Abstract
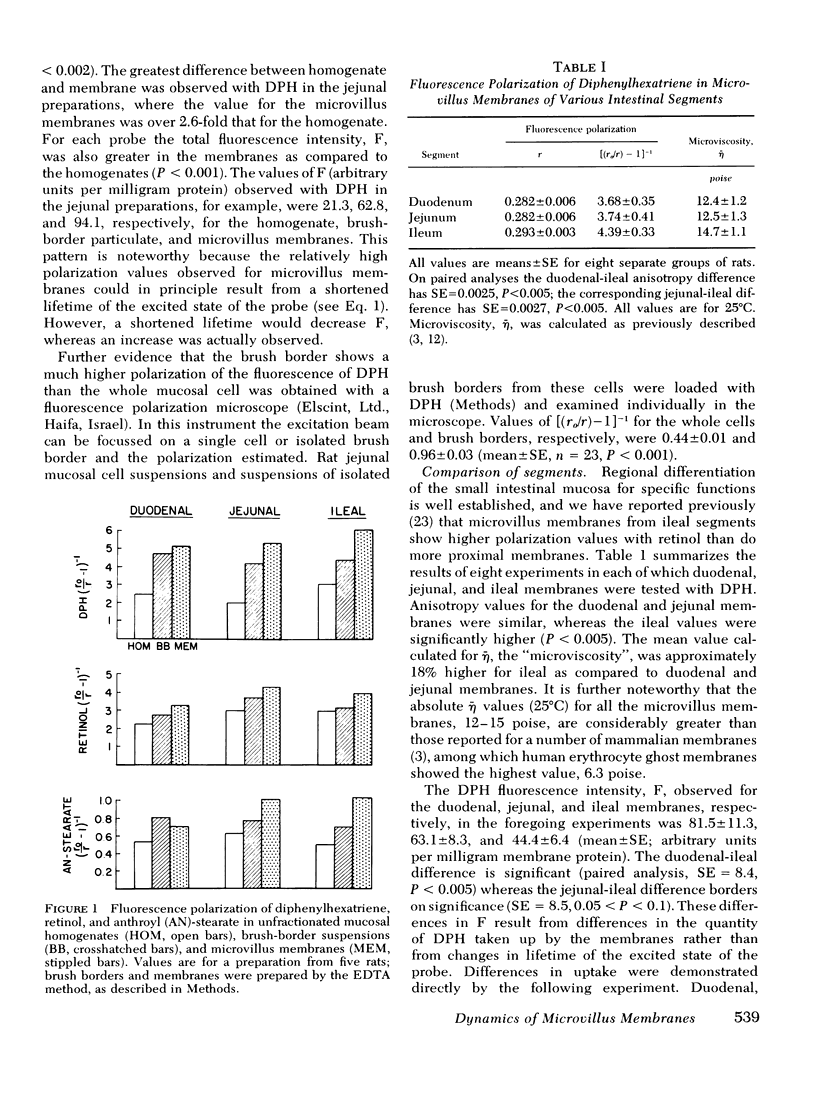
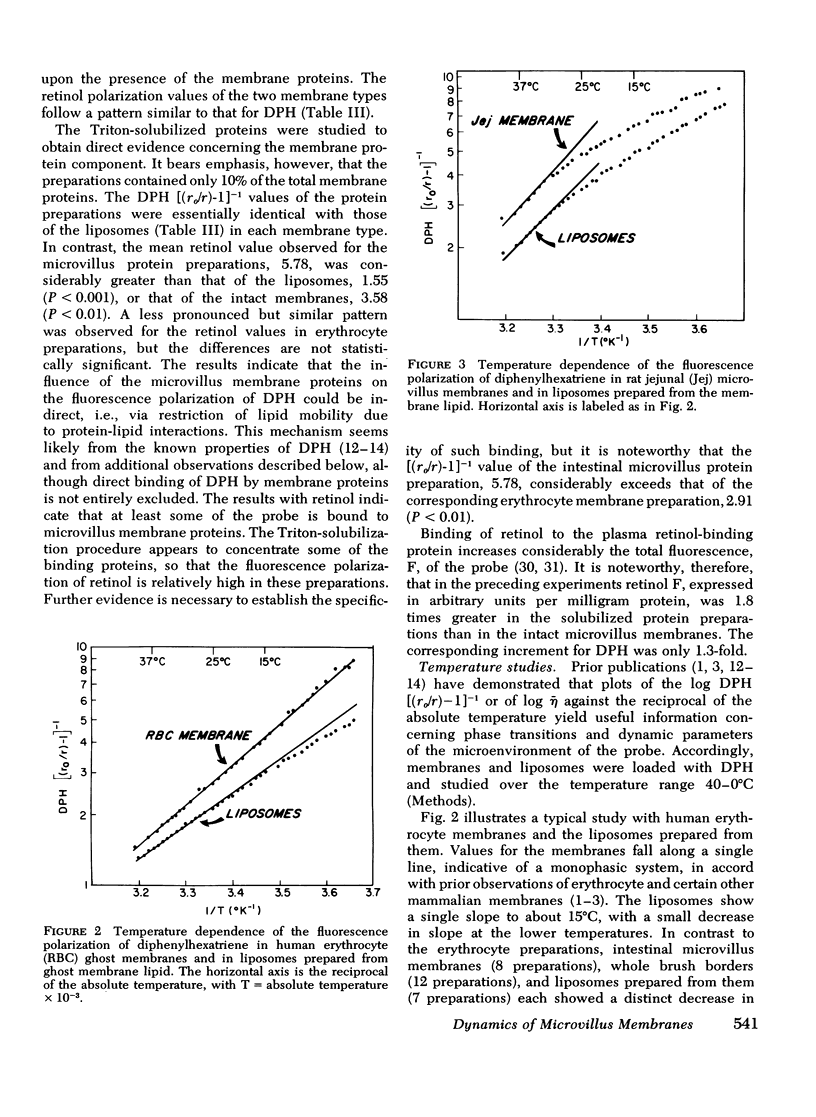
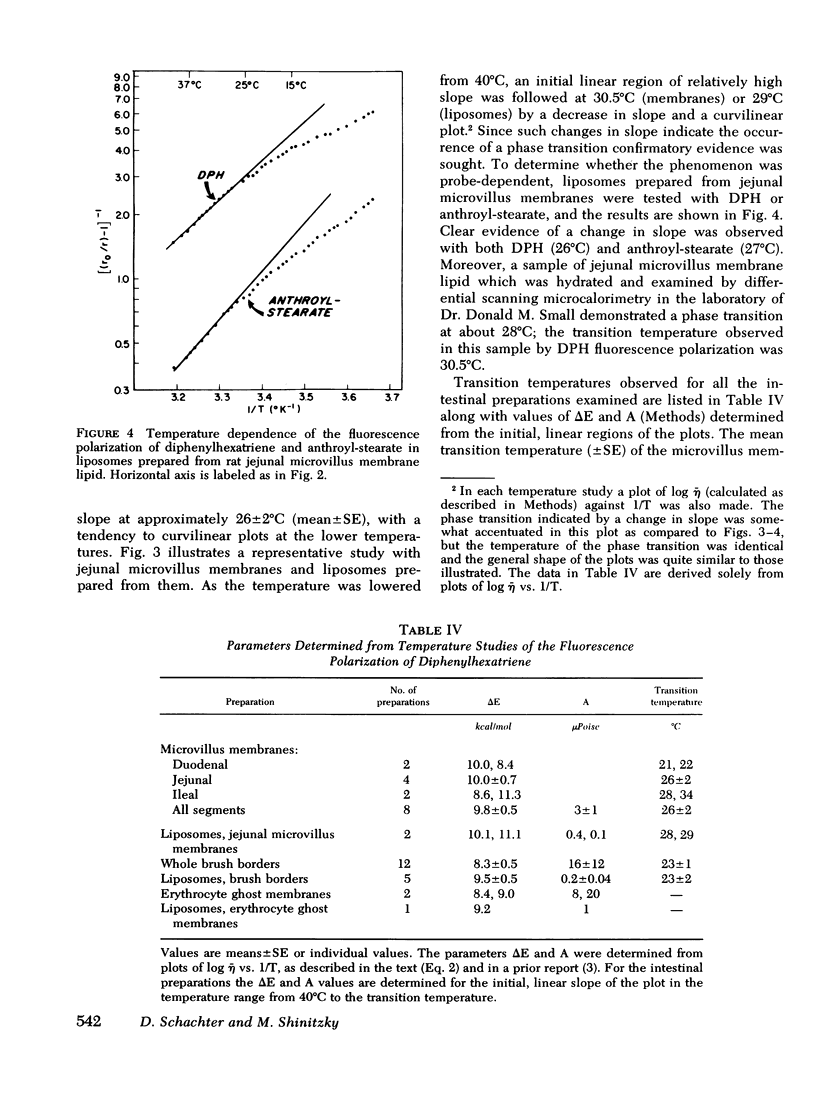
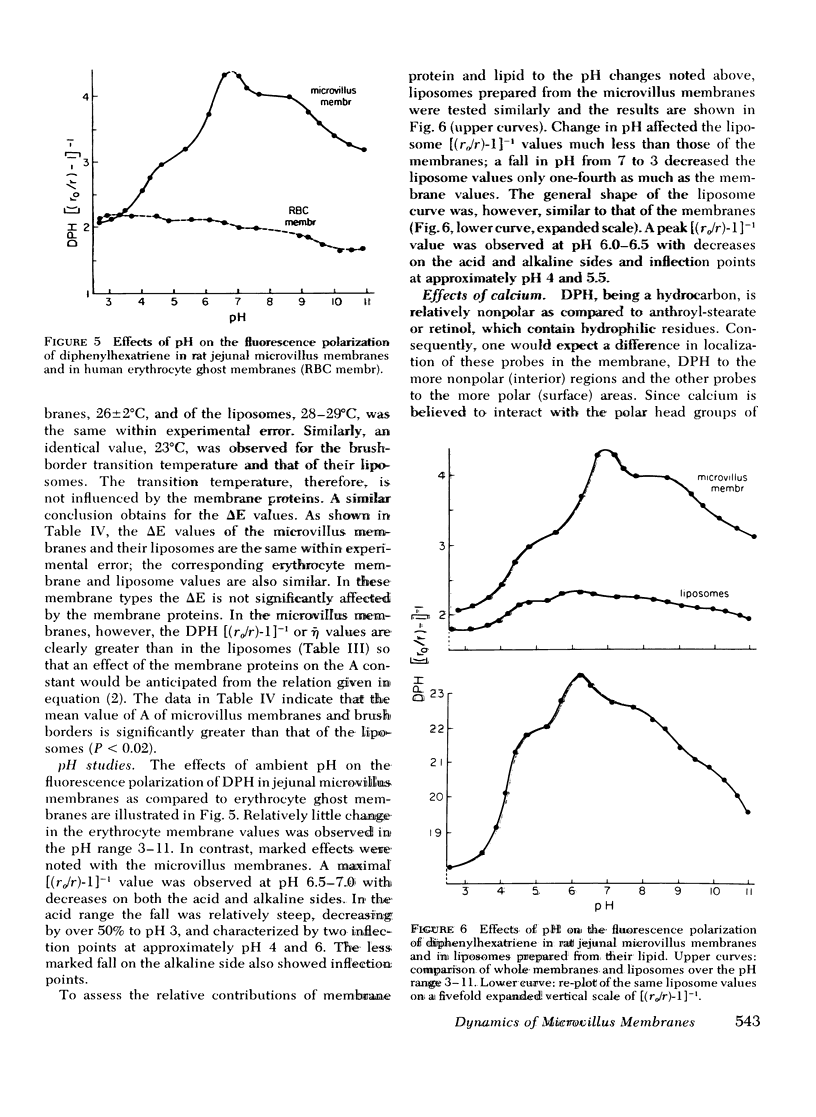
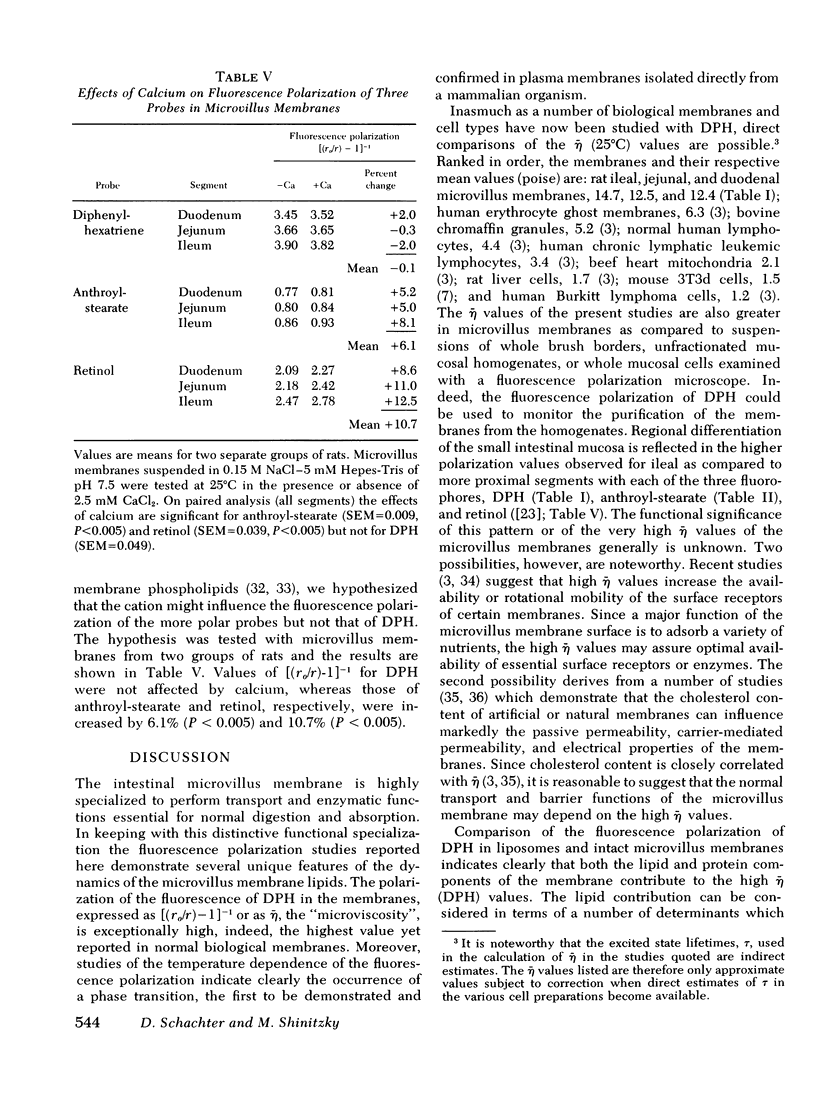
Rat intestinal microvillus membranes and lipid extracts prepared from them have been studied by fluorescence polarization with three lipid-soluble fluorophores: diphenylhexatriene, retinol, and anthroyl-stearate. The degree of fluorescence polarization of diphenylhexatriene, which provides an index of the "microviscosity" of