Abstract
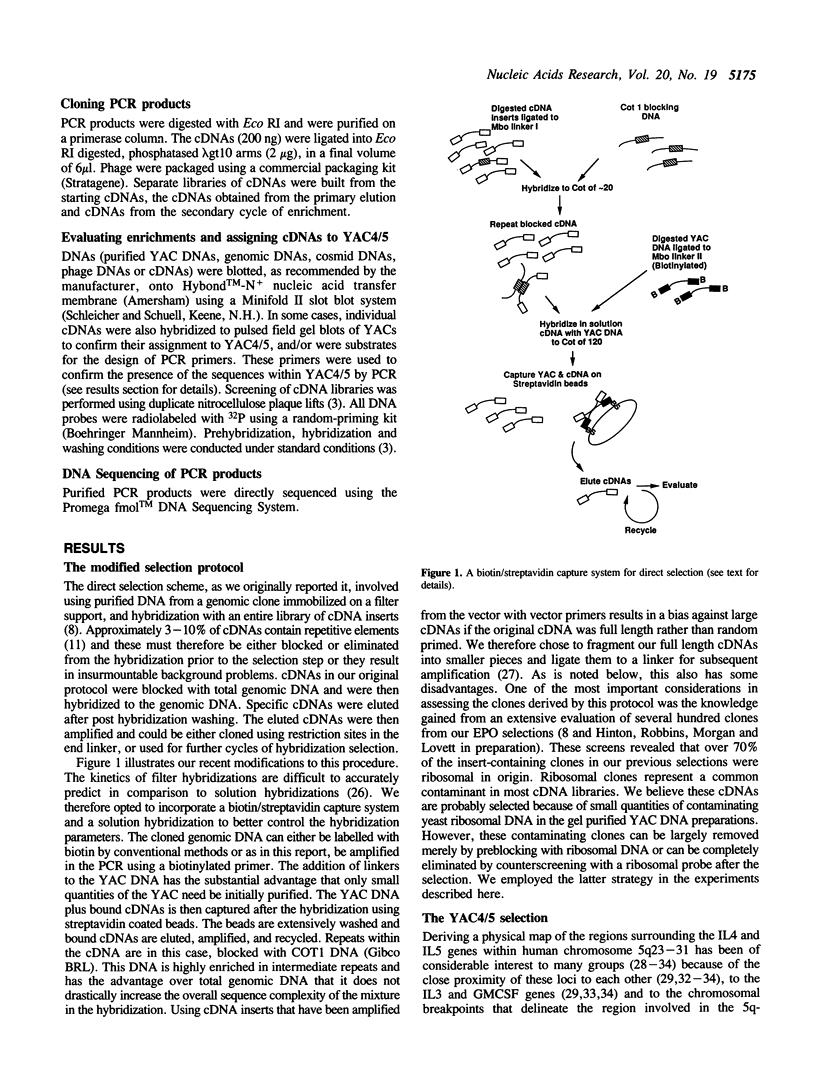
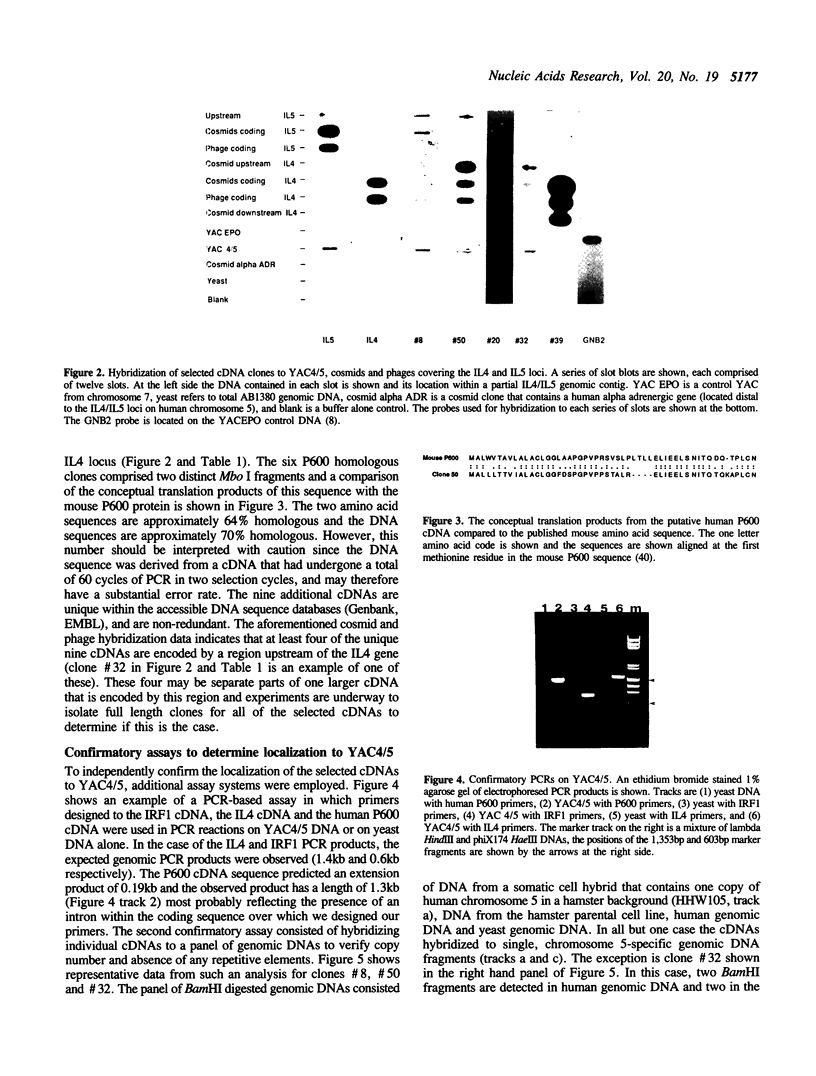
We have developed modifications to direct cDNA selection that allow the rapid and reproducible isolation of low abundance cDNAs encoded by large genomic clones. Biotinylated, cloned genomic DNAs are hybridized in solution with amplifiable cDNAs. The genomic clones and attached cDNAs are captured on streptavidin coated magnetic beads, the cDNAs are eluted and amplified. We have applied this protocol to a 425kb YAC that contains the human IL4 and IL5 genes. After two cycles of enrichment twenty-four cDNAs were evaluated, all of which were homologous to the YAC. DNA sequencing revealed that nine cDNAs were 100% homologous to the interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF1) gene. Six clones were 70% homologous to the murine P600 gene, which is coexpressed with IL4 and IL5 in mouse Th2 cells. The nine remaining clones were unique within the sequence databases and were non redundant. All of the selected cDNAs were initially present at very low abundance and were enriched by as much as 100,000-fold in two cycles of enrichment. This modified selection technique should be readily applicable to the isolation of many candidate disease loci as well as the derivation of detailed transcription maps across large genomic regions.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azuma C., Tanabe T., Konishi M., Kinashi T., Noma T., Matsuda F., Yaoita Y., Takatsu K., Hammarström L., Smith C. I. Cloning of cDNA for human T-cell replacing factor (interleukin-5) and comparison with the murine homologue. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):9149–9158. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.9149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O., Morton J. G., Rosbash M., Richardson M. Three abundance classes in HeLa cell messenger RNA. Nature. 1974 Jul 19;250(463):199–204. doi: 10.1038/250199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Zurawski S. M., Mosmann T. R., Zurawski G. A family of small inducible proteins secreted by leukocytes are members of a new superfamily that includes leukocyte and fibroblast-derived inflammatory agents, growth factors, and indicators of various activation processes. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):679–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckler A. J., Chang D. D., Graw S. L., Brook J. D., Haber D. A., Sharp P. A., Housman D. E. Exon amplification: a strategy to isolate mammalian genes based on RNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):4005–4009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.4005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. T., Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):806–812. doi: 10.1126/science.3033825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekharappa S. C., Rebelsky M. S., Firak T. A., Le Beau M. M., Westbrook C. A. A long-range restriction map of the interleukin-4 and interleukin-5 linkage group on chromosome 5. Genomics. 1990 Jan;6(1):94–99. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90452-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbo L., Maley J. A., Nelson D. L., Caskey C. T. Direct cloning of human transcripts with HnRNA from hybrid cell lines. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):652–655. doi: 10.1126/science.2382140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crampton J. M., Davies K. E., Knapp T. F. The occurrence of families of repetitive sequences in a library of cloned cDNA from human lymphocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3821–3834. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Eustachio P., Brown M., Watson C., Paul W. E. The IL-4 gene maps to chromosome 11, near the gene encoding IL-3. