Abstract
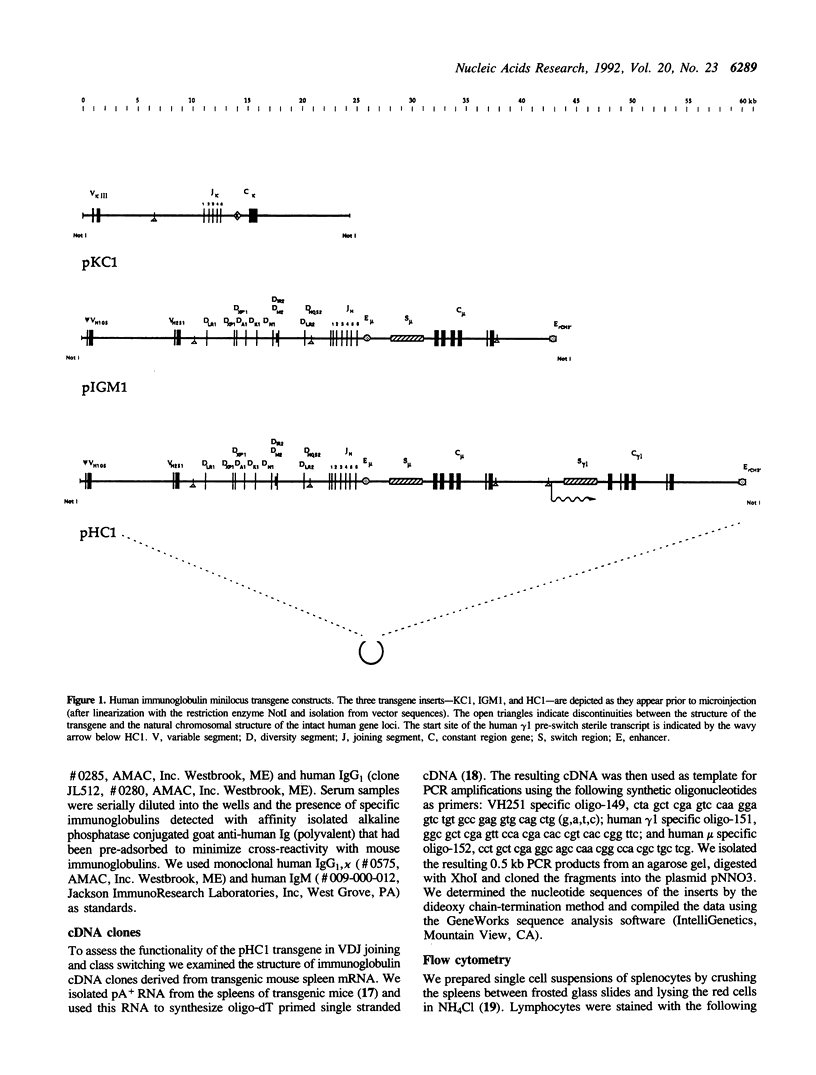
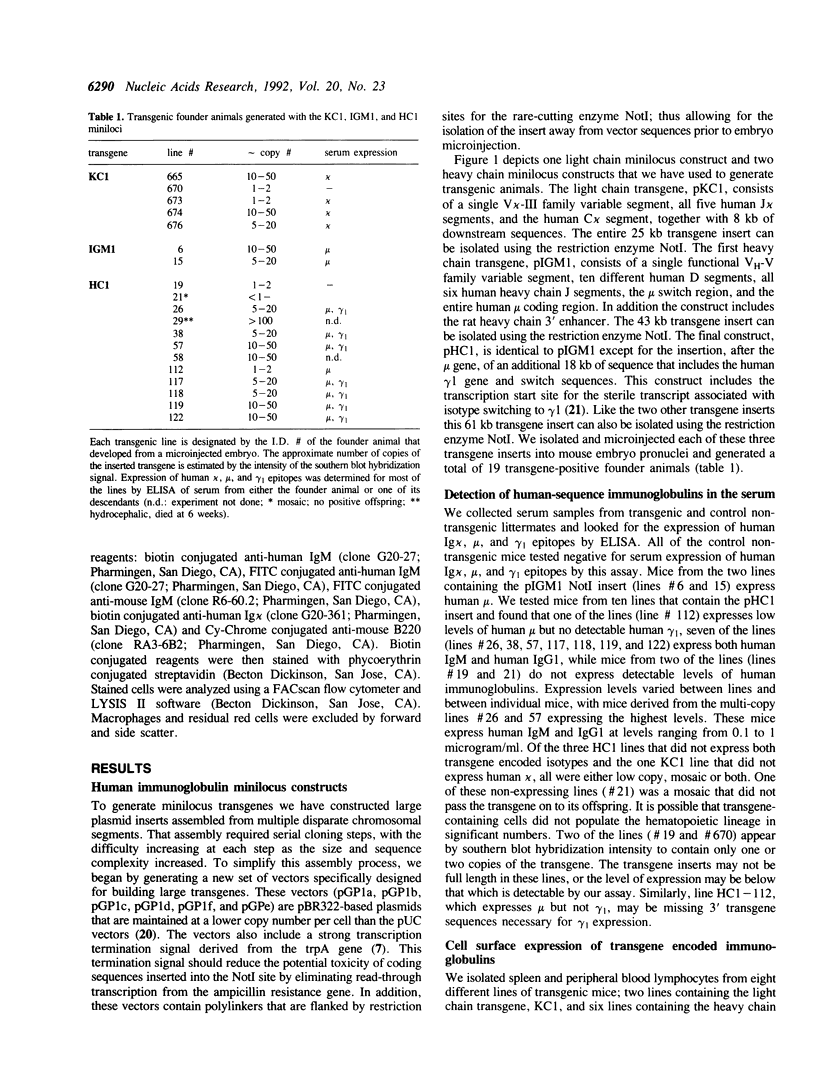
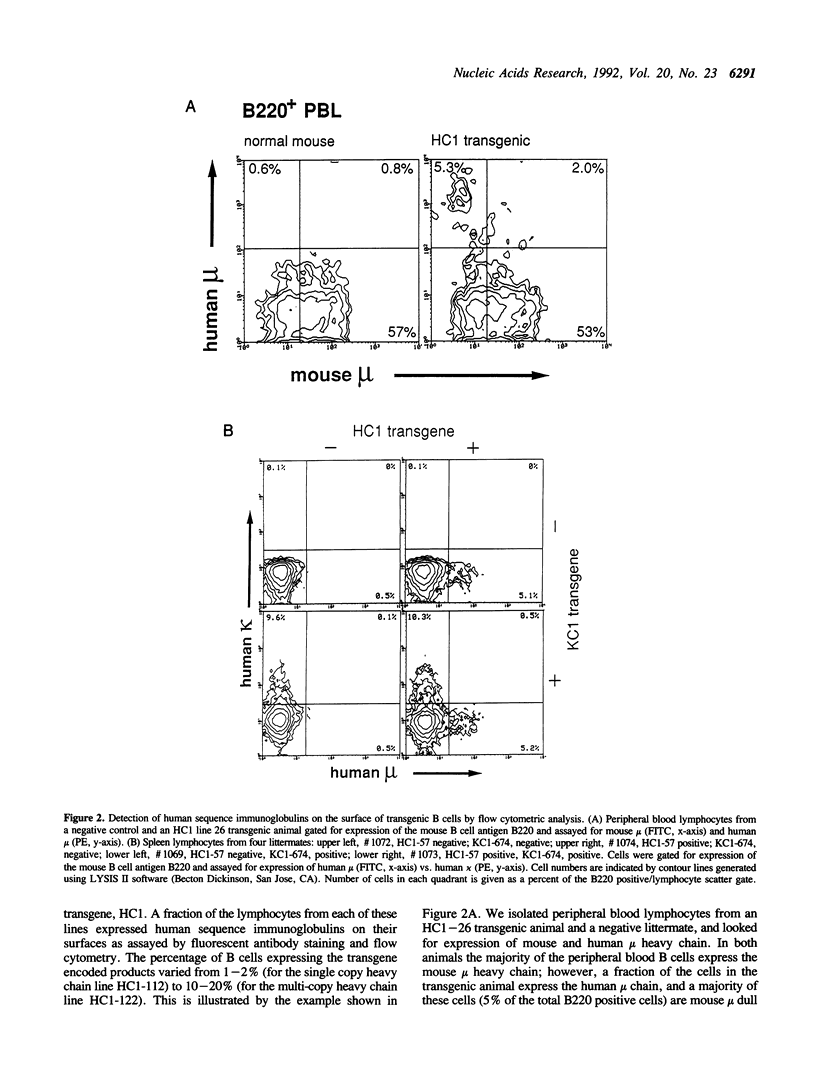
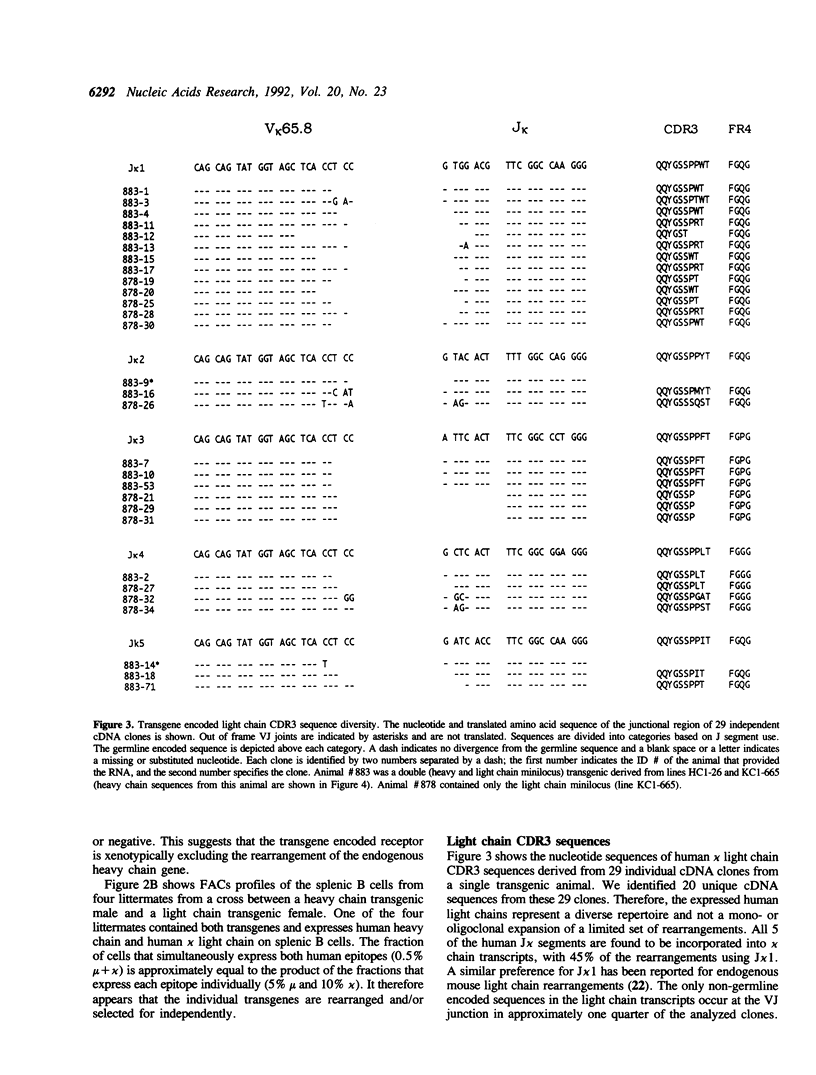
We have generated transgenic mice that express a diverse repertoire of human sequence immunoglobulins. The expression of this repertoire is directed by light and heavy chain minilocus transgenes comprised of human protein coding sequences in an unrearranged, germ-line configuration. In this paper we describe the construction of these miniloci and the composition of the CDR3 repertoire generated by the transgenic mice. The largest transgene discussed is a heavy chain minilocus that includes human mu and gamma 1 coding sequences together with their respective switch regions. It consists of a single 61 kb DNA fragment propagated in a bacterial plasmid vector. Both human heavy chain classes are expressed in animals that carry the transgene. In light chain transgenic animals the unrearranged minilocus sequences recombine to form VJ joints that use all five human J kappa segments, resulting in a diversity of human-like CDR3 regions. Similarly, in heavy chain transgenics the inserted sequences undergo VDJ joining complete with N region addition to generate a human-like VH CDR3 repertoire. All six human JH segments and at least eight of the ten transgene encoded human D segments are expressed. The transgenic animals described in this paper represent a potential source of human sequence antibodies for in vivo therapeutic applications.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brüggemann M., Caskey H. M., Teale C., Waldmann H., Williams G. T., Surani M. A., Neuberger M. S. A repertoire of monoclonal antibodies with human heavy chains from transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6709–6713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemann M., Spicer C., Buluwela L., Rosewell I., Barton S., Surani M. A., Rabbitts T. H. Human antibody production in transgenic mice: expression from 100 kb of the human IgH locus. Eur J Immunol. 1991 May;21(5):1323–1326. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucchini D., Reynaud C. A., Ripoche M. A., Grimal H., Jami J., Weill J. C. Rearrangement of a chicken immunoglobulin gene occurs in the lymphoid lineage of transgenic mice. 1987 Mar 26-Apr 1Nature. 326(6111):409–411. doi: 10.1038/326409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie G. E., Farnham P. J., Platt T. Synthetic sites for transcription termination and a functional comparison with tryptophan operon termination sites in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4180–4184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dersimonian H., McAdam K. P., Mackworth-Young C., Stollar B. D. The recurrent expression of variable region segments in human IgM anti-DNA autoantibodies. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):4027–4033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeney A. J. Lack of N regions in fetal and neonatal mouse immunoglobulin V-D-J junctional sequences. J Exp Med. 1990 Nov 1;172(5):1377–1390. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.5.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrier P., Krippl B., Blackwell T. K., Furley A. J., Suh H., Winoto A., Cook W. D., Hood L., Costantini F., Alt F. W. Separate elements control DJ and VDJ rearrangement in a transgenic recombination substrate. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):117–125. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. B. Ras C-terminal processing enzymes--new drug targets? Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90352-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodhardt M., Babinet C., Lutfalla G., Kallenbach S., Cavelier P., Rougeon F. Immunoglobulin kappa light chain gene promoter and enhancer are not responsible for B-cell restricted gene rearrangement. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7403–7415. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodhardt M., Cavelier P., Akimenko M. A., Lutfalla G., Babinet C., Rougeon F. Rearrangement and expression of rabbit immunoglobulin kappa light chain gene in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4229–4233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada K., Yamagishi H. Lack of feedback inhibition of V kappa gene rearrangement by productively rearranged alleles. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):409–415. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller M., Owens J. D., Mushinski J. F., Rudikoff S. Amino acids at the site of V kappa-J kappa recombination not encoded by germline sequences. J Exp Med. 1987 Sep 1;166(3):637–646. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries C. G., Shen A., Kuziel W. A., Capra J. D., Blattner F. R., Tucker P. W. A new human immunoglobulin VH family preferentially rearranged in immature B-cell tumours. Nature. 1988 Feb 4;331(6155):446–449. doi: 10.1038/331446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichihara Y., Matsuoka H., Kurosawa Y. Organization of human immunoglobulin heavy chain diversity gene loci. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4141–4150. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03309.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber M. R., Hesse J. E., Mizuuchi K., Gellert M. Lymphoid V(D)J recombination: nucleotide insertion at signal joints as well as coding joints. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8588–8592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manz J., Denis K., Witte O., Brinster R., Storb U. Feedback inhibition of immunoglobulin gene rearrangement by membrane mu, but not by secreted mu heavy chains. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1363–1381. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks J. D., Tristem M., Karpas A., Winter G. Oligonucleotide primers for polymerase chain reaction amplification of human immunoglobulin variable genes and design of family-specific oligonucleotide probes. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Apr;21(4):985–991. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuuchi L., Gold M. R., Travis A., Grosschedl R., DeFranco A. L., Kelly R. B. The membrane IgM-associated proteins MB-1 and Ig-beta are sufficient to promote surface expression of a partially functional B-cell antigen receptor in a nonlymphoid cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3404–3408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meindl A., Klobeck H. G., Ohnheiser R., Zachau H. G. The V kappa gene repertoire in the human germ line. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Aug;20(8):1855–1863. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenzweig M. C., Shaw A. C., Sinn E., Campos-Torres J., Leder P. Allelic exclusion in transgenic mice carrying mutant human IgM genes. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1969–1974. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenzweig M. C., Shaw A. C., Sinn E., Danner D. B., Holmes K. L., Morse H. C., 3rd, Leder P. Allelic exclusion in transgenic mice that express the membrane form of immunoglobulin mu. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):816–819. doi: 10.1126/science.3107126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson S., Cook G. P., Brüggemann M., Williams G. T., Neuberger M. S. A second B cell-specific enhancer 3' of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):165–168. doi: 10.1038/344165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radoux V., Chen P. P., Sorge J. A., Carson D. A. A conserved human germline V kappa gene directly encodes rheumatoid factor light chains. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):2119–2124. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.2119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reth M., Hombach J., Wienands J., Campbell K. S., Chien N., Justement L. B., Cambier J. C. The B-cell antigen receptor complex. Immunol Today. 1991 Jun;12(6):196–201. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90053-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanz I. Multiple mechanisms participate in the generation of diversity of human H chain CDR3 regions. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 1;147(5):1720–1729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. W., Jr, Wang J. Y. Preferential utilization of conserved immunoglobulin heavy chain variable gene segments during human fetal life. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6146–6150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sideras P., Mizuta T. R., Kanamori H., Suzuki N., Okamoto M., Kuze K., Ohno H., Doi S., Fukuhara S., Hassan M. S. Production of sterile transcripts of C gamma genes in an IgM-producing human neoplastic B cell line that switches to IgG-producing cells. Int Immunol. 1989;1(6):631–642. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.6.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straubinger B., Huber E., Lorenz W., Osterholzer E., Pargent W., Pech M., Pohlenz H. D., Zimmer F. J., Zachau H. G. The human VK locus. Characterization of a duplicated region encoding 28 different immunoglobulin genes. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 5;199(1):23–34. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90376-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. B., Word C. J., Humphries C. G., Blattner F. R., Tucker P. W. Immunoglobulin D switching can occur through homologous recombination in human B cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3690–3699. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada M., Wasserman R., Reichard B. A., Shane S., Caton A. J., Rovera G. Preferential utilization of specific immunoglobulin heavy chain diversity and joining segments in adult human peripheral blood B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):395–407. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Alt F. W. Regulation of the assembly and expression of variable-region genes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:339–368. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasui H., Akahori Y., Hirano M., Yamada K., Kurosawa Y. Class switch from mu to delta is mediated by homologous recombination between sigma mu and sigma mu sequences in human immunoglobulin gene loci. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Aug;19(8):1399–1403. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