the lipid regions of the membrane, is exceptionally high in microvillus membranes, the highest yet reported in normal biological membranes. Both the membrane proteins and lipids were found to contribute to the high values. With each of the three probes the polarization values are higher in ileal microvillus membranes as compared to membranes from proximal intestinal segments. Temperature-dependence studies of the fluorescence polarization of diphenylhexatriene and anthroylstearate demonstrate a phase transition in microvillus membranes and in liposomes prepared from their lipid extracts at approximately 26+/-2 degrees C. Ambient pH influences markedly the diphenylhexatriene fluorescence polarization in microvillus membranes but has little effect on that of human erythrocyte ghost membranes. The "microviscosity" of jejunal microvillus membranes is maximal at pH 6.5-7.0 and decreases as much as 50% at pH 3.0, an effect which depends largely upon the membrane proteins. Addition of calcium ions to suspensions of microvillus membranes increases the fluorescence polarization of retinol and anthroyl-stearate, but not that of diphenyl-hexatriene. This confirms the localization of the last compound to the hydrophobic interior of the membrane, relatively distant from the hydrophilic head groups of the polar lipids. Microvillus membrane proteins solubilized with Triton X-100 give relatively high fluorescence polarization and intensity values with retinol, suggesting the presence of binding proteins which could play a role in the normal absorptive mechanism for the vitamin.
