Abstract
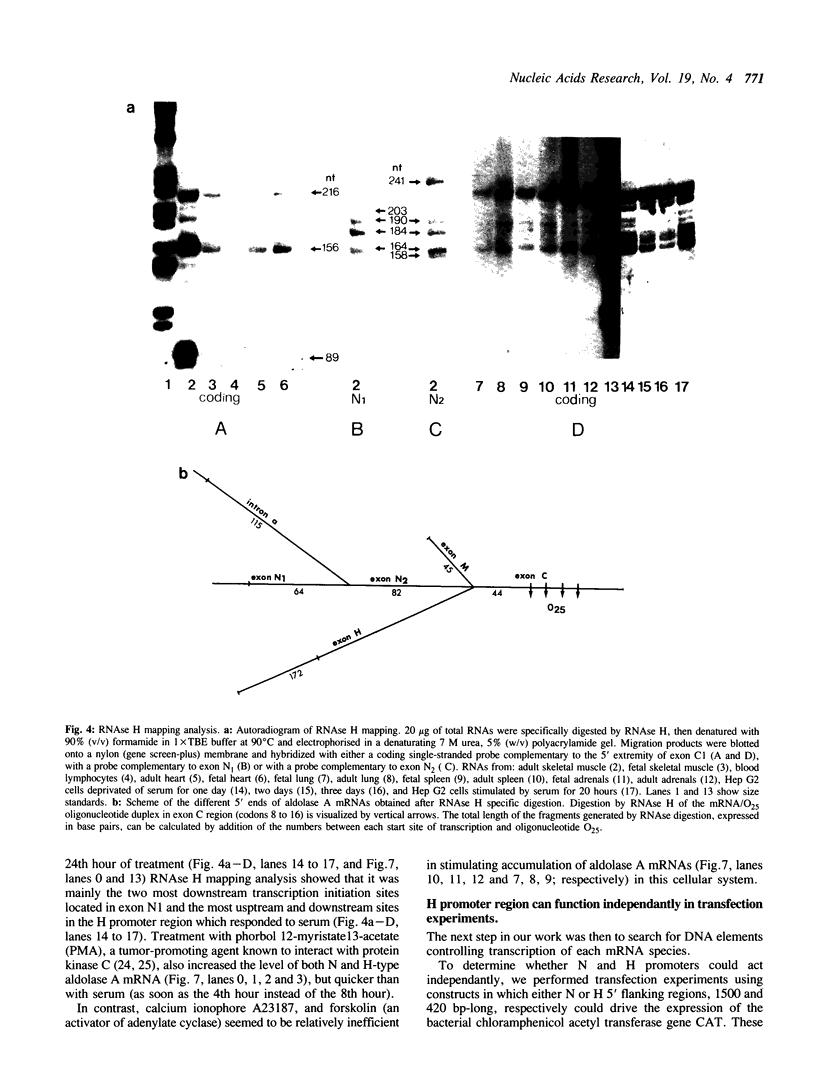
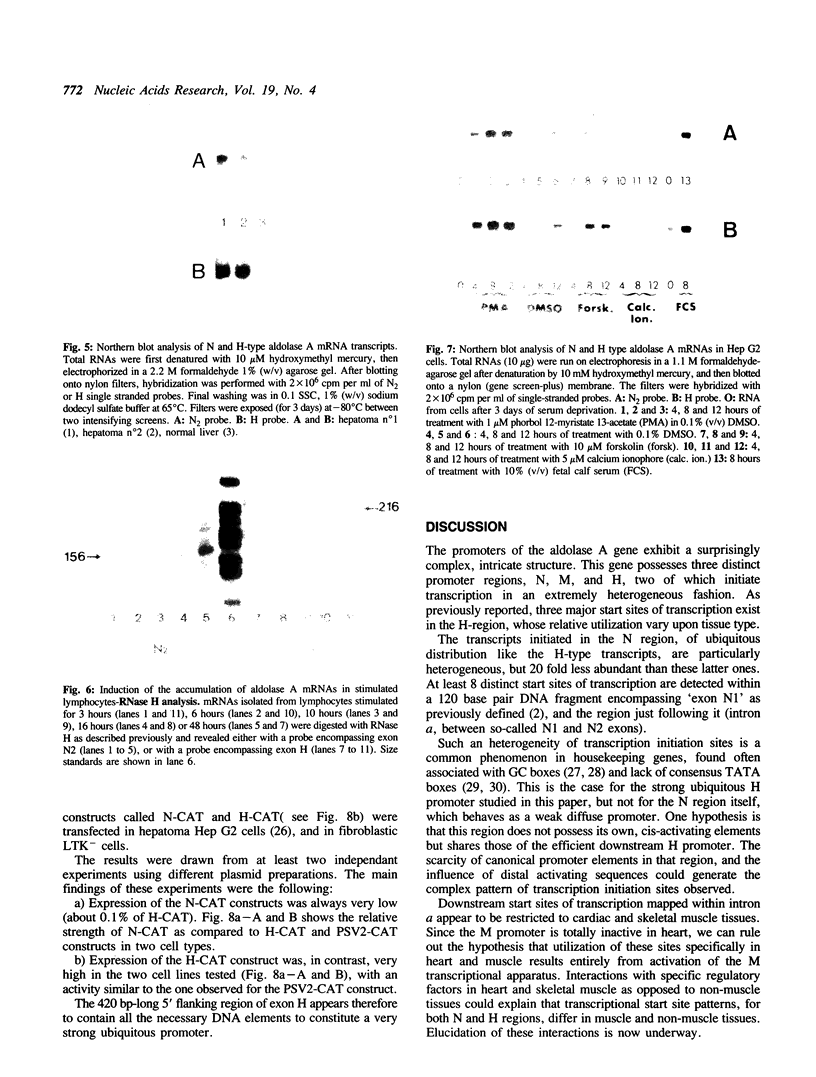
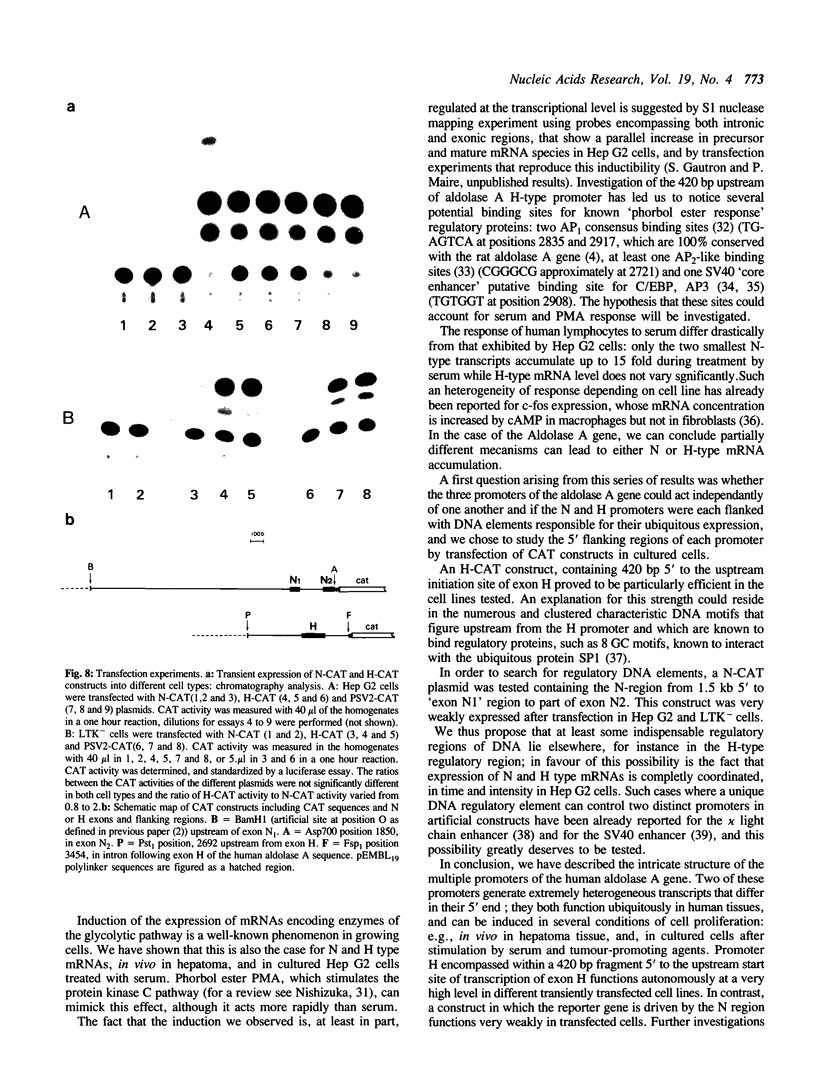
The human aldolase A gene is transcribed from three distinct promoters, the two ubiquitous promoters PN and PH and the muscle specific promoter PM. In the present study, we investigate further aldolase A mRNA structure and expression. We demonstrate that the upstream N-type exon is, in fact, extremely heterogeneous. RNAse H mapping experiments permit quantification of relative abundance of N, M, and H type mRNAs and show that the level of transcripts containing the downstream H-type exon is at least 30 times higher than that of those containing N exon, in all tissues tested. Aldolase A level is up-regulated in proliferating cells. Here we show that both N and H type mRNAs, although barely detectable in normal liver, are highly expressed in human hepatomas biopsies. Furthermore, in human lymphocytes, N-type mRNA level is enhanced by serum treatment, while in cultured Hep G2 cells, both N-type and H-type mRNA levels are increased by serum and by the tumor promoting agent PMA. Using CAT constructs in transfection experiments, we demonstrate that the H exon plus its upstream region can function autonomously: the 420 base pairs upstream of the H exon are sufficient to confer to promoter PH an efficiency comparable that of the complete SV40 early promoter and enhancer in two cell lines.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Baumann I., Stein B., Delius H., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate induction of the human collagenase gene is mediated by an inducible enhancer element located in the 5'-flanking region. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2256–2266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atchison M. L., Perry R. P. Tandem kappa immunoglobulin promoters are equally active in the presence of the kappa enhancer: implications for models of enhancer function. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90742-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Neuberg M., Burckhardt J., Almendral J., Wallich R., Müller R. Involvement of common and cell type-specific pathways in c-fos gene control: stable induction of cAMP in macrophages. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90428-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Lee W. M., Williams P. W., Giels G. M., Williams L. T. c-myc gene expression is stimulated by agents that activate protein kinase C and does not account for the mitogenic effect of PDGF. