Abstract
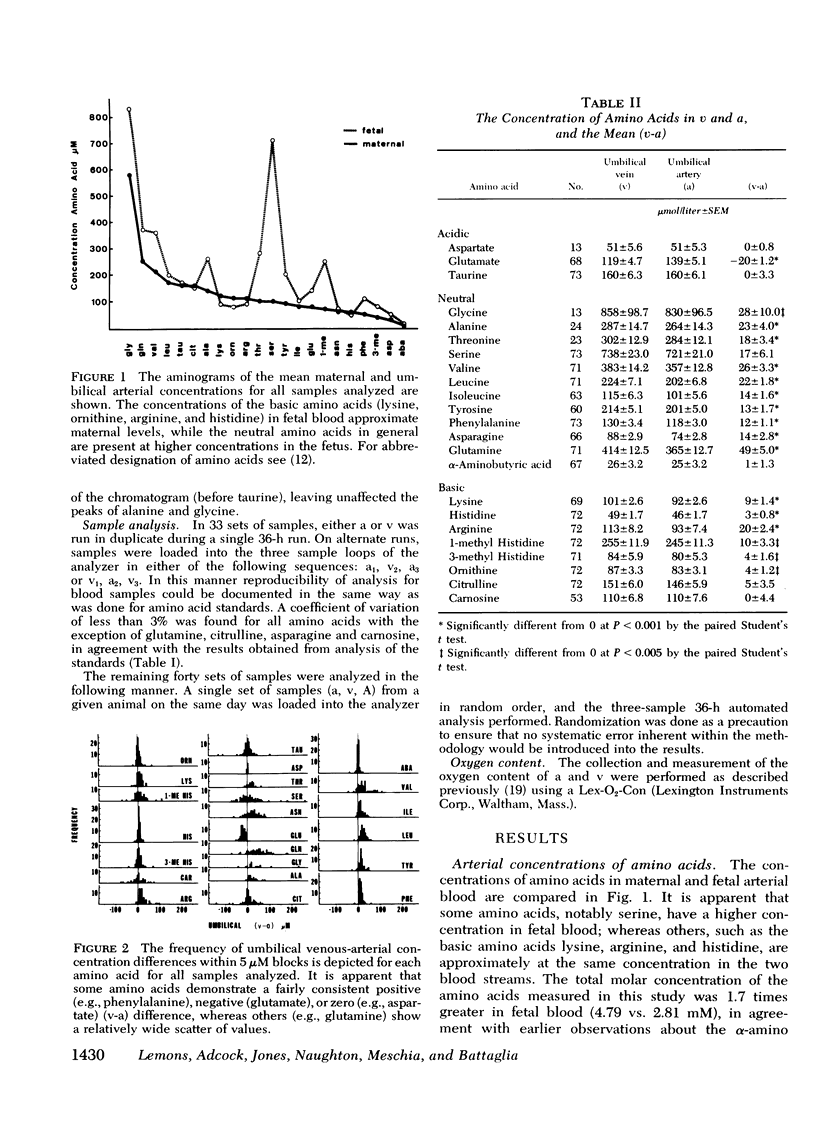
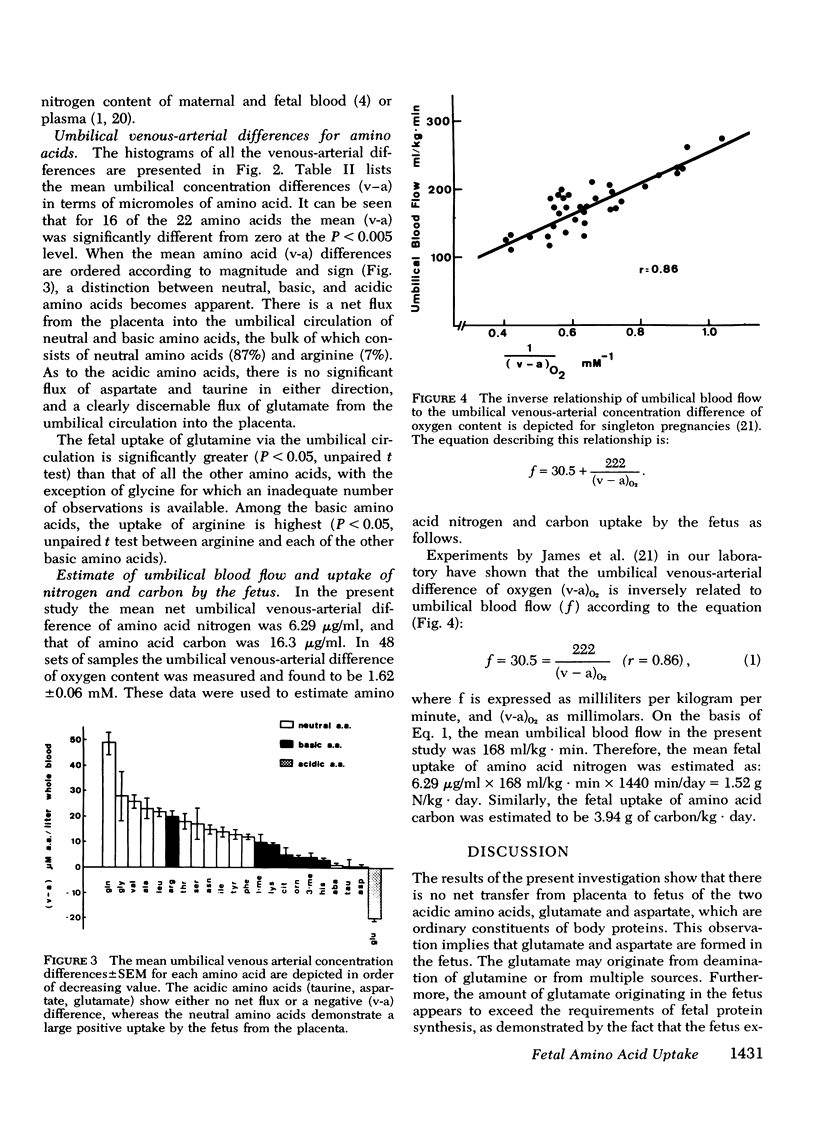
The whole blood concentrations of 22 amino acids were measured in a chronic, unstressed fetal lamb preparations. Samples were taken daily from the umbilical artery, umbilical vein, and maternal artery over the latter quarter of gestation. 73 sets of samples (from the umbilical artery and vein and the maternal artery) from 13 animals were analyzed for amino acid levels. Oxygen contents were determined simultaneously in 48 sets (umbilical artery and vein) to relate fetal oxygen consumption to amino acid uptake via the umbilical circulation. The results indicate that there is no umbilical uptake of the acidic amino acids, glutamate and aspartate; there is, in fact, a net flux of glutamate out of the fetus into the placenta. As both of these amino acids are major constituents of body proteins, the data indicate that they are formed within the fetus. The umbilical uptake of some neutral and basic amino acids (e.g., valine, leucine, isoleucine, arginine, phenylalanine, and tyrosine) is in considerable excess of estimated growth requirements, suggesting that some amino acids undergo extensive transamination and oxidative degradation in the fetus. Finally, the net uptake of nitrogen, carbon, and calories by the growing ovine fetus in the form of amino acids, glucose, and lactate is compared to estimated requirements as determined in previous studies.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burd L. I., Jones M. D., Jr, Simmons M. A., Makowski E. L., Meschia G., Battaglia F. C. Placental production and foetal utilisation of lactate and pyruvate. Nature. 1975 Apr 24;254(5502):710–711. doi: 10.1038/254710a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRUMPLER H. R., DENT C. E., LINDAN O. The amino-acid pattern in human foetal and maternal plasma at delivery. Biochem J. 1950 Aug;47(2):223–227. doi: 10.1042/bj0470223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curet L. B. Physiological aspects of amino acid transport across the placenta. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 1970 Sep;13(3):586–594. doi: 10.1097/00003081-197009000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLENDENING M. B., MARGOLIS A. J., PAGE E. W. Amino acid concentrations in fetal and maternal plasma. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1961 Mar;81:591–593. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(15)33674-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresham E. L., James E. J., Raye J. R., Battaglia F. C., Makowski E. L., Meschia G. Production and excretion of urea by the fetal lamb. Pediatrics. 1972 Sep;50(3):372–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill P. M., Young M. Net placental transfer of free amino acids against varying concentrations. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(2):409–422. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James E. J., Raye J. R., Gresham E. L., Makowski E. L., Meschia G., Battaglia F. C. Fetal oxygen consumption, carbon dioxide production, and glucose uptake in a chronic sheep preparation. Pediatrics. 1972 Sep;50(3):361–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeppsson J. O., Karlsson I. M. Ion-exchange chromatography of physiological sulphur amino acids on a highly crosslinked resin. J Chromatogr. 