Full text
PDF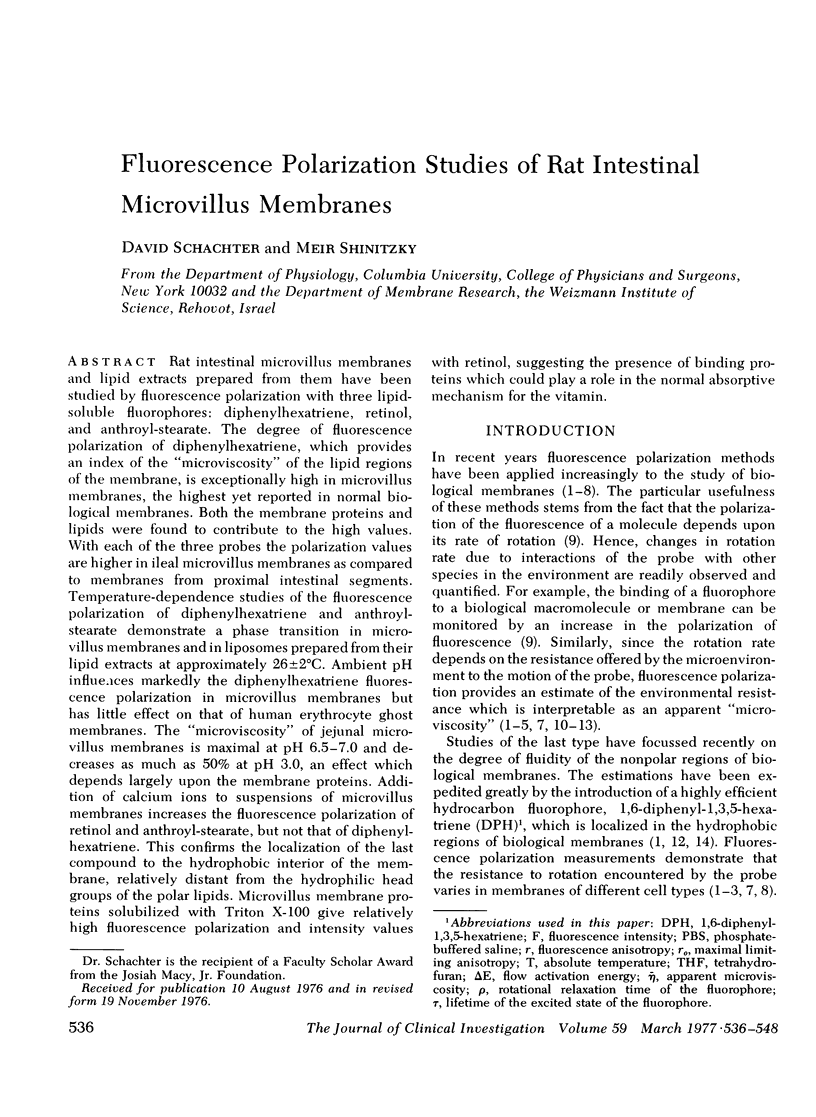







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aloni B., Shinitzky M., Livne A. Dynamics of erythrocyte lipids in intact cells, in ghost membranes and in liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jun 26;348(3):438–441. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(74)90223-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrich M. P., Vanderkooi J. M. Temperature dependence of 1,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-hexatriene fluorescence in phophoslipid artificial membranes. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 23;15(6):1257–1261. doi: 10.1021/bi00651a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt-Jovin D. J., Ostertag W., Eisen H., Klimek F., Jovin T. M. Studies of cellular differentiation by automated cell separation. Two model systems: Friend virus-transformed cells and Hydra attenuata. J Histochem Cytochem. 1976 Jan;24(1):332–347. doi: 10.1177/24.1.1254928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bangham A. D. Lipid bilayers and biomembranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:753–776. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.003541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batt E. R., Schachter D. Transport of monosaccharides. I. Asymmetry in the human erythrocyte mechanism. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jul;52(7):1686–1697. doi: 10.1172/JCI107350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron F., Mateu L. Chain motions in lipid-water and protein-lipid-water phases: a spin-label and x-ray diffraction study. J Mol Biol. 1974 May 15;85(2):279–300. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90364-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D., Penkett S. A. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic studies of the interaction of phospholipids with cholesterol. Nature. 1966 Sep 17;211(5055):1304–1305. doi: 10.1038/2111304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogan U., Kopelman M., Mokady S., Shinitzky M. Binding affinities of retinol and related compounds to retinol binding proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1976 May 17;65(1):71–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10390.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogan U., Shinitzky M., Weber G., Nishida T. Microviscosity and order in the hydrocarbon region of phospholipid and phospholipid-cholesterol dispersions determined with fluorescent probes. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 30;12(3):521–528. doi: 10.1021/bi00727a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE J. T., MITCHELL C., HANAHAN D. J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:119–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forstner G. G., Sabesin S. M., Isselbacher K. J. Rat intestinal microvillus membranes. Purification and biochemical characterization. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(2):381–390. doi: 10.1042/bj1060381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forstner G. G., Tanaka K., Isselbacher K. J. Lipid composition of the isolated rat intestinal microvillus membrane. Biochem J. 1968 Aug;109(1):51–59. doi: 10.1042/bj1090051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P., Parola A., Robbins P. W., Blout E. R. Fluorescence polarization and viscosities of membrane lipids of 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3351–3354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helgerson S. L., Cramer W. A., Harris J. M., Lytle F. E. Evidence for a microviscosity increase in the Escherichia coli cell envelope caused by colicin E1. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 16;13(15):3057–3061. doi: 10.1021/bi00712a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfer U., Nelson K., Perrotto J., Isselbacher K. J. Glucose transport in isolated brush border membrane from rat small intestine. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):25–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz A. F., Klein M. P., Michaelson D. M., Kohler S. J. Magnetic resonance studies of membrane and model membrane systems. V. Comparisons of aqueous dispersions of pure and mixed phospholipids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Dec 31;222:468–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb15281.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbell W. L., McConnell H. M. Molecular motion in spin-labeled phospholipids and membranes. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Jan 27;93(2):314–326. doi: 10.1021/ja00731a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbell W. L., McConnell H. M. Spin-label studies of the excitable membranes of nerve and muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):12–16. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson K., Papahadjopoulos D. Phase transitions and phase separations in phospholipid membranes induced by changes in temperature, pH, and concentration of bivalent cations. Biochemistry. 1975 Jan 14;14(1):152–161. doi: 10.1021/bi00672a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai M., Raz A., Goodman D. S. Retinol-binding protein: the transport protein for vitamin A in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1968 Sep;47(9):2025–2044. doi: 10.1172/JCI105889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowarski S., Schachter D. Vitamin D and adenosine triphosphatase dependent on divalent cations in rat intestinal mucosa. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2765–2773. doi: 10.1172/JCI107472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladbrooke B. D., Williams R. M., Chapman D. Studies on lecithin-cholesterol-water interactions by differential scanning calorimetry and X-ray diffraction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 29;150(3):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90132-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzati V., Gulik-Krzywicki T., Tardieu A. Polymorphism of lecithins. Nature. 1968 Jun 15;218(5146):1031–1034. doi: 10.1038/2181031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldfield E., Chapman D. Effects of cholesterol and cholesterol derivatives on hydrocarbon chain mobility in lipids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 May 7;43(3):610–616. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90658-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Cowden M., Kimelberg H. Role of cholesterol in membranes. Effects on phospholipid-protein interactions, membrane permeability and enzymatic activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 30;330(1):8–26. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D. Surface properties of acidic phospholipids: interaction of monolayers and hydrated liquid crystals with uni- and bi-valent metal ions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 17;163(2):240–254. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raison J. K. Temperature-induced phase changes in membrane lipids and their influence on metabolic regulation. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1973;27:485–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Guidotti G. The protein of human erythrocyte membranes. I. Preparation, solubilization, and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 25;243(8):1985–1992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scandella C. J., Devaux P., McConnell H. M. Rapid lateral diffusion of phospholipids in rabbit sarcoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2056–2060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter D., Cogan U., Shinitzky M. Interaction of retinol and intestinal microvillus membranes studied by flourescence polarization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 2;448(4):620–624. