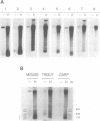
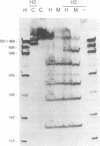
Abstract
In the vertebrate genomes studied to date the 5' end of many genes are associated with distinctive sequences known as CpG islands. CpG islands have three properties: they are non-methylated; the dinucleotide CpG occurs at the frequency predicted by base composition; and they are GC-rich. Unexpectedly we have found that CpG islands in certain fish only have the first two properties; that is, their GC-content is not elevated compared to bulk genomic DNA. Based on this finding, we speculate that the GC-richness of CpG islands in vertebrates other than fish is a passive consequence of a higher mutation rate in regions of open chromatin under conditions where the nucleotide precursor pools are biased.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antequera F., Boyes J., Bird A. High levels of de novo methylation and altered chromatin structure at CpG islands in cell lines. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G., Bernardi G. Compositional patterns in the nuclear genome of cold-blooded vertebrates. J Mol Evol. 1990 Oct;31(4):265–281. doi: 10.1007/BF02101122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G., Bernardi G. Compositional transitions in the nuclear genomes of cold-blooded vertebrates. J Mol Evol. 1990 Oct;31(4):282–293. doi: 10.1007/BF02101123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohr V. A., Okumoto D. S., Ho L., Hanawalt P. C. Characterization of a DNA repair domain containing the dihydrofolate reductase gene in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16666–16672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. N., Taggart M. H., Bird A. P. Unmethylated domains in vertebrate DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):647–658. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulondre C., Miller J. H., Farabaugh P. J., Gilbert W. Molecular basis of base substitution hotspots in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1978 Aug 24;274(5673):775–780. doi: 10.1038/274775a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner-Garden M., Frommer M. CpG islands in vertebrate genomes. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):261–282. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90689-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Richards R. I. Human metallothionein genes--primary structure of the metallothionein-II gene and a related processed gene. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):797–802. doi: 10.1038/299797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeds J. M., Slabaugh M. B., Mathews C. K. DNA precursor pools and ribonucleotide reductase activity: distribution between the nucleus and cytoplasm of mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3443–3450. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z., Zhu Z., Roberg K., Faras A. J., Guise K. S., Kapuscinski A. R., Hackett P. B. The beta-actin gene of carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 25;17(14):5850–5850. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.14.5850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroni G., Otto E., Lastowski-Perry D. Molecular and cytogenetic characterization of a metallothionein gene of Drosophila. Genetics. 1986 Mar;112(3):493–504. doi: 10.1093/genetics/112.3.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M. F., Collier J., Koutz P., Howard B. Nucleotide sequence of the trout metallothionein A gene 5' regulatory region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4622–4622. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng S. Y., Gunning P., Eddy R., Ponte P., Leavitt J., Shows T., Kedes L. Evolution of the functional human beta-actin gene and its multi-pseudogene family: conservation of noncoding regions and chromosomal dispersion of pseudogenes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2720–2732. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel U., Zakut R., Shani M., Neuman S., Levy Z., Yaffe D. The nucleotide sequence of the rat cytoplasmic beta-actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1759–1771. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P., Ng S. Y., Engel J., Gunning P., Kedes L. Evolutionary conservation in the untranslated regions of actin mRNAs: DNA sequence of a human beta-actin cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1687–1696. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Bird A. Alternative chromatin structure at CpG islands. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):909–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90339-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf S. F., Jolly D. J., Lunnen K. D., Friedmann T., Migeon B. R. Methylation of the hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase locus on the human X chromosome: implications for X-chromosome inactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2806–2810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe K. H., Sharp P. M., Li W. H. Mutation rates differ among regions of the mammalian genome. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):283–285. doi: 10.1038/337283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zafarullah M., Bonham K., Gedamu L. Structure of the rainbow trout metallothionein B gene and characterization of its metal-responsive region. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4469–4476. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]