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wener J. A., Gorton S. J., Raisz L. G. Escape from inhibition or resorption in cultures of fetal bone treated with calcitoninand parathyroid hromone. Endocrinology. 1972 Mar;90(3):752–759. doi: 10.1210/endo-90-3-752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Blondel B., Trueheart P. A., Renold A. E., Sharp G. W. Calcium-induced insulin release in monolayer culture of the endocrine pancreas. Studies with ionophore A23187. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1354–1360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


