Abstract
The three-dimensional structure of the self-complementary DNA octamer d(GCCCGpGGC) has been determined in the crystalline state using X-ray diffraction data to a nominal resolutoin of 2.12 measured from a very small crystal at DESY, Hamburg. The structure was refined with stereochemical restraints to an R value of 17.1%. d(GCCCGpGGC), containing one single 3'-methylene phosphonate linkage (denoted p), forms an A-DNA double helix with strict dyad symmetry, that is distinct from canonical A-DNA by a wide open major groove and a small average base-pair inclination against the helix axis. The conformation of the unmodified control d(GCCCGGGC) is known from an X-ray analysis of isomorphous crystals (Heinemann et al. (1987) Nucleic Acids Res. 15, 9531-9550). Comparison of the two structures reveals only minor conformational differences, most notably in the pucker of the reduced deoxyribose. It is suggested that oligonucleotides with charged 3'-methylene phosphonate groups may form stable duplexes with complementary DNA or RNA strands rendering them candidates for use as gene-regulatory antisense probes.
Full text
PDF
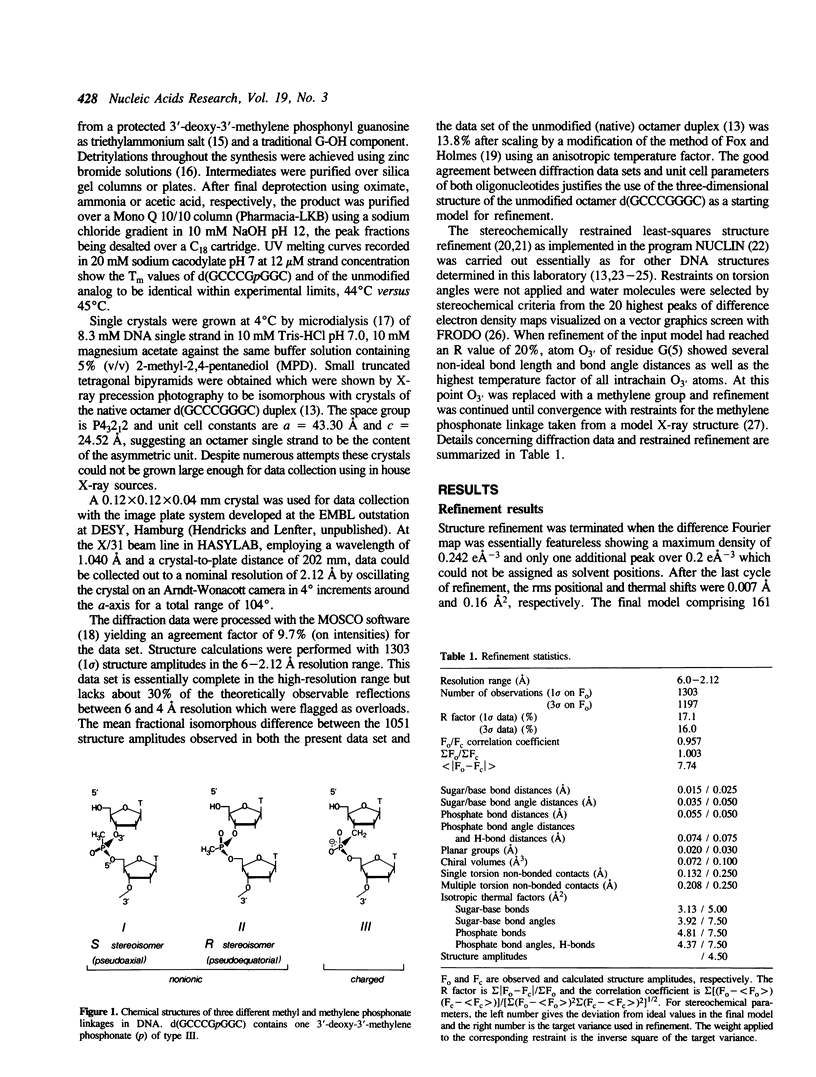
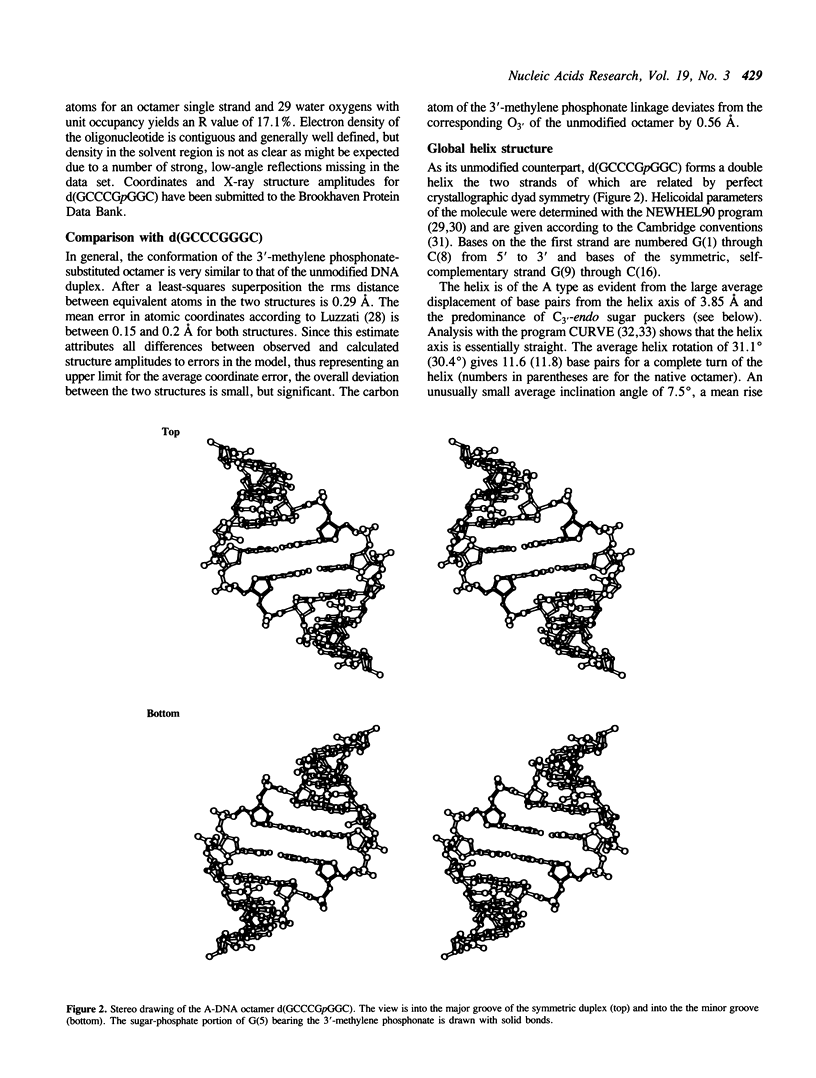
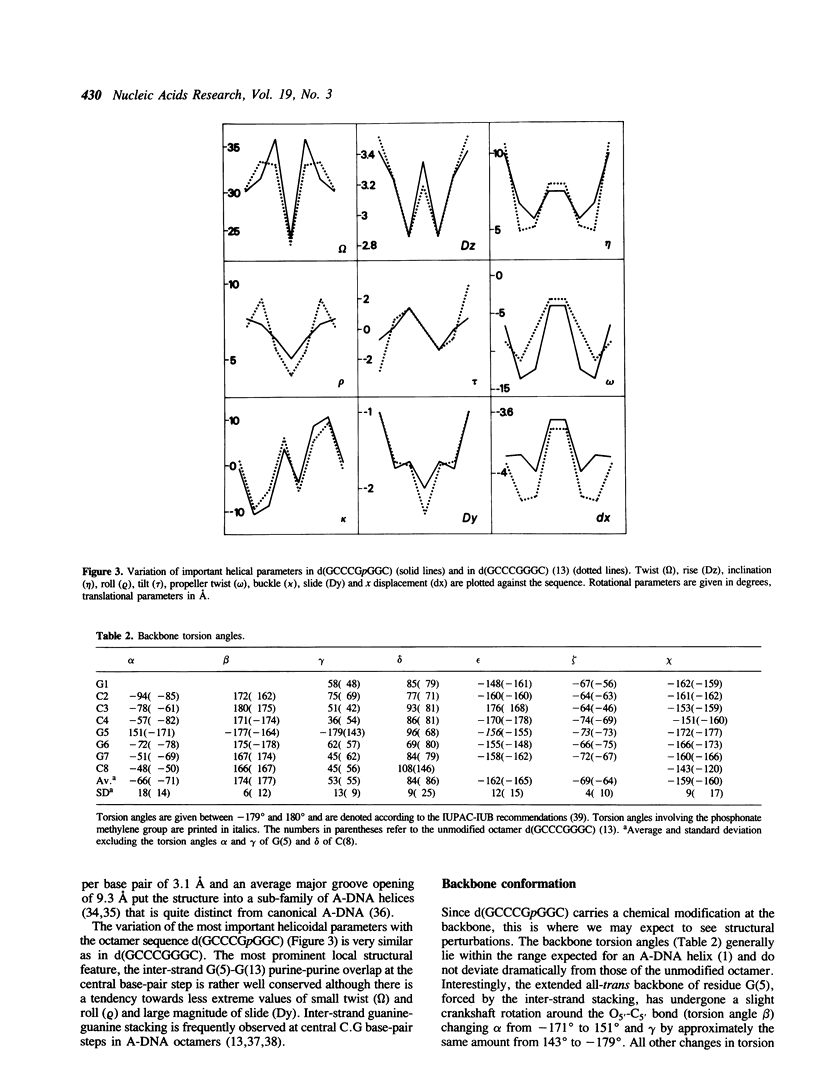


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altona C., Sundaralingam M. Conformational analysis of the sugar ring in nucleosides and nucleotides. A new description using the concept of pseudorotation. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 Nov 15;94(23):8205–8212. doi: 10.1021/ja00778a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruse W. B., Salisbury S. A., Brown T., Cosstick R., Eckstein F., Kennard O. Chiral phosphorothioate analogues of B-DNA. The crystal structure of Rp-d[Gp(S)CpGp(S)CpGp(S)C]. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 20;192(4):891–905. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90035-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dattagupta J. K., Fujiwara T., Grishin E. V., Lindner K., Manor P. C., Pieniazek N. J., Saenger R., Suck D. Crystallization of the fungal enzyme proteinase K and amino acid composition. J Mol Biol. 1975 Sep 15;97(2):267–271. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Definitions and nomenclature of nucleic acid structure parameters. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):1–4. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03339.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Goodsell D. S., Kopka M. L., Pjura P. E. The effect of crystal packing on oligonucleotide double helix structure. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1987 Dec;5(3):557–579. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1987.10506413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand M., Maurizot J. C., Asseline U., Barbier C., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Oligothymidylates covalently linked to an acridine derivative and with modified phosphodiester backbone: circular dichroism studies of their interactions with complementary sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1823–1837. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank R., Meyerhans A., Schwellnus K., Blöcker H. Simultaneous synthesis and biological applications of DNA fragments: an efficient and complete methodology. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:221–249. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54079-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fratini A. V., Kopka M. L., Drew H. R., Dickerson R. E. Reversible bending and helix geometry in a B-DNA dodecamer: CGCGAATTBrCGCG. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14686–14707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haran T. E., Shakked Z., Wang A. H., Rich A. The crystal structure of d(CCCCGGGG): a new A-form variant with an extended backbone conformation. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1987 Oct;5(2):199–217. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1987.10506390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann U., Alings C. Crystallographic study of one turn of G/C-rich B-DNA. J Mol Biol. 1989 Nov 20;210(2):369–381. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann U., Lauble H., Frank R., Blöcker H. Crystal structure analysis of an A-DNA fragment at 1.8 A resolution: d(GCCCGGGC). Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9531–9550. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson W. A. Stereochemically restrained refinement of macromolecular structures. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:252–270. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain S., Sundaralingam M. Effect of crystal packing environment on conformation of the DNA duplex. Molecular structure of the A-DNA octamer d(G-T-G-T-A-C-A-C) in two crystal forms. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):12780–12784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kean J. M., Murakami A., Blake K. R., Cushman C. D., Miller P. S. Photochemical cross-linking of psoralen-derivatized oligonucleoside methylphosphonates to rabbit globin messenger RNA. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 27;27(26):9113–9121. doi: 10.1021/bi00426a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulka M., Smith C. C., Aurelian L., Fishelevich R., Meade K., Miller P., Ts'o P. O. Site specificity of the inhibitory effects of oligo(nucleoside methylphosphonate)s complementary to the acceptor splice junction of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early mRNA 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6868–6872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauble H., Frank R., Blöcker H., Heinemann U. Three-dimensional structure of d(GGGATCCC) in the crystalline state. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 25;16(16):7799–7816. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.16.7799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavery R., Sklenar H. Defining the structure of irregular nucleic acids: conventions and principles. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1989 Feb;6(4):655–667. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1989.10507728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavery R., Sklenar H. The definition of generalized helicoidal parameters and of axis curvature for irregular nucleic acids. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1988 Aug;6(1):63–91. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1988.10506483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B. L., Murakami A., Blake K. R., Lin S. B., Miller P. S. Interaction of psoralen-derivatized oligodeoxyribonucleoside methylphosphonates with single-stranded DNA. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3197–3203. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. B., Blake K. R., Miller P. S., Ts'o P. O. Use of EDTA derivatization to characterize interactions between oligodeoxyribonucleoside methylphosphonates and nucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):1054–1061. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus-Sekura C. J. Techniques for using antisense oligodeoxyribonucleotides to study gene expression. Anal Biochem. 1988 Aug 1;172(2):289–295. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90447-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quartin R. S., Wetmur J. G. Effect of ionic strength on the hybridization of oligodeoxynucleotides with reduced charge due to methylphosphonate linkages to unmodified oligodeoxynucleotides containing the complementary sequence. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):1040–1047. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovich D., Haran T., Eisenstein M., Shakked Z. Structures of the mismatched duplex d(GGGTGCCC) and one of its Watson-Crick analogues d(GGGCGCCC). J Mol Biol. 1988 Mar 5;200(1):151–161. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90340-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarin P. S., Agrawal S., Civeira M. P., Goodchild J., Ikeuchi T., Zamecnik P. C. Inhibition of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome virus by oligodeoxynucleoside methylphosphonates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7448–7451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakked Z., Guerstein-Guzikevich G., Eisenstein M., Frolow F., Rabinovich D. The conformation of the DNA double helix in the crystal is dependent on its environment. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):456–460. doi: 10.1038/342456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakked Z., Rabinovich D. The effect of the base sequence on the fine structure of the DNA double helix. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1986;47(3):159–195. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(86)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhof E., Dumas P., Moras D. Crystallographic refinement of yeast aspartic acid transfer RNA. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):119–145. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90048-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


