Abstract
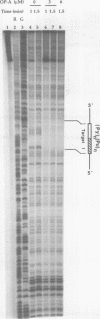
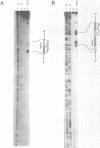
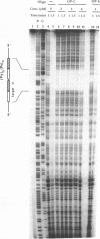
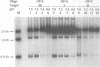
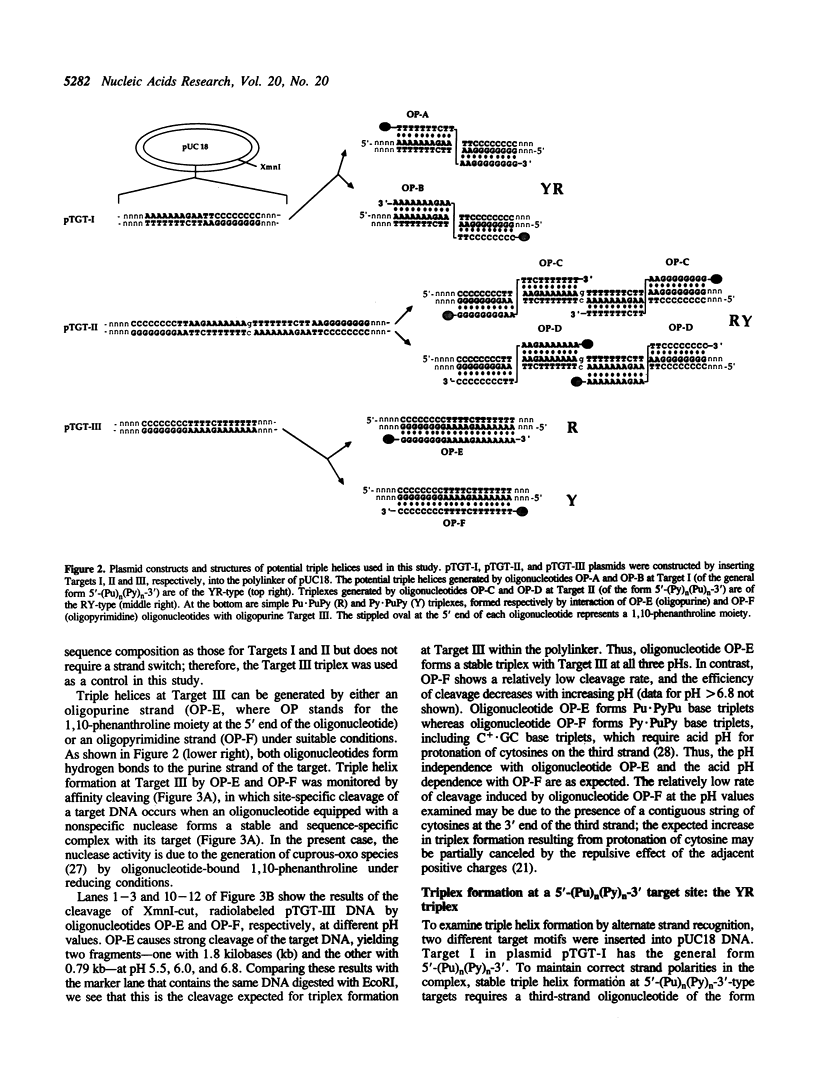
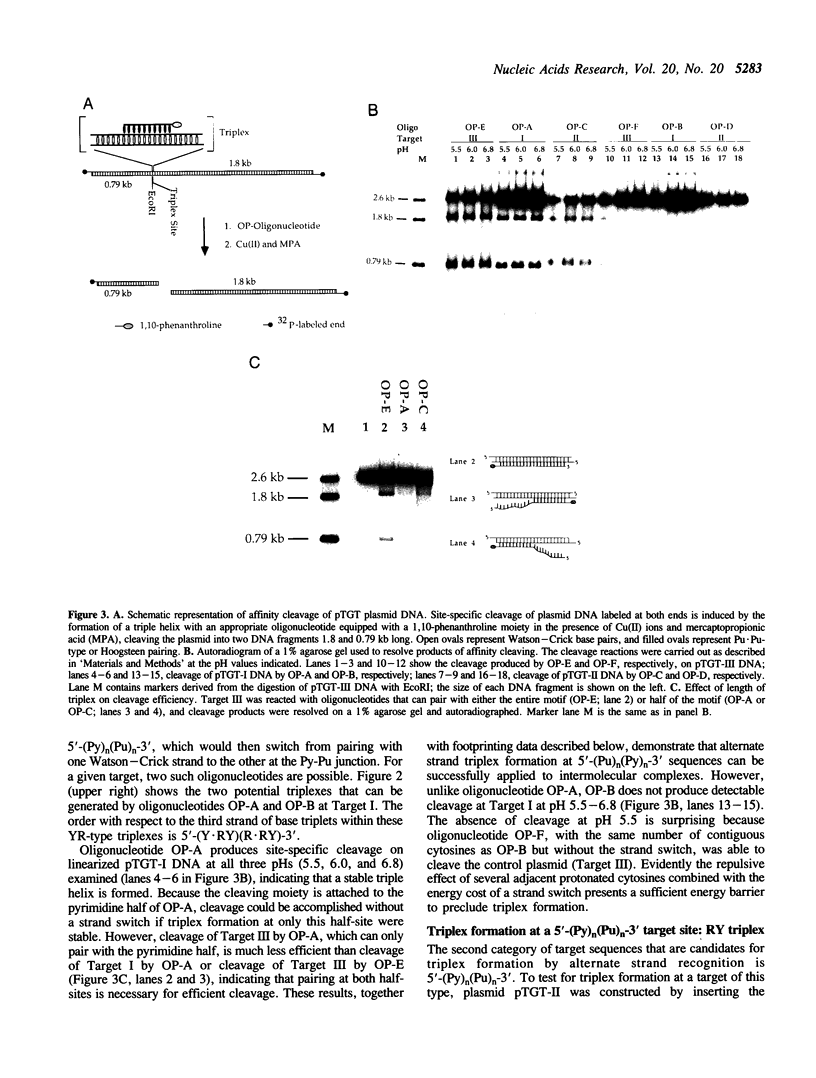
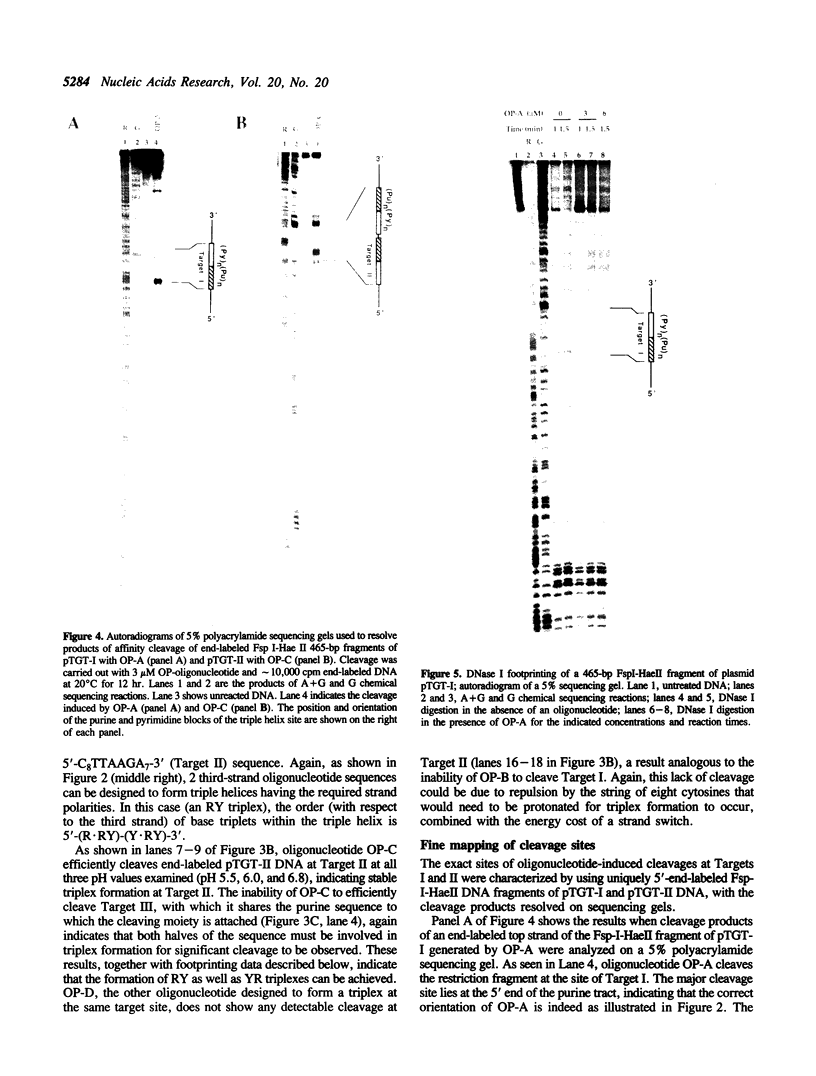
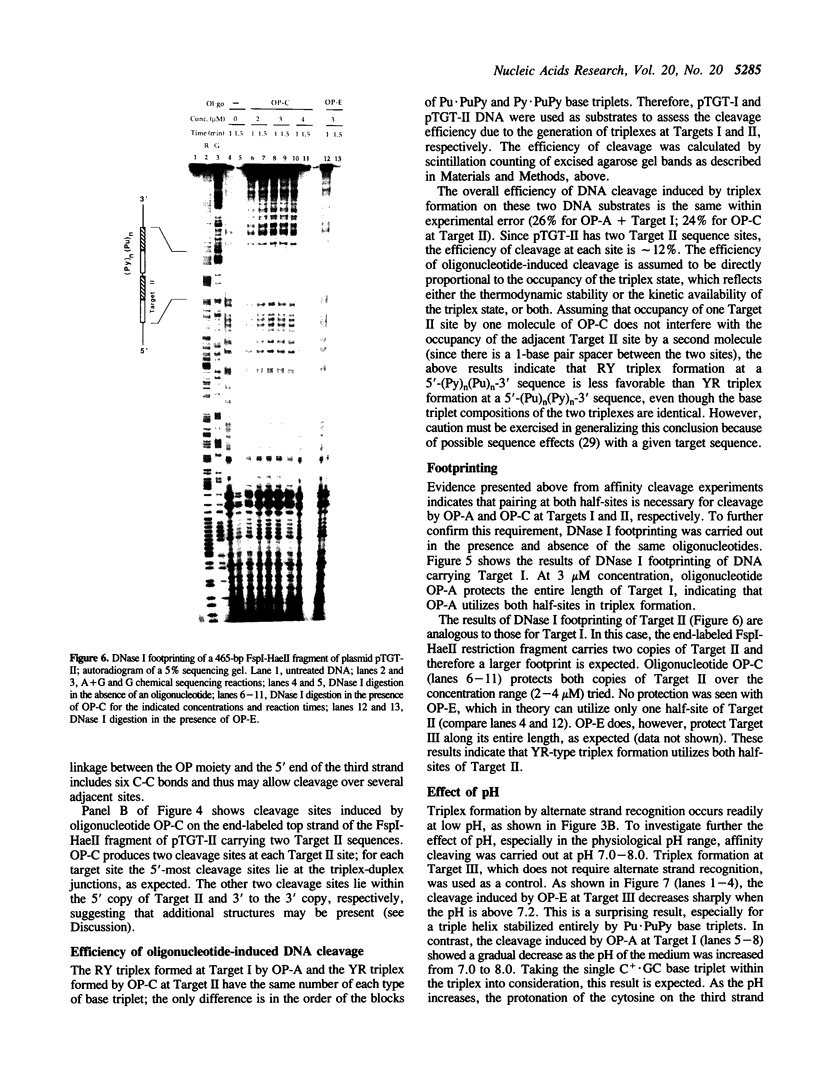
A significant limitation to the practical application of triplex DNA is its requirement for oligopurine tracts in target DNA sequences. The repertoire of triplex-forming sequences can potentially be expanded to adjacent blocks of purines and pyrimidines by allowing the third strand to pair with purines on alternate strands, while maintaining the required strand polarities by combining the two major classes of base triplets, Py.PuPy and Pu.PuPy. The formation of triplex DNA in this fashion requires no unusual bases or backbone linkages on the third strand. This approach has previously been demonstrated for target sequences of the type 5'-(Pu)n(Py)n-3' in intramolecular complexes. Using affinity cleaving and DNase I footprinting, we show here that intermolecular triplexes can also be formed at both 5'-(Pu)n(Py)n-3' and 5'-(Py)n(Pu)n-3' target sequences. However, triplex formation at a 5'-(Py)n(Pu)n-3' sequence occurs with lower yield. Triplex formation is disfavored, even at acid pH, when a number of contiguous C+.GC base triplets are required. These results suggest that triplex formation via alternate strand recognition at sequences made up of blocks of purines and pyrimidines may be generally feasible.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beal P. A., Dervan P. B. Second structural motif for recognition of DNA by oligonucleotide-directed triple-helix formation. Science. 1991 Mar 15;251(4999):1360–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.2003222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. H., Sigman D. S. Nuclease activity of 1,10-phenanthroline-copper: sequence-specific targeting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7147–7151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coll M., Frederick C. A., Wang A. H., Rich A. A bifurcated hydrogen-bonded conformation in the d(A.T) base pairs of the DNA dodecamer d(CGCAAATTTGCG) and its complex with distamycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8385–8389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney M., Czernuszewicz G., Postel E. H., Flint S. J., Hogan M. E. Site-specific oligonucleotide binding represses transcription of the human c-myc gene in vitro. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):456–459. doi: 10.1126/science.3293213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duval-Valentin G., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Specific inhibition of transcription by triple helix-forming oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):504–508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froehler B. C., Terhorst T., Shaw J. P., McCurdy S. N. Triple-helix formation and cooperative binding by oligodeoxynucleotides with a 3'-3' internucleotide junction. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 18;31(6):1603–1609. doi: 10.1021/bi00121a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin L. C., Dervan P. B. Recognition of thymine adenine.base pairs by guanine in a pyrimidine triple helix motif. Science. 1989 Sep 1;245(4921):967–971. doi: 10.1126/science.2549639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayasena S. D., Johnston B. H. Intramolecular triple-helix formation at (PunPyn).(PunPyn) tracts: recognition of alternate strands via Pu.PuPy and Py.PuPy base triplets. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 21;31(2):320–327. doi: 10.1021/bi00117a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayasena S. D., Johnston B. H. Site-specific cleavage of the transactivation response site of human immunodeficiency virus RNA with a tat-based chemical nuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3526–3530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling L. L., Griffin L. C., Dervan P. B. Flanking sequence effects within the pyrimidine triple-helix motif characterized by affinity cleaving. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 17;31(10):2829–2834. doi: 10.1021/bi00125a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohwi Y., Kohwi-Shigematsu T. Magnesium ion-dependent triple-helix structure formed by homopurine-homopyrimidine sequences in supercoiled plasmid DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3781–3785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Doan T., Perrouault L., Praseuth D., Habhoub N., Decout J. L., Thuong N. T., Lhomme J., Hélène C. Sequence-specific recognition, photocrosslinking and cleavage of the DNA double helix by an oligo-[alpha]-thymidylate covalently linked to an azidoproflavine derivative. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7749–7760. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyamichev V. I., Voloshin O. N., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D., Soyfer V. N. Photofootprinting of DNA triplexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1633–1638. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd, Dervan P. B., Wold B. Analysis of promoter-specific repression by triple-helical DNA complexes in a eukaryotic cell-free transcription system. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 14;31(1):70–81. doi: 10.1021/bi00116a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd, Wold B., Dervan P. B. Inhibition of DNA binding proteins by oligonucleotide-directed triple helix formation. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):725–730. doi: 10.1126/science.2549631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkin S. M., Lyamichev V. I., Drushlyak K. N., Dobrynin V. N., Filippov S. A., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. DNA H form requires a homopurine-homopyrimidine mirror repeat. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):495–497. doi: 10.1038/330495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H. E., Dervan P. B. Sequence-specific cleavage of double helical DNA by triple helix formation. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):645–650. doi: 10.1126/science.3118463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono A., Chen C. N., Kan L. S. DNA triplex formation of oligonucleotide analogues consisting of linker groups and octamer segments that have opposite sugar-phosphate backbone polarities. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 15;30(41):9914–9912. doi: 10.1021/bi00105a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orson F. M., Thomas D. W., McShan W. M., Kessler D. J., Hogan M. E. Oligonucleotide inhibition of IL2R alpha mRNA transcription by promoter region collinear triplex formation in lymphocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3435–3441. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrouault L., Asseline U., Rivalle C., Thuong N. T., Bisagni E., Giovannangeli C., Le Doan T., Hélène C. Sequence-specific artificial photo-induced endonucleases based on triple helix-forming oligonucleotides. Nature. 1990 Mar 22;344(6264):358–360. doi: 10.1038/344358a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peticolas W. L., Wang Y., Thomas G. A. Some rules for predicting the base-sequence dependence of DNA conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2579–2583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch D. S., Levenson C., Shafer R. H. Structure, stability, and thermodynamics of a short intermolecular purine-purine-pyrimidine triple helix. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 25;30(25):6081–6088. doi: 10.1021/bi00239a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radhakrishnan I., de los Santos C., Patel D. J. Nuclear magnetic resonance structural studies of intramolecular purine.purine.pyrimidine DNA triplexes in solution. Base triple pairing alignments and strand direction. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 20;221(4):1403–1418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigman D. S., Chen C. H. Chemical nucleases: new reagents in molecular biology. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:207–236. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel S. A., Dervan P. B. Site-specific cleavage of a yeast chromosome by oligonucleotide-directed triple-helix formation. Science. 1990 Jul 6;249(4964):73–75. doi: 10.1126/science.2195655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel S. A., Doucette-Stamm L. A., Riba L., Housman D. E., Dervan P. B. Site-specific cleavage of human chromosome 4 mediated by triple-helix formation. Science. 1991 Dec 13;254(5038):1639–1642. doi: 10.1126/science.1836279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J. S., De Bizemont T., Duval-Valentin G., Montenay-Garestier T., Hélène C. Extension of the range of recognition sequences for triple helix formation by oligonucleotides containing guanines and thymines. C R Acad Sci III. 1991;313(13):585–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. L., Krawczyk S. H., Matteucci M. D., Toole J. J. Triple helix formation inhibits transcription elongation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10023–10026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]