Abstract
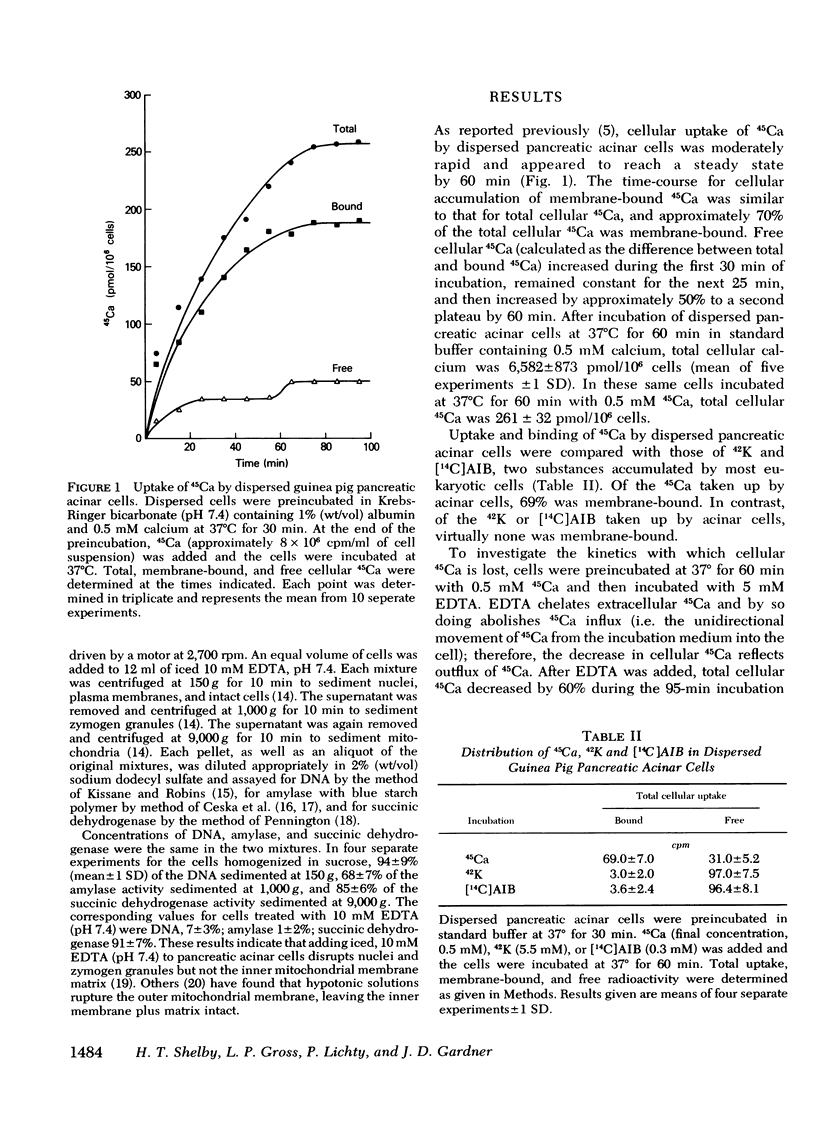
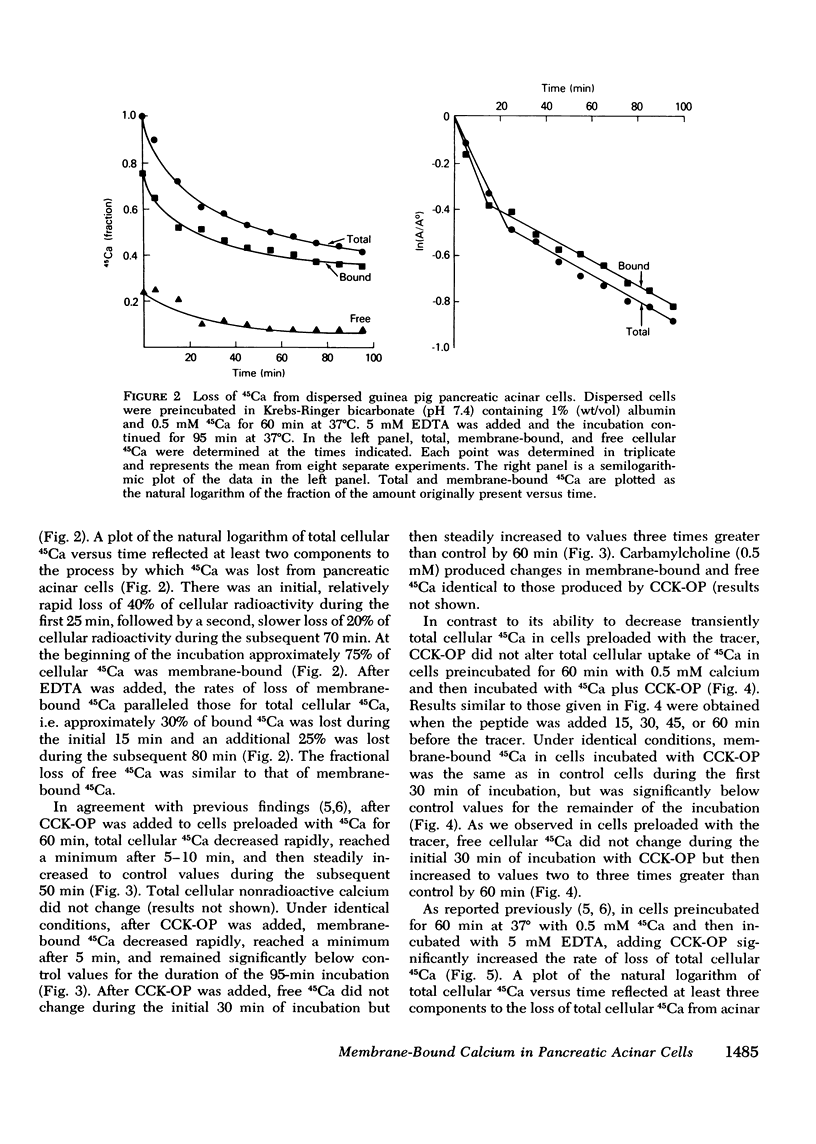
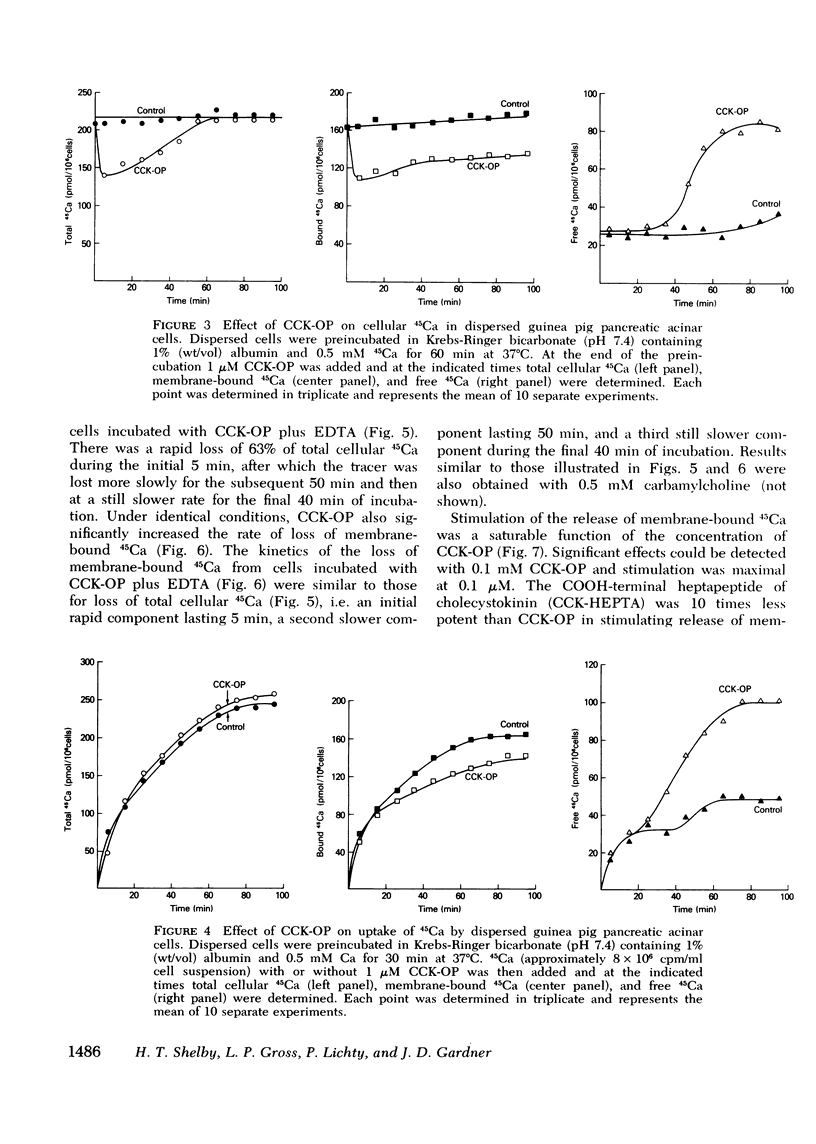
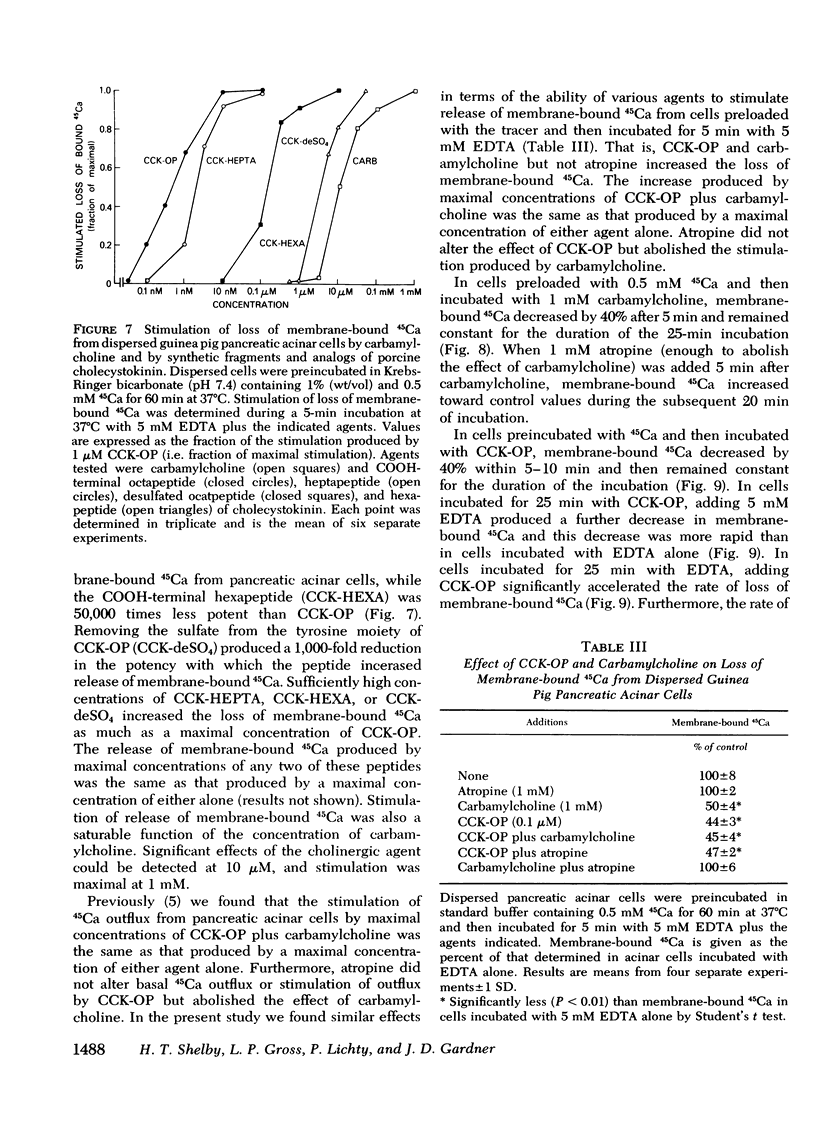
In dispersed acinar cells prepared from guinea pig pancreas, cellular uptake of 45Ca was moderately rapid and reached a steady state by 60 min. At the steady state, 69% of total cellular 45Ca was membrane-bound. In acinar cells preloaded with 45Ca and then incubated with COOH-terminal octapeptide of cholecystokinin (CCK-OP) or carbamylcholine, total cellular 45Ca decreased by approximately 40% within 5-10 min and then steadily increased to control values by 60 min. Under identical conditions, membrane-bound 45Ca decreased by 40% within 5-10 min and remained constant for the duration of the incubation. Free cellular 45Ca did not change during the initial 30 min but then increased steadily to values three times those in control cells by 60 min. In cells preloaded with 45Ca and then incubated with EDTA, the loss of total cellular radioactivity stimulated by CCK-OP could be accounted for by loss of membrane-bound 45Ca. CCK-OP failed to alter total cellular uptake of 45Ca when both tracer and peptide were added at the beginning of the incubation. Under identical conditions, membrane-bound 45Ca was not altered by CCK-OP during the first 30 min of incubation but was significantly below control values after this time. The effect of CCK-OP on free cellular 45Ca was the same as in cells preloaded with the tracer. These results suggest that CCK-OP causes release of 45Ca from a membrane-bound compartment that equilibrates slowly with extracellular fluid and that the change in free cellular 45Ca is a secondary effect.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amsterdam A., Jamieson J. D. Structural and functional characterization of isolated pancreatic exocrine cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):3028–3032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.3028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amsterdam A., Jamieson J. D. Studies on dispersed pancreatic exocrine cells. I. Dissociation technique and morphologic characteristics of separated cells. J Cell Biol. 1974 Dec;63(3):1037–1056. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.3.