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 1;141(9):3067–3071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duyk G. M., Kim S. W., Myers R. M., Cox D. R. Exon trapping: a genetic screen to identify candidate transcribed sequences in cloned mammalian genomic DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8995–8999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elvin P., Slynn G., Black D., Graham A., Butler R., Riley J., Anand R., Markham A. F. Isolation of cDNA clones using yeast artificial chromosome probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3913–3917. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong T. A., Mosmann T. R. Alloreactive murine CD8+ T cell clones secrete the Th1 pattern of cytokines. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1744–1752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galau G. A., Klein W. H., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Significance of rare m RNA sequences in liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Mar;179(2):584–599. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green E. D., Olson M. V. Systematic screening of yeast artificial-chromosome libraries by use of the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1213–1217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochgeschwender U., Sutcliffe J. G., Brennan M. B. Construction and screening of a genomic library specific for mouse chromosome 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8482–8486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huebner K., Nagarajan L., Besa E., Angert E., Lange B. J., Cannizzaro L. A., van den Berghe H., Santoli D., Finan J., Croce C. M. Order of genes on human chromosome 5q with respect to 5q interstitial deletions. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jan;46(1):26–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh S., Harada H., Nakamura Y., White R., Taniguchi T. Assignment of the human interferon regulatory factor-1 (IRF1) gene to chromosome 5q23-q31. Genomics. 1991 Aug;10(4):1097–1099. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90208-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko M. S. An 'equalized cDNA library' by the reassociation of short double-stranded cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5705–5711. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Beau M. M., Lemons R. S., Espinosa R., 3rd, Larson R. A., Arai N., Rowley J. D. Interleukin-4 and interleukin-5 map to human chromosome 5 in a region encoding growth factors and receptors and are deleted in myeloid leukemias with a del(5q). Blood. 1989 Feb 15;73(3):647–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Campbell H. D., Kozak C. A., Young I. G. The IL-4 and IL-5 genes are closely linked and are part of a cytokine gene cluster on mouse chromosome 11. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1989 Mar;15(2):143–152. doi: 10.1007/BF01535075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon G. G., Lehrach H. Hybridization analyses of arrayed cDNA libraries. Trends Genet. 1991 Oct;7(10):314–317. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90420-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P., Legerski R., Siciliano M. J. Isolation of human transcribed sequences from human-rodent somatic cell hybrids. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):813–815. doi: 10.1126/science.2479099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett M., Kere J., Hinton L. M. Direct selection: a method for the isolation of cDNAs encoded by large genomic regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9628–9632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama M., Fujita T., Taniguchi T. Sequence of a cDNA coding for human IRF-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):3292–3292. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.3292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner R. J., Lai C., Lenoir D., Nave K., Bakhit C., Malfroy B. Brain-specific gene expression. Biochem Soc Symp. 1986;52:107–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson R. Growth factors, protooncogenes and human placental development. Cell Differ Dev. 1989 Oct;28(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0922-3371(89)90018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parimoo S., Patanjali S. R., Shukla H., Chaplin D. D., Weissman S. M. cDNA selection: efficient PCR approach for the selection of cDNAs encoded in large chromosomal DNA fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9623–9627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patanjali S. R., Parimoo S., Weissman S. M. Construction of a uniform-abundance (normalized) cDNA library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1943–1947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes G. R., Kim J. P. Sequence-independent, single-primer amplification (SISPA) of complex DNA populations. Mol Cell Probes. 1991 Dec;5(6):473–481. doi: 10.1016/s0890-8508(05)80020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Yoshida M. C., Satoh H., Hilgers J., Yaoita Y., Honjo T. Chromosomal mapping of the mouse IL-4 and human IL-5 genes. Genomics. 1989 Jan;4(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90313-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. R., Marchuk D. A., Andersen L. B., Letcher R., Odeh H. M., Saulino A. M., Fountain J. W., Brereton A., Nicholson J., Mitchell A. L. Type 1 neurofibromatosis gene: identification of a large transcript disrupted in three NF1 patients. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):181–186. doi: 10.1126/science.2134734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrington J. A., Bailey S. K., Armstrong E., Aprelikova O., Alitalo K., Dolganov G. M., Wilcox A. S., Sikela J. M., Wolfe S. F., Lovett M. A radiation hybrid map of 18 growth factor, growth factor receptor, hormone receptor, or neurotransmitter receptor genes on the distal region of the long arm of chromosome 5. Genomics. 1992 Jul;13(3):803–808. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90156-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrington J. A., Hall L. V., Hinton L. M., Miller J. N., Wasmuth J. J., Lovett M. Radiation hybrid map of 13 loci on the long arm of chromosome 5. Genomics. 1991 Nov;11(3):701–708. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90078-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasmuth J. J., Park C., Ferrell R. E. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of chromosome 5. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):137–148. doi: 10.1159/000132789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman S. M. Molecular genetic techniques for mapping the human genome. Mol Biol Med. 1987 Jun;4(3):133–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Arai N., de Vries J., Spits H., Banchereau J., Zlotnik A., Rennick D., Howard M., Takebe Y., Miyatake S. Molecular biology of interleukin 4 and interleukin 5 genes and biology of their products that stimulate B cells, T cells and hemopoietic cells. Immunol Rev. 1988 Feb;102:137–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00744.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Leeuwen B. H., Martinson M. E., Webb G. C., Young I. G. Molecular organization of the cytokine gene cluster, involving the human IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, and GM-CSF genes, on human chromosome 5. Blood. 1989 Apr;73(5):1142–1148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]