Abstract
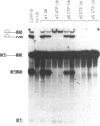
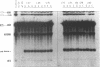
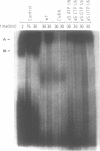
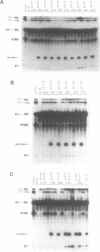
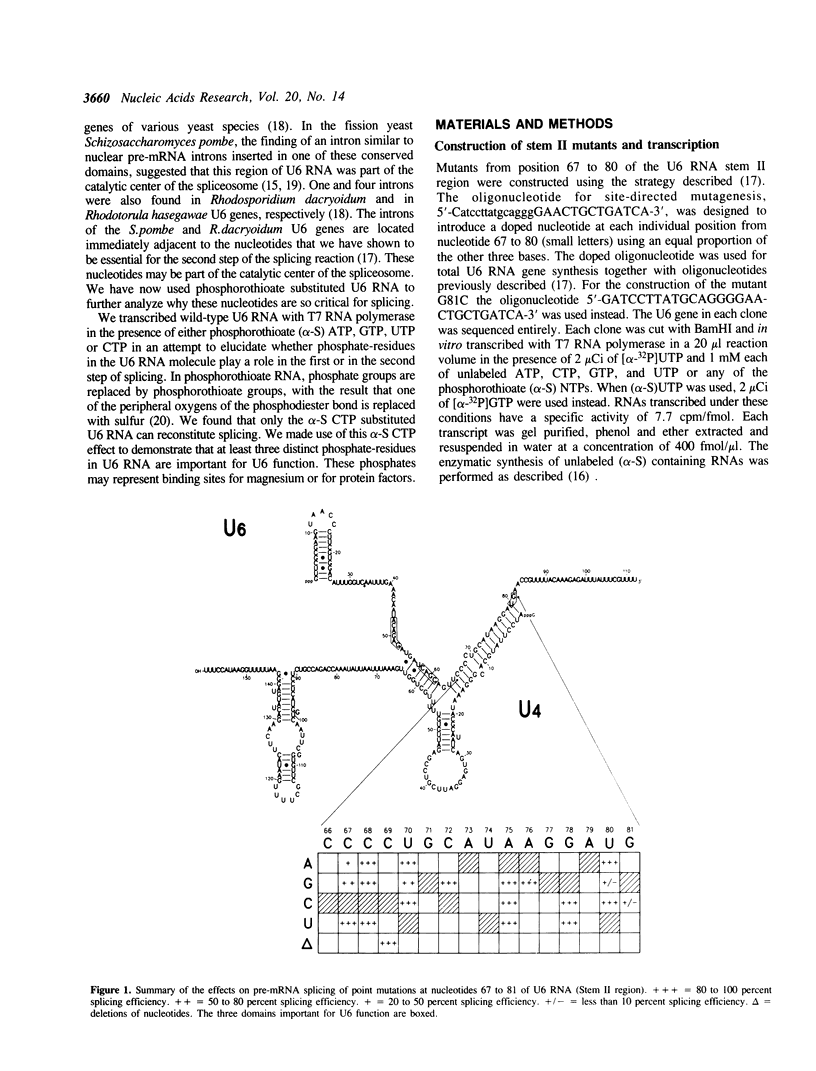
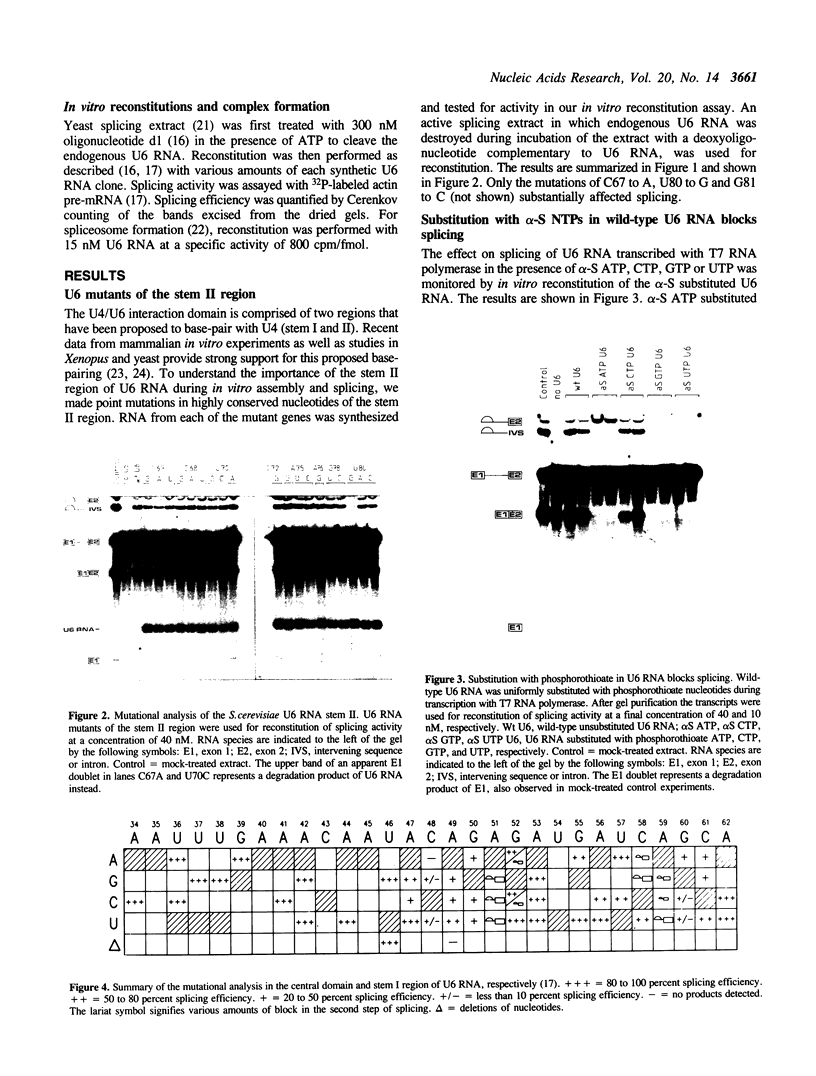
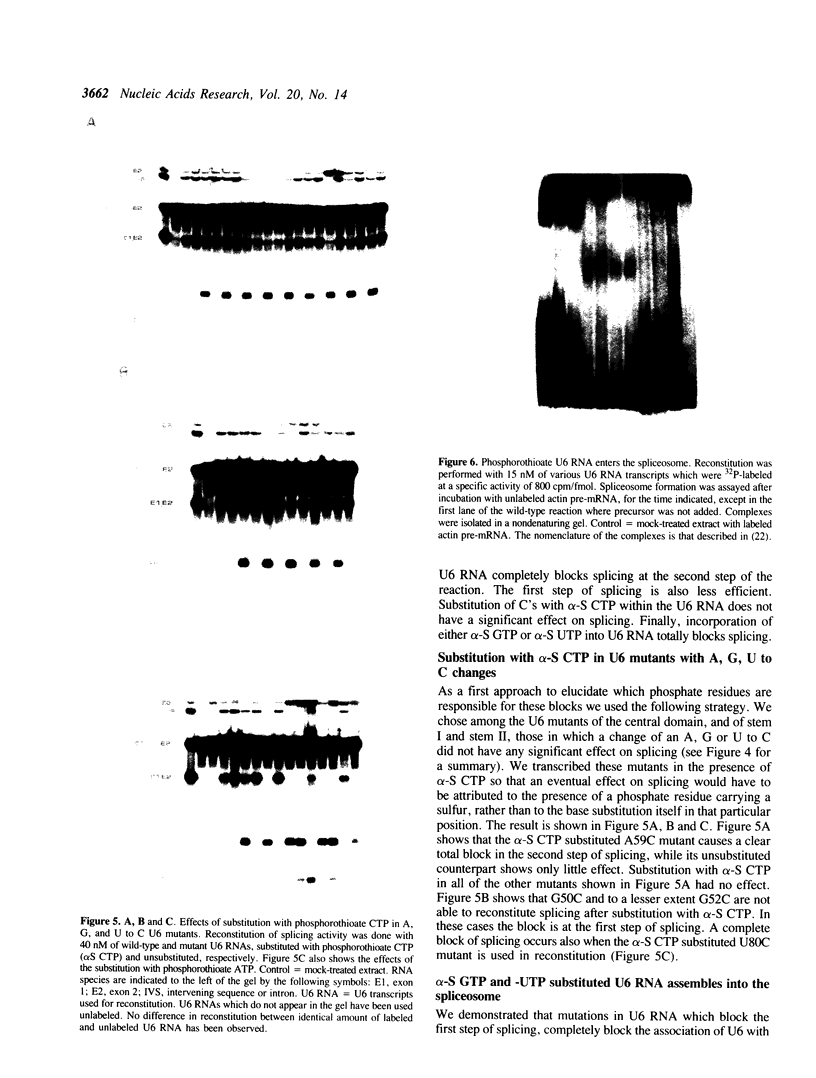
A thorough mutational analysis of U6 RNA in combination with a functional reconstitution assay, revealed that three domains are important for U6 function in pre-mRNA splicing. In order to further analyze why these regions are so critical for splicing, we make use of phosphorothioate substituted U6 RNAs. Wild-type U6 RNA was transcribed in vitro with T7 RNA polymerase in the presence of either phosphorothiate (alpha-S) ATP, GTP, UTP or CTP. The functionality of the transcripts was monitored by in vitro reconstitution. While substitution with alpha-S ATP, GTP or UTP blocked splicing, substitution with alpha-S CTP had little or no effect on splicing. We made use of this alpha-S CTP effect in an attempt to elucidate which phosphates in the U6 RNA molecule play a role in the first or in the second step of splicing. U6 mutants in which a change of an A, G or U to C does not have any significant effect on splicing were transcribed in the presence of alpha-S CTP. Observed effects on splicing thus have to be attributed to the presence of the thio-substituted phosphate group rather than the nucleotide change. The results of in vitro reconstitution give a clear answer for at least three phosphates; two of them play a role in the first step, while one of them is involved in the second step of splicing.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bindereif A., Wolff T., Green M. R. Discrete domains of human U6 snRNA required for the assembly of U4/U6 snRNP and splicing complexes. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):251–255. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08102.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blencowe B. J., Sproat B. S., Ryder U., Barabino S., Lamond A. I. Antisense probing of the human U4/U6 snRNP with biotinylated 2'-OMe RNA oligonucleotides. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):531–539. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody E., Abelson J. The "spliceosome": yeast pre-messenger RNA associates with a 40S complex in a splicing-dependent reaction. Science. 1985 May 24;228(4702):963–967. doi: 10.1126/science.3890181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brow D. A., Guthrie C. Splicing a spliceosomal RNA. Nature. 