Abstract
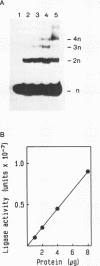
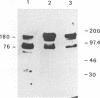
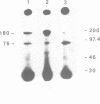
We have purified the major DNA ligase from Xenopus laevis eggs and raised antibodies against it. Estimates from SDS PAGE indicate that this DNA ligase is a 180 kDa protein. This enzyme is similar to the mammalian type I DNA ligase which is presumed to be involved in DNA replication. We have also analysed DNA ligase activity during X. laevis early development. Unfertilized eggs contain the highest level of activity reflecting the requirement for a large amount of DNA replicative enzymes for the period of intense replication following fertilization. In contrast with previous studies on the amphibians axolotl and Pleurodeles, the major DNA ligase activity detected during X. laevis early development is catalysed by a single enzyme: DNA ligase I. And the presence of this DNA ligase I in Xenopus egg before fertilization clearly demonstrates that the exclusion process of two forms of DNA ligase does not occur during X. laevis early development.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrand J. E., Willis A. E., Goldsmith I., Lindahl T. Different substrate specificities of the two DNA ligases of mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9079–9082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attardi D. G., De Paolis A., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Purification and characterization of Xenopus laevis type I topoisomerase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3654–3661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks G. R., Barker D. G. DNA ligase-AMP adducts: identification of yeast DNA ligase polypeptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 18;826(4):180–185. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes D. E., Johnston L. H., Kodama K., Tomkinson A. E., Lasko D. D., Lindahl T. Human DNA ligase I cDNA: cloning and functional expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6679–6683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti P., Baldi M. I., Mattoccia E., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Purification and characterization of Xenopus laevis topoisomerase II. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1303–1308. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01585.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat R., Grossman L. Purification and properties of two DNA ligases from human placenta. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Feb 1;244(2):801–812. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90649-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow J. J., Laskey R. A. Initiation of DNA replication in nuclei and purified DNA by a cell-free extract of Xenopus eggs. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):577–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90622-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J. Y., Becker F. F. DNA ligase activities during hepatocarcinogenesis induced by N-2-acetylaminofluorene. Carcinogenesis. 1985 Sep;6(9):1275–1277. doi: 10.1093/carcin/6.9.1275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creissen D., Shall S. Regulation of DNA ligase activity by poly(ADP-ribose). Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):271–272. doi: 10.1038/296271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David J. C., Vinson D., Lefresne J., Signoret J. Evidence for a DNA ligase change related to early cleavage in axolotl egg. Cell Differ. 1979 Dec;8(6):451–459. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(79)90041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder R. H., Rossignol J. M. DNA ligases from rat liver. Purification and partial characterization of two molecular forms. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 26;29(25):6009–6017. doi: 10.1021/bi00477a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insdorf N. F., Bogenhagen D. F. DNA polymerase gamma from Xenopus laevis. I. The identification of a high molecular weight catalytic subunit by a novel DNA polymerase photolabeling procedure. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21491–21497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler B. Isolation, characterization and distribution of a DNA ligase from higher plants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 29;240(4):496–505. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90706-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasko D. D., Tomkinson A. E., Lindahl T. Mammalian DNA ligases. Biosynthesis and intracellular localization of DNA ligase I. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12618–12622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legerski R. J., Penkala J. E., Peterson C. A., Wright D. A. Repair of UV-induced lesions in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4317–4323. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman I. R. DNA ligase: structure, mechanism, and function. Science. 1974 Nov 29;186(4166):790–797. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4166.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto Y., Bogenhagen D. F. Repair of a synthetic abasic site in DNA in a Xenopus laevis oocyte extract. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3750–3757. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mezzina M., Rossignol J. M., Philippe M., Izzo R., Bertazzoni U., Sarasin A. Mammalian DNA ligase. Structure and function in rat-liver tissues. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jan 15;162(2):325–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10604.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mezzina M., Suarez H. G., Cassingena R., Sarasin A. Increased activity of polynucleotide ligase in 5-iodo-2'-deoxyuridine and mitomycin C-pretreated simian virus 40 (SV40)-infected monkey kidney cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 25;10(16):5073–5084. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.16.5073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrich P., Anraku Y., Lehman I. R. Deoxyribonucleic acid ligase. Isolation and physical characterization of the homogeneous enzyme from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 10;248(21):7495–7501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson E. M., Stowers D. J., Bayne M. L., Benbow R. M. Classification of DNA polymerase activities from ovaries of the frog, Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1983 Mar;96(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90306-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J., Kirschner M. A major developmental transition in early Xenopus embryos: I. characterization and timing of cellular changes at the midblastula stage. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):675–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poll E. H., Benbow R. M. A DNA helicase from Xenopus laevis ovaries. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8701–8706. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prigent C., Aoufouchi S., Philippe M. Identification of DNA ligase I related polypeptides in three different human cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jun 29;169(3):888–895. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91976-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin B. A., Hawley R. S., Chase J. W. DNA ligase from Drosophila melanogaster embryos. Purification and physical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10637–10645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard R. E., Bogenhagen D. F. A high molecular weight topoisomerase I from Xenopus laevis ovaries. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4704–4709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Signoret J., David J. C., Lefresne J., Houillon C. Control of DNA ligase molecular forms in nucleocytoplasmic combinations of axolotl and Pleurodeles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3368–3371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderhäll S. DNA ligases during rat liver regeneration. Nature. 1976 Apr 15;260(5552):640–642. doi: 10.1038/260640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderhäll S., Lindahl T. DNA ligases of eukaryotes. FEBS Lett. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80858-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderhäll S., Lindahl T. Mammalian DNA ligases. Serological evidence for two separate enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 10;250(21):8438–8444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderhäll S., Lindahl T. Two DNA ligase activities from calf thymus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 6;53(3):910–916. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Senshu M. Two distinct DNA ligases from Drosophila melanogaster embryos. FEBS Lett. 1987 Mar 23;213(2):345–352. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81520-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Yamaguchi E., Uchida T. Thermophilic DNA ligase. Purification and properties of the enzyme from Thermus thermophilus HB8. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10041–10047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teraoka H., Shimoyachi M., Tsukada K. Two distinct polynucleotide ligases from rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jun 15;54(2):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teraoka H., Sumikawa T., Tsukada K. Purification of DNA ligase II from calf thymus and preparation of rabbit antibody against calf thymus DNA ligase II. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):6888–6892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teraoka H., Tsukada K. Immunochemical analysis of molecular forms of mammalian DNA ligases I and II. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Sep 26;873(2):297–303. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teraoka H., Tsukada K. Immunohistochemical and biochemical studies on DNA ligase from a rat liver parenchymal cell line. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1985 Apr;9(4):351–355. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(85)90030-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkinson A. E., Lasko D. D., Daly G., Lindahl T. Mammalian DNA ligases. Catalytic domain and size of DNA ligase I. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12611–12617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]