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond I., Legg A., Schneider J. A., Rozengurt E. Glycolysis in quiescent cultures of 3T3 cells. Stimulation by serum, epidermal growth factor, and insulin in intact cells and persistence of the stimulation after cell homogenization. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):866–871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautron S., Daegelen D., Mennecier F., Dubocq D., Kahn A., Dreyfus J. C. Molecular mechanisms of McArdle's disease (muscle glycogen phosphorylase deficiency). RNA and DNA analysis. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):275–281. doi: 10.1172/JCI112794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Multiple specific contacts between a mammalian transcription factor and its cognate promoters. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):409–413. doi: 10.1038/312409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginot F., Decaux J. F., Cognet M., Berbar T., Levrat F., Kahn A., Weber A. Transfection of hepatic genes into adult rat hepatocytes in primary culture and their tissue-specific expression. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Mar 15;180(2):289–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14646.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillouzo A., Weber A., Le Provost E., Rissel M., Schapira F. Cell types involved in the expression of foetal aldolases during rat azo-dye hepatocarcinogenesis. J Cell Sci. 1981 Jun;49:249–260. doi: 10.1242/jcs.49.1.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Chiu R., Karin M. Transcription factor AP-2 mediates induction by two different signal-transduction pathways: protein kinase C and cAMP. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izzo P., Costanzo P., Lupo A., Rippa E., Paolella G., Salvatore F. Human aldolase A gene. Structural organization and tissue-specific expression by multiple promoters and alternate mRNA processing. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jul 1;174(4):569–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14136.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joh K., Arai Y., Mukai T., Hori K. Expression of three mRNA species from a single rat aldolase A gene, differing in their 5' non-coding regions. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 5;190(3):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Identification of a rat liver nuclear protein that binds to the enhancer core element of three animal viruses. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):133–146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T., Berg P. Effects of the position of the simian virus 40 enhancer on expression of multiple transcription units in a single plasmid. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2593–2601. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Howe C. C., Aden D. P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.6248960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamas E., Kahn A., Guillouzo A. Detection of mRNAs present at low concentrations in rat liver by in situ hybridization: application to the study of metabolic regulation and azo dye hepatocarcinogenesis. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 May;35(5):559–563. doi: 10.1177/35.5.3104450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebherz H. G., Rutter W. J. Distribution of fructose diphosphate aldolase variants in biological systems. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):109–121. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maire P., Gautron S., Hakim V., Gregori C., Mennecier F., Kahn A. Characterization of three optional promoters in the 5' region of the human aldolase A gene. J Mol Biol. 1987 Oct 5;197(3):425–438. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90556-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Rautmann G., Magun B. E., Breathnach R. Epidermal growth factor or serum stimulation of rat fibroblasts induces an elevation in mRNA levels for lactate dehydrogenase and other glycolytic enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):711–726. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meienhofer M. C., Dreyfus J. C., Kahn A. Induction of glycolytic enzyme synthesis in proliferating fibroblasts. Study of phosphofructokinase, glucose phosphate isomerase and pyruvate kinase. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 15;214(1):195–201. doi: 10.1042/bj2140195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mennecier F., Daegelen D., Schweighoffer F., Levin M., Kahn A. Expression of aldolase A messenger RNAs in human adult and foetal tissues and in hepatoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 13;134(3):1093–1100. