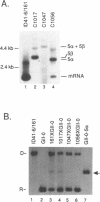
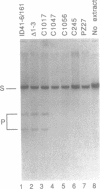
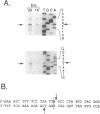
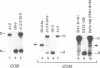Abstract
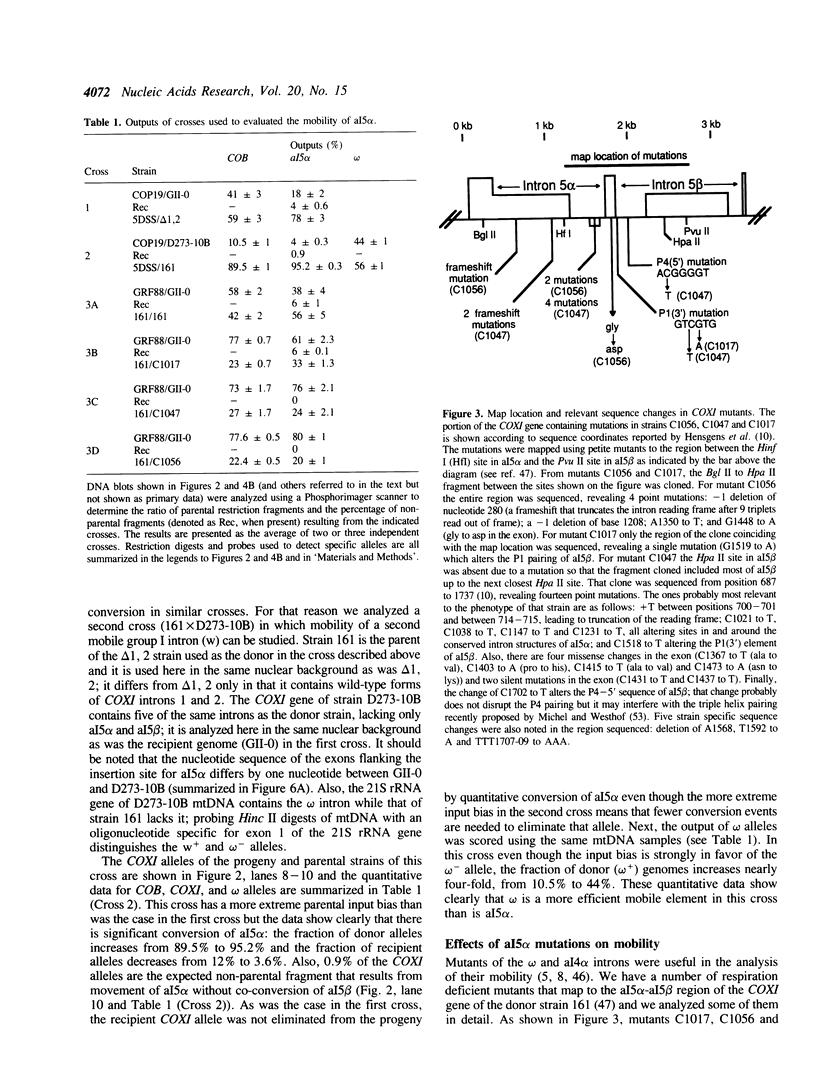
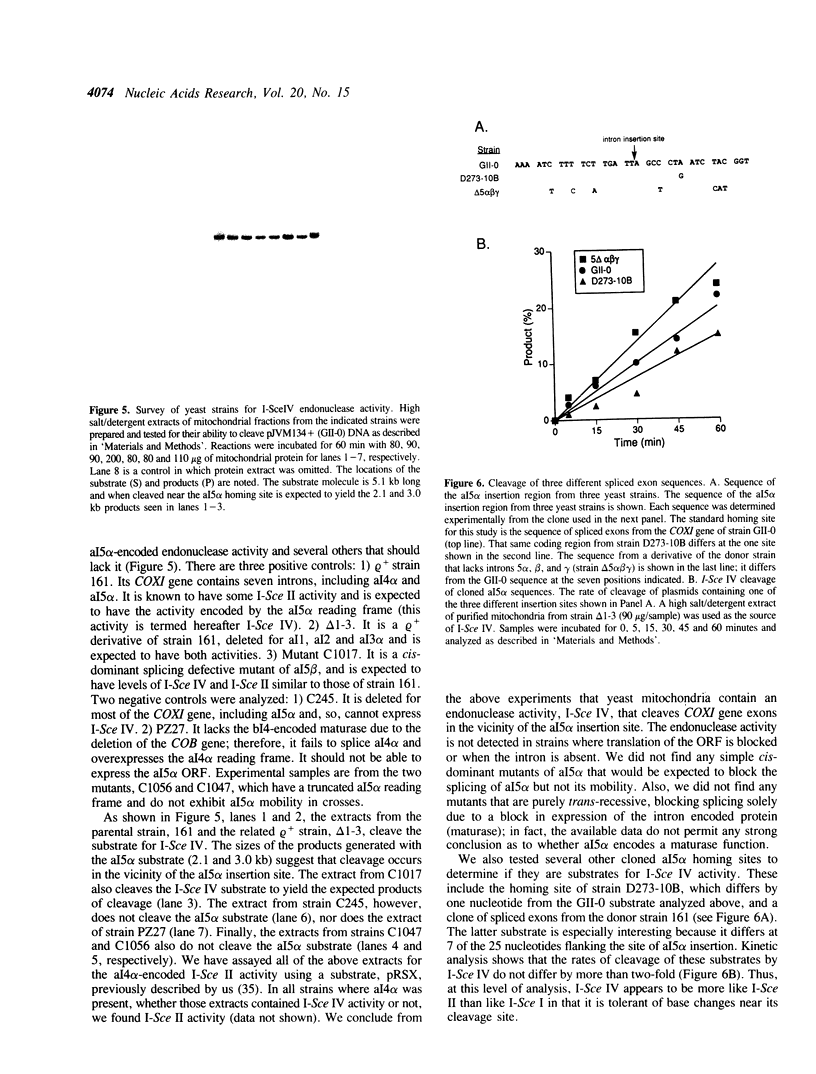
We have found that intron 5 alpha of the COXI gene (al5 alpha) of yeast mtDNA is a mobile group I intron in crosses between strains having or lacking the intron. We have demonstrated the following hallmarks of that process: 1) co-conversion of flanking optional intron markers; 2) mutations that truncate the intron open reading frame block intron mobility; and 3) the intron open reading frame encodes an endonuclease activity that is required for intron movement. The endonuclease activity, termed I-Sce IV, cleaves the COXI allele lacking al5 alpha near the site of intron insertion, making a four-base staggered cut with 3' OH overhangs. Three cloned DNAs derived from different forms of the COXI gene, which differ in primary sequence at up to seven nucleotides around the cleavage site, are all good substrates for in vitro I-Sce IV cleavage activity. Two of the strains from which these substrates were derived were tested in crosses and are comparably efficient as al5 alpha recipients. When compared with omega mobility occurring simultaneously in one cross, al5 alpha is less efficient as a mobile element.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad I., Finkelstein J. A., Steggles A. W. The analysis of RNA by in situ agarose gel hybridization is more sensitive than the equivalent northern blot analysis. Biotechniques. 1990 Feb;8(2):162–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anziano P. Q., Hanson D. K., Mahler H. R., Perlman P. S. Functional domains in introns: trans-acting and cis-acting regions of intron 4 of the cob gene. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):925–932. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90297-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell-Pedersen D., Quirk S. M., Aubrey M., Belfort M. A site-specific endonuclease and co-conversion of flanking exons associated with the mobile td intron of phage T4. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell-Pedersen D., Quirk S., Clyman J., Belfort M. Intron mobility in phage T4 is dependent upon a distinctive class of endonucleases and independent of DNA sequences encoding the intron core: mechanistic and evolutionary implications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3763–3770. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonitz S. G., Coruzzi G., Thalenfeld B. E., Tzagoloff A., Macino G. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system. Structure and nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for subunit 1 of yeast cytochrme oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11927–11941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger G., Werner S. The mitochondrial URF1 gene in Neurospora crassa has an intron that contains a novel type of URF. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 20;186(2):231–242. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90100-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colleaux L., D'Auriol L., Galibert F., Dujon B. Recognition and cleavage site of the intron-encoded omega transposase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6022–6026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colleaux L., d'Auriol L., Betermier M., Cottarel G., Jacquier A., Galibert F., Dujon B. Universal code equivalent of a yeast mitochondrial intron reading frame is expressed into E. coli as a specific double strand endonuclease. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):521–533. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conde J., Fink G. R. A mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae defective for nuclear fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3651–3655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings D. J., Michel F., McNally K. L. DNA sequence analysis of the apocytochrome b gene of Podospora anserina: a new family of intronic open reading frame. Curr Genet. 1989 Dec;16(5-6):407–418. doi: 10.1007/BF00340720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delahodde A., Goguel V., Becam A. M., Creusot F., Perea J., Banroques J., Jacq C. Site-specific DNA endonuclease and RNA maturase activities of two homologous intron-encoded proteins from yeast mitochondria. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):431–441. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90246-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujardin G., Jacq C., Slonimski P. P. Single base substitution in an intron of oxidase gene compensates splicing defects of the cytochrome b gene. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):628–632. doi: 10.1038/298628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujon B., Belfort M., Butow R. A., Jacq C., Lemieux C., Perlman P. S., Vogt V. M. Mobile introns: definition of terms and recommended nomenclature. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujon B. Sequence of the intron and flanking exons of the mitochondrial 21S rRNA gene of yeast strains having different alleles at the omega and rib-1 loci. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):185–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90246-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürrenberger F., Rochaix J. D. Chloroplast ribosomal intron of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: in vitro self-splicing, DNA endonuclease activity and in vivo mobility. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3495–3501. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04913.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy S. R., Gold L. The phage T4 nrdB intron: a deletion mutant of a version found in the wild. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):1032–1041. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.1032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier A., Turmel M., Lemieux C. A group I intron in the chloroplast large subunit rRNA gene of Chlamydomonas eugametos encodes a double-strand endonuclease that cleaves the homing site of this intron. Curr Genet. 1991 Jan;19(1):43–47. doi: 10.1007/BF00362086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensgens L. A., Bonen L., de Haan M., van der Horst G., Grivell L. A. Two intron sequences in yeast mitochondrial COX1 gene: homology among URF-containing introns and strain-dependent variation in flanking exons. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):379–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90457-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudspeth M. E., Shumard D. S., Tatti K. M., Grossman L. I. Rapid purification of yeast mitochondrial DNA in high yield. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 11;610(2):221–228. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquier A., Dujon B. An intron-encoded protein is active in a gene conversion process that spreads an intron into a mitochondrial gene. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):383–394. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrell K. A., Dietrich R. C., Perlman P. S. Group II intron domain 5 facilitates a trans-splicing reaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2361–2366. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston S. A., Anziano P. Q., Shark K., Sanford J. C., Butow R. A. Mitochondrial transformation in yeast by bombardment with microprojectiles. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1538–1541. doi: 10.1126/science.2836954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostriken R., Strathern J. N., Klar A. J., Hicks J. B., Heffron F. A site-specific endonuclease essential for mating-type switching in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90219-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazowska J., Jacq C., Slonimski P. P. Sequence of introns and flanking exons in wild-type and box3 mutants of cytochrome b reveals an interlaced splicing protein coded by an intron. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90344-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemieux C., Lee R. W. Nonreciprocal recombination between alleles of the chloroplast 23S rRNA gene in interspecific Chlamydomonas crosses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4166–4170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macreadie I. G., Scott R. M., Zinn A. R., Butow R. A. Transposition of an intron in yeast mitochondria requires a protein encoded by that intron. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):395–402. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall P., Lemieux C. Cleavage pattern of the homing endonuclease encoded by the fifth intron in the chloroplast large subunit rRNA-encoding gene of Chlamydomonas eugametos. Gene. 1991 Aug 15;104(2):241–245. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90256-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Dujon B. Genetic exchanges between bacteriophage T4 and filamentous fungi? Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):323–323. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90651-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Westhof E. Modelling of the three-dimensional architecture of group I catalytic introns based on comparative sequence analysis. J Mol Biol. 1990 Dec 5;216(3):585–610. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90386-Z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscarella D. E., Ellison E. L., Ruoff B. M., Vogt V. M. Characterization of I-Ppo, an intron-encoded endonuclease that mediates homing of a group I intron in the ribosomal DNA of Physarum polycephalum. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3386–3396. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscarella D. E., Vogt V. M. A mobile group I intron in the nuclear rDNA of Physarum polycephalum. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):443–454. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90247-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagley P., Linnane A. W. Expression of mitochondrial DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: the construction of sets of isonuclear haploid strains containing different specified mitochondrial genomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Nov 29;85(2):585–592. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91203-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobrega F. G., Tzagoloff A. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system. DNA sequence and organization of the cytochrome b gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae D273-10B. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9828–9837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman P. S., Butow R. A. Mobile introns and intron-encoded proteins. Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1106–1109. doi: 10.1126/science.2479980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman P. S. Genetic analysis of RNA splicing in yeast mitochondria. Methods Enzymol. 1990;181:539–558. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)81150-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirk S. M., Bell-Pedersen D., Belfort M. Intron mobility in the T-even phages: high frequency inheritance of group I introns promoted by intron open reading frames. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):455–465. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90248-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargueil B., Delahodde A., Hatat D., Tian G. L., Lazowska J., Jacq C. A new specific DNA endonuclease activity in yeast mitochondria. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Feb;225(2):340–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00269867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargueil B., Hatat D., Delahodde A., Jacq C. In vivo and in vitro analyses of an intron-encoded DNA endonuclease from yeast mitochondria. Recognition site by site-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5659–5665. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skelly P. J., Hardy C. M., Clark-Walker G. D. A mobile group II intron of a naturally occurring rearranged mitochondrial genome in Kluyveromyces lactis. Curr Genet. 1991 Jul;20(1-2):115–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00312773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathern J. N., Klar A. J., Hicks J. B., Abraham J. A., Ivy J. M., Nasmyth K. A., McGill C. Homothallic switching of yeast mating type cassettes is initiated by a double-stranded cut in the MAT locus. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90418-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watabe H., Iino T., Kaneko T., Shibata T., Ando T. A new class of site-specific endodeoxyribonucleases. Endo.Sce I isolated from a eukaryote, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4663–4665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzlau J. M., Saldanha R. J., Butow R. A., Perlman P. S. A latent intron-encoded maturase is also an endonuclease needed for intron mobility. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):421–430. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90245-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernette C. M., Saldahna R., Perlman P. S., Butow R. A. Purification of a site-specific endonuclease, I-Sce II, encoded by intron 4 alpha of the mitochondrial coxI gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18976–18982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernette C., Saldanha R., Smith D., Ming D., Perlman P. S., Butow R. A. Complex recognition site for the group I intron-encoded endonuclease I-SceII. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):716–723. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zassenhaus H. P., Hofmann T. J., Uthayashanker R., Vincent R. D., Zona M. Construction of a yeast mutant lacking the mitochondrial nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3283–3296. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn A. R., Butow R. A. Kinetics and intermediates of yeast mitochondrial DNA recombination. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:115–121. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn A. R., Butow R. A. Nonreciprocal exchange between alleles of the yeast mitochondrial 21S rRNA gene: kinetics and the involvement of a double-strand break. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):887–895. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90348-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Zamaroczy M., Bernardi G. The GC clusters of the mitochondrial genome of yeast and their evolutionary origin. Gene. 1986;41(1):1–22. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90262-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]