1972 Oct 5;72(1):93–103. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(72)80011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marliss E. B., Aoki T. T., Pozefsky T., Most A. S., Cahill G. F., Jr Muscle and splanchnic glutmine and glutamate metabolism in postabsorptive andstarved man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):814–817. doi: 10.1172/JCI106552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meschia G., Makowski E. L., Battaglia F. C. The use of indwelling catheters in the uterine and umbilical veins of sheep for a description of fetal acid-base balance and oxygenation. Yale J Biol Med. 1969 Dec;42(3-4):154–165. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan L. P. Energetic efficiency and metabolic transformations. Fed Proc. 1971 Jul-Aug;30(4):1454–1458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellett P. L., Kaba H. Carcass amino acids of the rat under conditions of determination of net protein utilization. J Nutr. 1972 Jan;102(1):61–68. doi: 10.1093/jn/102.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry T. L., Hansen S. Technical pitfalls leading to errors in the quantitation of plasma amino acids. Clin Chim Acta. 1969 Jul;25(1):53–58. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(69)90226-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rattray P. V., Garrett W. N., East N. E., Hinman N. Growth, development and composition of the ovine conceptus and mammary gland during pregnancy. J Anim Sci. 1974 Mar;38(3):613–626. doi: 10.2527/jas1974.383613x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds M. L., Young M. The transfer of free alpha-amino nitrogen across the placental membrane in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1971 May;214(3):583–597. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SETNIKAR I., BARRON D. H. The maternal-fetal nitrogen exchange in the goat. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1958 Jul;43(3):284–294. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1958.sp001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shambaugh G. E., 3rd, Mrozak S. C., Metzger B. E., Freinkel N. Glutamine-dependent carbamyl phosphate synthetase during fetal and neonatal life in the rat. Dev Biol. 1974 Mar;37(1):171–185. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90177-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegink L. D., Pitkin R. M., Reynolds W. A., Filer L. J., Jr, Boaz D. P., Brummel M. C. Placental transfer of glutamate and its metabolites in the primate. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1975 May 1;122(1):70–78. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(75)90616-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsoulos N. G., Schneider J. M., Colwill J. R., Meschia G., Makowski E. L., Battaglia F. C. Cerebral glucose utilization during aerobic metabolism in fetal sheep. Pediatr Res. 1972 Mar;6(3):182–186. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197203000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M., Mc Fadyen I. R. Placental transfer and fetal uptake of amino acids in the pregnant ewe. J Perinat Med. 1973;1(3):174–182. doi: 10.1515/jpme.1973.1.3.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


