Abstract
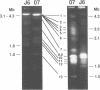
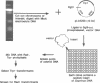
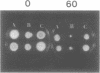
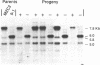
We have constructed cosmid libraries from electrophoretically separated chromosomes of the basidiomycete Coprinus cinereus. These libraries greatly facilitate the isolation of genes by complementation of mutant phenotypes and are particularly useful for map-based cloning strategies. From a library constructed from two co-migrating C.cinereus chromosomes, we isolated a clone that complements the C.cinereus rad9-1 mutation. Examination of this clone showed that it complements both the repair and meiotic defects of this mutant. Restriction fragment length polymorphism mapping using a portion of this clone showed that it maps to the rad9 locus. In addition, a single copy of transforming DNA is sufficient to complement the rad9-1 defects. Thus, we believe we have cloned the rad9 gene itself. We also used a chromosome-specific library and backcrossed isolates to rapidly identify a cosmid clone which is tightly linked to the rad11 locus and is therefore a suitable starting point for a chromosome walk. These rapid methods of gene mapping and isolation should be applicable to any organism with separable chromosomes.
Full text
PDF

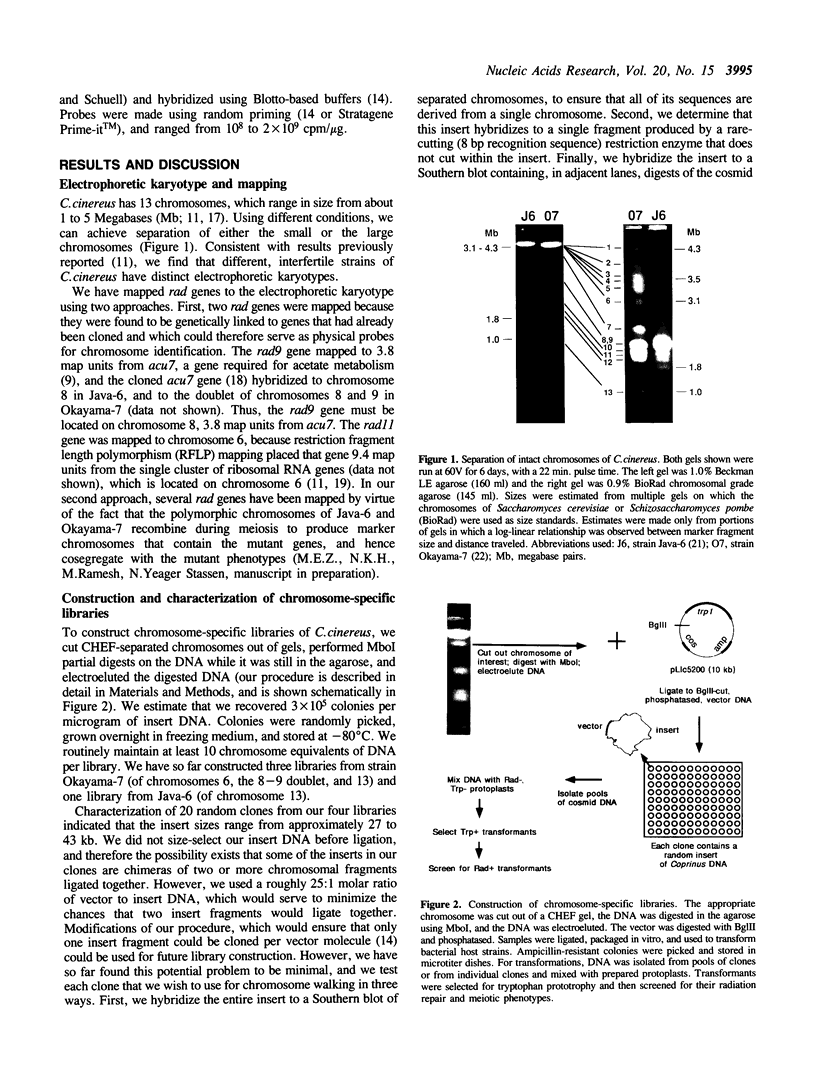
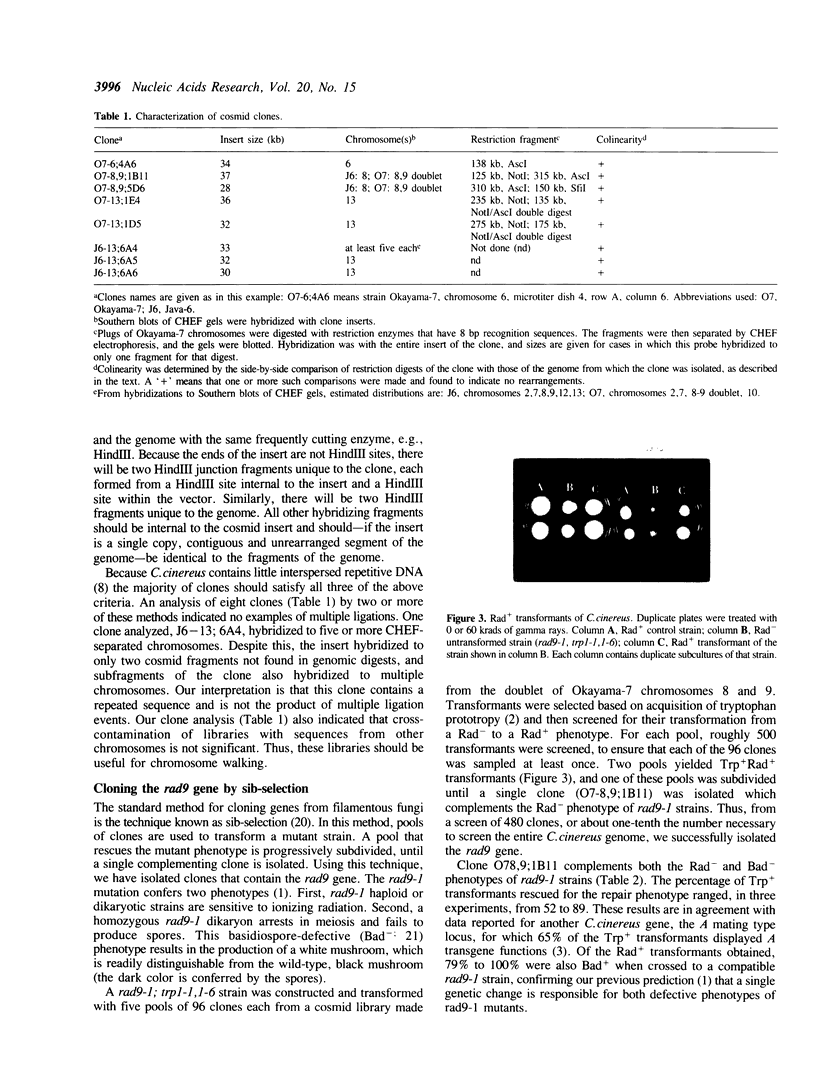
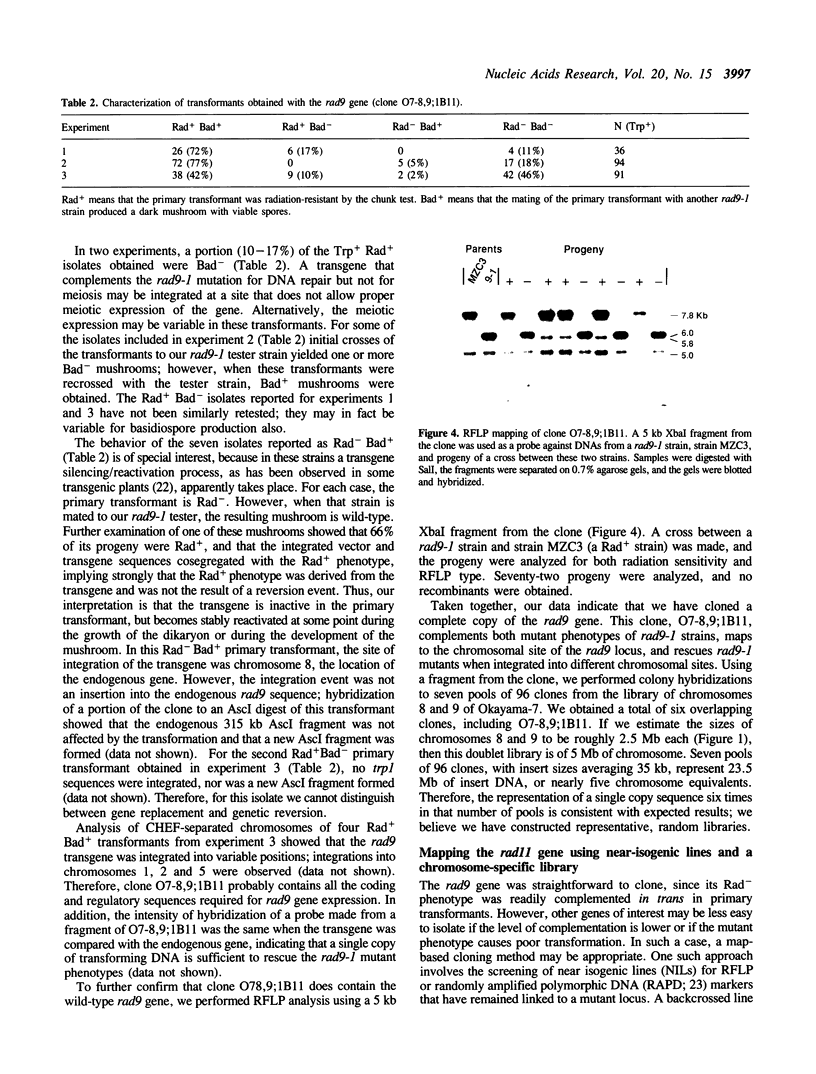


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binninger D. M., Le Chevanton L., Skrzynia C., Shubkin C. D., Pukkila P. J. Targeted transformation in Coprinus cinereus. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Jun;227(2):245–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00259677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binninger D. M., Skrzynia C., Pukkila P. J., Casselton L. A. DNA-mediated transformation of the basidiomycete Coprinus cinereus. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):835–840. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04828.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody H., Griffith J., Cuticchia A. J., Arnold J., Timberlake W. E. Chromosome-specific recombinant DNA libraries from the fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 11;19(11):3105–3109. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.11.3105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. A colony bank containing synthetic Col El hybrid plasmids representative of the entire E. coli genome. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta S. K. Repeated DNA sequences in fungi. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Nov;1(11):1411–1419. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.11.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King H. B., Casselton L. A. Genetics and function of isocitrate lyase in Coprinus. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Dec 9;157(3):319–325. doi: 10.1007/BF00268669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May G., Le Chevanton L., Pukkila P. J. Molecular analysis of the Coprinus cinereus mating type A factor demonstrates an unexpectedly complex structure. Genetics. 1991 Jul;128(3):529–538. doi: 10.1093/genetics/128.3.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittelsten Scheid O., Paszkowski J., Potrykus I. Reversible inactivation of a transgene in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Aug;228(1-2):104–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00282454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pukkila P. J., Lu B. C. Silver staining of meiotic chromosomes in the fungus, Coprinus cinereus. Chromosoma. 1985;91(2):108–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00294053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raleigh E. A., Murray N. E., Revel H., Blumenthal R. M., Westaway D., Reith A. D., Rigby P. W., Elhai J., Hanahan D. McrA and McrB restriction phenotypes of some E. coli strains and implications for gene cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1563–1575. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Smits M., Ponnudurai T., Vermeulen A., Meuwissen J. H., Langsley G. Chromosome-sized DNA molecules of Plasmodium falciparum. Science. 1985 Aug 16;229(4714):658–661. doi: 10.1126/science.3895435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Kubelik A. R., Livak K. J., Rafalski J. A., Tingey S. V. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6531–6535. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood S., Schertzer M., Drabkin H., Patterson D., Longmire J. L., Deaven L. L. Characterization of a human chromosome 8 cosmid library constructed from flow-sorted chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1992;59(4):243–247. doi: 10.1159/000133260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young N. D., Zamir D., Ganal M. W., Tanksley S. D. Use of isogenic lines and simultaneous probing to identify DNA markers tightly linked to the tm-2a gene in tomato. Genetics. 1988 Oct;120(2):579–585. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.2.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zolan M. E., Pukkila P. J. Inheritance of DNA methylation in Coprinus cinereus. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):195–200. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zolan M. E., Tremel C. J., Pukkila P. J. Production and characterization of radiation-sensitive meiotic mutants of Coprinus cinereus. Genetics. 1988 Oct;120(2):379–387. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.2.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]