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amsterdam A., Jamieson J. D. Studies on dispersed pancreatic exocrine cells. II. Functional characteristics of separated cells. J Cell Biol. 1974 Dec;63(3):1057–1073. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.3.1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argent B. E., Case R. M., Scratcherd T. Amylase secretion by the perfused cat pancreas in relation to the secretion of calcium and other electrolytes and as influenced by the external ionic environment. J Physiol. 1973 May;230(3):575–593. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Hodgkin A. L., Ridgway E. B. Depolarization and calcium entry in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):709–755. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F. Transport and metabolism of calcium ions in nerve. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1972;24:177–223. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(72)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz L., Eckstein B., Matthews E. K., Williams J. A. Control of pancreatic amylase release in vitro: effects of ions, cyclic AMP, and colchicine. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Sep;46(1):66–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb06849.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinley F. J., Jr Calcium and magnesium transport in single cells. Fed Proc. 1973 Jul;32(7):1735–1739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B. THE ENERGY-LINKED REACTION OF CALCIUM WITH MITOCHONDRIA. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2729–2748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E. In vivo effect of uncoupling agents on the incorporation of calcium and strontium into mitochondria and other subcellular fractions of rat liver. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Aug;50(7):1849–1864. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.7.1849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case R. M., Clausen T. The relationship between calcium exchange and enzyme secretion in the isolated rat pancreas. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;235(1):75–102. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceska M., Birath K., Brown B. A new and rapid method for the clinical determination of alpha-amylase activities in human serum and urine. Optimal conditions. Clin Chim Acta. 1969 Dec;26(3):437–444. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(69)90071-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceska M., Brown B., Birath K. Ranges of alpha-amylase activities in human serum and urine and correlations with some other alpha-amylase methods. Clin Chim Acta. 1969 Dec;26(3):445–453. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(69)90072-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler D. E., Williams J. A. Pancreatic acinar cells: effects of lanthanum ions on amylase release and calcium ion fluxes. J Physiol. 1974 Dec;243(3):831–846. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christophe J. P., Frandsen E. K., Conlon T. P., Krishna G., Gardner J. D. Action of cholecystokinin, cholinergic agents, and A-23187 on accumulation of guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate in dispersed guinea pig pancreatic acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4640–4645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cittadini A., Scarpa A., Chance B. Calcium transport in intact Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 2;291(1):246–259. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90416-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemente F., Meldolesi J. Calcium and pancreatic secretion-dynamics of subcellur calcium pools in resting and stimulated acinar cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Nov;55(3):369–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb06940.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemente F., Meldolesi J. Calcium and pancreatic secretion. I. Subcellular distribution of calcium and magnesium in the exocrine pancreas of the guinea pig. J Cell Biol. 1975 Apr;65(1):88–102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.1.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W. Stimulus-secretion coupling: the concept and clues from chromaffin and other cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1968 Nov;34(3):451–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb08474.