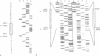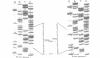Abstract
We have sequenced the deletion borders of the muscle mitochondrial DNA from 24 patients with heteroplasmic deletions. The length of these deletions varies from 2.310 bp to 8.476 bp and spans from position 5.786 to 15.925 of the human mitochondrial genome preserving the heavy chain and light chain origins of replication. 12 cases are common deletions identical to the mutation already described by other workers and characterized by 13 bp repeats at the deletion boundaries, one of these repeats being retained during the deletion process. The other cases (10 out of 12) have shown deletions which have not been previously described. All these deletions are located in the H strand DNA region which is potentially single stranded during mitochondrial DNA replication. In two cases, the retained Adenosine from repeat closed to the heavy strand origin of replication would indicate slippage mispairing. Furthermore in one patient two mt DNA molecules have been cloned and their sequences showed the difference of four nucleotides in the breakpoint of the deletion, possibly dued to slippage mispairing. Taken together our results suggest that deletions occur either by slippage mispairing or by internal recombination at the direct repeat level. They also suggest that different mechanisms account for the deletions since similarly located deletions may display different motives at the boundaries including the absence of any direct repeat.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S., Bankier A. T., Barrell B. G., de Bruijn M. H., Coulson A. R., Drouin J., Eperon I. C., Nierlich D. P., Roe B. A., Sanger F. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):457–465. doi: 10.1038/290457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bae Y. S., Kawasaki I., Ikeda H., Liu L. F. Illegitimate recombination mediated by calf thymus DNA topoisomerase II in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2076–2080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boursot P., Yonekawa H., Bonhomme F. Heteroplasmy in mice with deletion of a large coding region of mitochondrial DNA. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jan;4(1):46–55. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen A., Camerini-Otero R. D. A recombinase from Drosophila melanogaster embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7481–7485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank-Kamenetskii M. Gene transcription. Waves of DNA supercoiling. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):206–206. doi: 10.1038/337206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Nash H. Communication between segments of DNA during site-specific recombination. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):401–404. doi: 10.1038/325401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golic K. G., Lindquist S. The FLP recombinase of yeast catalyzes site-specific recombination in the Drosophila genome. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90033-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoess R., Wierzbicki A., Abremski K. Isolation and characterization of intermediates in site-specific recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6840–6844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt I. J., Harding A. E., Morgan-Hughes J. A. Deletions of muscle mitochondrial DNA in mitochondrial myopathies: sequence analysis and possible mechanisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4465–4469. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt I. J., Harding A. E., Morgan-Hughes J. A. Deletions of muscle mitochondrial DNA in patients with mitochondrial myopathies. Nature. 1988 Feb 25;331(6158):717–719. doi: 10.1038/331717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns D. R., Rutledge S. L., Stine O. C., Hurko O. Directly repeated sequences associated with pathogenic mitochondrial DNA deletions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8059–8062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lestienne P., Ponsot G. Kearns-Sayre syndrome with muscle mitochondrial DNA deletion. Lancet. 1988 Apr 16;1(8590):885–885. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91632-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Rowe T. C., Yang L., Tewey K. M., Chen G. L. Cleavage of DNA by mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15365–15370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez B., Coppey J. Molecular analysis of homologous recombination catalysed by human nuclear extract: fidelity and DNase protection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 31;158(2):454–461. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80069-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer-Leon L., Gates C. A., Attwood J. M., Wood E. A., Cox M. M. Purification of the FLP site-specific recombinase by affinity chromatography and re-examination of basic properties of the system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6469–6488. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mita S., Rizzuto R., Moraes C. T., Shanske S., Arnaudo E., Fabrizi G. M., Koga Y., DiMauro S., Schon E. A. Recombination via flanking direct repeats is a major cause of large-scale deletions of human mitochondrial DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):561–567. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moraes C. T., DiMauro S., Zeviani M., Lombes A., Shanske S., Miranda A. F., Nakase H., Bonilla E., Werneck L. C., Servidei S. Mitochondrial DNA deletions in progressive external ophthalmoplegia and Kearns-Sayre syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1989 May 18;320(20):1293–1299. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198905183202001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moritz C., Brown W. M. Tandem duplication of D-loop and ribosomal RNA sequences in lizard mitochondrial DNA. Science. 1986 Sep 26;233(4771):1425–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.3018925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson I., Degoul F., Obermaier-Kusser B., Romero N., Borrone C., Marsac C., Vayssiere J. L., Gerbitz K., Fardeau M., Ponsot G. Mapping of heteroplasmic mitochondrial DNA deletions in Kearns-Sayre syndrome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 25;17(20):8117–8124. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.20.8117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson I., d'Auriol L., Galibert F., Ponsot G., Lestienne P. Identification nucléotidique et modèle cinétique d'une délétion hétéroplasmique de 4,666 paires de bases de l'ADN mitochondrial dans le syndrome de Kearns-Sayre. C R Acad Sci III. 1989;309(10):403–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obermaier-Kusser B., Müller-Höcker J., Nelson I., Lestienne P., Enter C., Riedele T., Gerbitz K. D. Different copy numbers of apparently identically deleted mitochondrial DNA in tissues from a patient with Kearns-Sayre syndrome detected by PCR. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jun 29;169(3):1007–1015. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91994-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa T., Yoneda M., Tanaka M., Ohno K., Sato W., Suzuki H., Nishikimi M., Yamamoto M., Nonaka I., Horai S. Maternal inheritance of deleted mitochondrial DNA in a family with mitochondrial myopathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 15;154(3):1240–1247. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. Homologous pairing and strand exchange in genetic recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:405–437. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rötig A., Colonna M., Blanche S., Fischer A., Le Deist F., Frezal J., Saudubray J. M., Munnich A. Deletion of blood mitochondrial DNA in pancytopenia. Lancet. 1988 Sep 3;2(8610):567–568. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92687-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski P. Site-specific recombinases: changing partners and doing the twist. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):341–347. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.341-347.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schon E. A., Rizzuto R., Moraes C. T., Nakase H., Zeviani M., DiMauro S. A direct repeat is a hotspot for large-scale deletion of human mitochondrial DNA. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):346–349. doi: 10.1126/science.2711184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanske S., Moraes C. T., Lombes A., Miranda A. F., Bonilla E., Lewis P., Whelan M. A., Ellsworth C. A., DiMauro S. Widespread tissue distribution of mitochondrial DNA deletions in Kearns-Sayre syndrome. Neurology. 1990 Jan;40(1):24–28. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.1.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoffner J. M., Lott M. T., Voljavec A. S., Soueidan S. A., Costigan D. A., Wallace D. C. Spontaneous Kearns-Sayre/chronic external ophthalmoplegia plus syndrome associated with a mitochondrial DNA deletion: a slip-replication model and metabolic therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7952–7956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solignac M., Monnerot M., Mounolou J. C. Mitochondrial DNA heteroplasmy in Drosophila mauritiana. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6942–6946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thode S., Schäfer A., Pfeiffer P., Vielmetter W. A novel pathway of DNA end-to-end joining. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90340-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkinson A. E., Bonk R. T., Kim J., Bartfeld N., Linn S. Mammalian mitochondrial endonuclease activities specific for ultraviolet-irradiated DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):929–935. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkinson A. E., Linn S. Purification and properties of a single strand-specific endonuclease from mouse cell mitochondria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):9579–9593. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.9579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. Y., Shyy S. H., Wang J. C., Liu L. F. Transcription generates positively and negatively supercoiled domains in the template. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90163-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeviani M., Moraes C. T., DiMauro S., Nakase H., Bonilla E., Schon E. A., Rowland L. P. Deletions of mitochondrial DNA in Kearns-Sayre syndrome. Neurology. 1988 Sep;38(9):1339–1346. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.9.1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeviani M., Servidei S., Gellera C., Bertini E., DiMauro S., DiDonato S. An autosomal dominant disorder with multiple deletions of mitochondrial DNA starting at the D-loop region. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):309–311. doi: 10.1038/339309a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]