1989 Jan 5;337(6202):14–15. doi: 10.1038/337014a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. C., Abelson J. Spliceosome assembly in yeast. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):1014–1027. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.1014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahm S. C., Uhlenbeck O. C. Role of divalent metal ions in the hammerhead RNA cleavage reaction. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 1;30(39):9464–9469. doi: 10.1021/bi00103a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein F. Nucleoside phosphorothioates. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:367–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabrizio P., Abelson J. Two domains of yeast U6 small nuclear RNA required for both steps of nuclear precursor messenger RNA splicing. Science. 1990 Oct 19;250(4979):404–409. doi: 10.1126/science.2145630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabrizio P., McPheeters D. S., Abelson J. In vitro assembly of yeast U6 snRNP: a functional assay. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2137–2150. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:671–708. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie C., Patterson B. Spliceosomal snRNAs. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:387–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.002131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampel A., Tritz R. RNA catalytic properties of the minimum (-)sTRSV sequence. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 13;28(12):4929–4933. doi: 10.1021/bi00438a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R. J., Newman A. J., Cheng S. C., Abelson J. Yeast mRNA splicing in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14780–14792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lührmann R., Kastner B., Bach M. Structure of spliceosomal snRNPs and their role in pre-mRNA splicing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Nov 30;1087(3):265–292. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90001-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Uhlenbeck O. C. Determination of RNA-protein contacts using thiophosphate substitutions. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 4;28(7):2849–2855. doi: 10.1021/bi00433a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Siliciano P. G., Guthrie C. Recognition of the TACTAAC box during mRNA splicing in yeast involves base pairing to the U2-like snRNA. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90564-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peebles C. L., Perlman P. S., Mecklenburg K. L., Petrillo M. L., Tabor J. H., Jarrell K. A., Cheng H. L. A self-splicing RNA excises an intron lariat. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90755-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffner D. E., Uhlenbeck O. C. Thiophosphate interference experiments locate phosphates important for the hammerhead RNA self-cleavage reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6025–6029. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon K. W., Guthrie C. Suppressors of a U4 snRNA mutation define a novel U6 snRNP protein with RNA-binding motifs. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):773–785. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Science. 1987 Feb 13;235(4790):766–771. doi: 10.1126/science.3544217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano P. G., Guthrie C. 5' splice site selection in yeast: genetic alterations in base-pairing with U1 reveal additional requirements. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1258–1267. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani T., Ohshima Y. The gene for the U6 small nuclear RNA in fission yeast has an intron. Nature. 1989 Jan 5;337(6202):87–90. doi: 10.1038/337087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani T., Ohshima Y. mRNA-type introns in U6 small nuclear RNA genes: implications for the catalysis in pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):1022–1031. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.1022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vankan P., McGuigan C., Mattaj I. W. Domains of U4 and U6 snRNAs required for snRNP assembly and splicing complementation in Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3397–3404. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijayraghavan U., Company M., Abelson J. Isolation and characterization of pre-mRNA splicing mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1206–1216. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Weiner A. M. A compensatory base change in U1 snRNA suppresses a 5' splice site mutation. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Weiner A. M. A compensatory base change in human U2 snRNA can suppress a branch site mutation. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1545–1552. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Veen R., Arnberg A. C., van der Horst G., Bonen L., Tabak H. F., Grivell L. A. Excised group II introns in yeast mitochondria are lariats and can be formed by self-splicing in vitro. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90756-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]