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eimerl S., Savion N., Heichal O., Selinger Z. Induction of enzyme secretion in rat pancreatic slices using the ionophore A-23187 and calcium. An experimental bypass of the hormone receptor pathway. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 25;249(12):3991–3993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. D., Conlon T. P., Adams T. D. Cyclic AMP in pancreatic acinar cells: effects of gastrointestinal hormones. Gastroenterology. 1976 Jan;70(1):29–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. D., Conlon T. P., Kleveman H. L., Adams T. D., Ondetti M. A. Action of cholecystokinin and cholinergic agents on calcium transport in isolated pancreatic acinar cells. J Clin Invest. 1975 Aug;56(2):366–375. doi: 10.1172/JCI108101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisler S., Fast D., Tenenhouse A. Role of Ca 2+ and cyclic AMP in protein secretion from rat exocrine pancreas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Oct 25;279(3):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90178-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisler S., Grondin G. Effect of lanthanum on 45Ca flux and secretion of protein from rat exocrine pancreas. Life Sci. 1973 Oct 1;13(7):783–794. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(73)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokin L. E. Effects of calcium omission on acetylcholine-stimulated amylase secretion and phospholipid synthesis in pigeon pancreas slices. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 25;115(1):219–221. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanno T. Calcium-dependent amylase release and electrophysiological measurements in cells of the pancreas. J Physiol. 1972 Oct;226(2):353–371. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo S., Schulz I. Calcium ion uptake in isolated pancreas cells induced by secretagogues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 8;419(1):76–92. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90373-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehninger A. L. Mitochondria and calcium ion transport. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(2):129–138. doi: 10.1042/bj1190129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews E. K., Petersen O. H., Williams J. A. Pancreatic acinar cells: acetylcholine-induced membrane depolarization, calcium efflux and amylase release. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;234(3):689–701. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mela L., Chance B. Spectrophotometric measurements of the kinetics of Ca2+ and Mn2+ accumulation in mitochondria. Biochemistry. 1968 Nov;7(11):4059–4063. doi: 10.1021/bi00851a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldolesi J., Jamieson J. D., Palade G. E. Composition of cellular membranes in the pancreas of the guinea pig. I. Isolation of membrane fractions. J Cell Biol. 1971 Apr;49(1):109–129. doi: 10.1083/jcb.49.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENNINGTON R. J. Biochemistry of dystrophic muscle. Mitochondrial succinate-tetrazolium reductase and adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem J. 1961 Sep;80:649–654. doi: 10.1042/bj0800649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robberecht P., Christophe J. Secretion of hydrolases by perfused fragments of rat pancreas: effect of calcium. Am J Physiol. 1971 Apr;220(4):911–917. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.4.911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robberecht P., Conlon T. P., Gardner J. D. Interaction of porcine vasoactive intestinal peptide with dispersed pancreatic acinar cells from the guinea pig. Structural requirements for effects of vasoactive intestinal peptide and secretin on cellular adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4635–4639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzmann H. J., Vincenzi F. F. Calcium movements across the membrane of human red cells. J Physiol. 1969 Apr;201(2):369–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. A., Chandler D. Ca++ and pancreatic amylase release. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jun;228(6):1729–1732. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.6.1729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. A., Lee M. Pancreatic acinar cells: use of Ca++ ionophore to separate enzyme release from the earlier steps in stimulus-secretion coupling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 23;60(2):542–548. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90274-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