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90363-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Kedes L. Upstream regions of the human cardiac actin gene that modulate its transcription in muscle cells: presence of an evolutionarily conserved repeated motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2125–2136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Wang C., Tjian R. Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):847–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers P. A., Brenton D. P., Hopkinson D. A. Changes in the activity and isozyme patterns of glycolytic enzymes during stimulation of normal human lymphocytes with phytohaemagglutinin. Ann Hum Genet. 1980 Jan;43(3):213–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1980.tb01555.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira F. Resurgence of fetal isozymes in cancer: study of aldolase, pyruvate kinase, lactic dehydrogenase, and beta-hexosaminidase. Isozymes Curr Top Biol Med Res. 1981;5:27–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Sierra F. Alternative promoters in developmental gene expression. Annu Rev Genet. 1987;21:237–257. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.21.120187.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal A., Patil N., Chao M. A constitutive promoter directs expression of the nerve growth factor receptor gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3160–3167. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L., Levanon D., Lieman-Hurwitz J., Dafni N., Groner Y. Human Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene: molecular characterization of its two mRNA species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9349–9365. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaquero C., Sanceau J., Sondermeyer P., Falcoff R. Kinetics of messenger accumulation coding for IFN gamma, related to modifications in the poly(A) RNA population of activated human lymphocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2629–2640. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A., Le Provost E., Boisnard-Rissel M., Berges J., Schapira F., Guillouzo A. Localization of fetal aldolases during early stages of azo-dye hepatocarcinogenesis in rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 29;92(2):591–597. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90374-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]