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90115-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J., Preiser H., Maestracci D., Ghosh B. K., Cerda J. J., Crane R. K. Purification of the human intestinal brush border membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 27;323(1):98–112. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90434-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuldiner S., Kerwar G. K., Kaback H. R., Weil R. Energy-dependent binding of dansylgalactosides to the beta-galactoside carrier protein. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1361–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah D. O., Schulman J. H. The ionic structure of lecithin monolayers. J Lipid Res. 1967 May;8(3):227–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattil S. J., Anaya-Galindo R., Bennett J., Colman R. W., Cooper R. A. Platelet hypersensitivity induced by cholesterol incorporation. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):636–643. doi: 10.1172/JCI107971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P., Chan S. I. Effect of sonication on the structure of lecithin bilayers. Biochemistry. 1972 Nov 21;11(24):4573–4581. doi: 10.1021/bi00774a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinitzky M., Barenholz Y. Dynamics of the hydrocarbon layer in liposomes of lecithin and sphingomyelin containing dicetylphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 25;249(8):2652–2657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinitzky M., Dianoux A. C., Gitler C., Weber G. Microviscosity and order in the hydrocarbon region of micelles and membranes determined with fluorescent probes. I. Synthetic micelles. Biochemistry. 1971 May 25;10(11):2106–2113. doi: 10.1021/bi00787a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinitzky M., Inbar M. Difference in microviscosity induced by different cholesterol levels in the surface membrane lipid layer of normal lymphocytes and malignant lymphoma cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 5;85(4):603–615. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90318-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinitzky M., Inbar M. Microviscosity parameters and protein mobility in biological membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 16;433(1):133–149. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90183-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderkooi J., Fischkoff S., Chance B., Cooper R. A. Fluorescent probe analysis of the lipid architecture of natural and experimental cholesterol-rich membranes. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 9;13(8):1589–1595. doi: 10.1021/bi00705a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER G. Rotational Brownian motion and polarization of the fluorescence of solutions. Adv Protein Chem. 1953;8:415–459. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60096-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley J. S., Cooper R. A. Inhibition of cation cotransport by cholesterol enrichment of human red cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Dec 16;413(3):425–431. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90125-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisnieski B. J., Huang Y. O., Fox C. F. Physical properties of the lipid phase of membranes from cultured animal cells. J Supramol Struct. 1974;2(5-6):593–608. doi: 10.1002/jss.400020507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisnieski B. J., Parkes J. G., Huang Y. O., Fox C. F. Physical and physiological evidence for two phase transitions in cytoplasmic membranes of animal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4381–4385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yavin E., Yavin Z., Menkes J. H. Polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolism in neuroblastoma cells in culture. J Neurochem. 1975 Jan;24(1):71–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb07630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


