Abstract
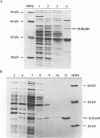
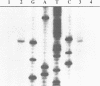
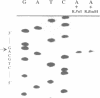
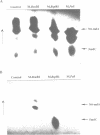
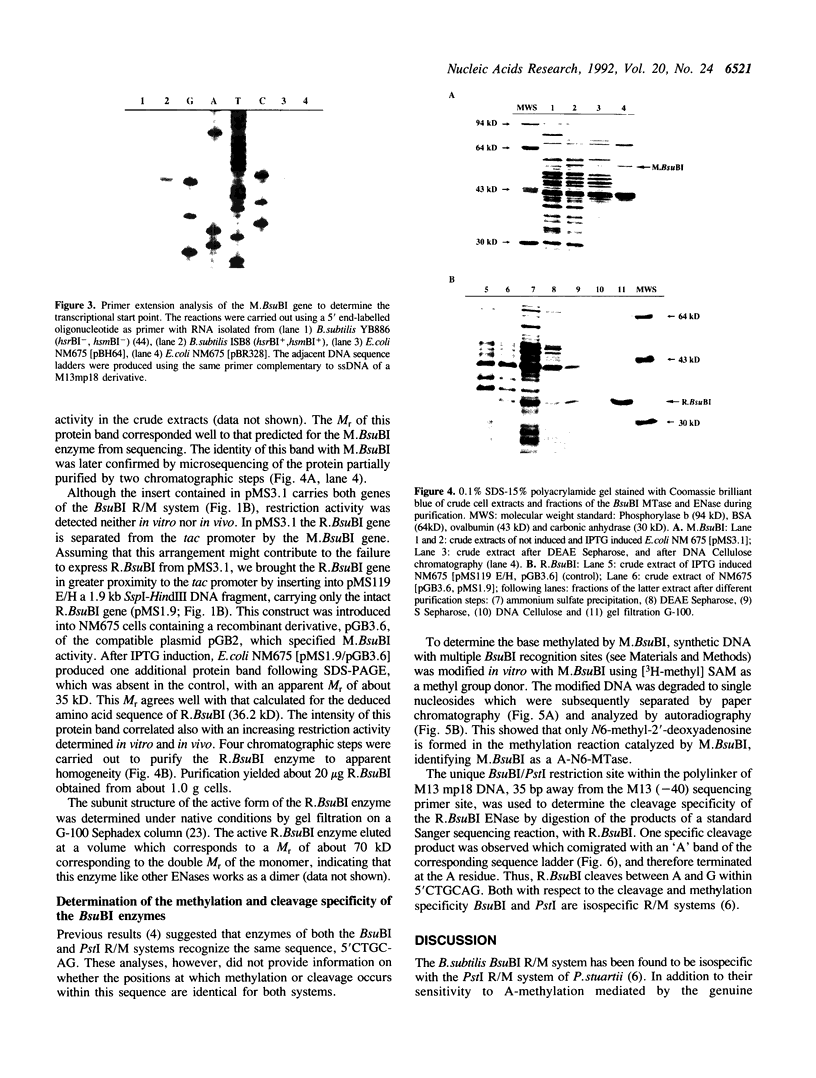
The enzymes of the Bacillus subtilis BsuBI restriction/modification (R/M) system recognize the target sequence 5'CTGCAG. The genes of the BsuBI R/M system have been cloned and sequenced and their products have been characterized following overexpression and purification. The gene of the BsuBI DNA methyltransferase (M.BsuBI) consists of 1503 bp, encoding a protein of 501 amino acids with a calculated M(r) of 57.2 kD. The gene of the restriction endonuclease (R.BsuBI), comprising 948 bp, codes for a protein of 316 amino acids with a predicted M(r) of 36.2 kD. M.BsuBI modifies the adenine (A) residue of the BsuBI target site, thus representing the first A-N6-DNA methyltransferase identified in B. subtilis. Like R.PstI, R.BsuBI cleaves between the A residue and the 3' terminal G of the target site. Both enzymes of the BsuBI R/M system are, therefore, functionally identical with those of the PstI R/M system, encoded by the Gram negative species Providencia stuartii. This functional equivalence coincides with a pronounced similarity of the BsuBI/PstI DNA methyltransferases (41% amino acid identity) and restriction endonucleases (46% amino acid identity). Since the genes are also very similar (58% nucleotide identity), the BsuBI and PstI R/M systems apparently have a common evolutionary origin. In spite of the sequence conservation the gene organization is strikingly different in the two R/M systems. While the genes of the PstI R/M system are separated and transcribed divergently, the genes of the BsuBI R/M system are transcribed in the same direction, with the 3' end of the M gene overlapping the 5' end of the R gene by 17 bp.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barany F., Danzitz M., Zebala J., Mayer A. Cloning and sequencing of genes encoding the TthHB8I restriction and modification enzymes: comparison with the isoschizomeric TaqI enzymes. Gene. 1992 Mar 1;112(1):3–12. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90296-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswal N., Kleinschmidt A. K., Spatz H. C., Trautner T. A. Physical properties of the DNA of bacteriophage SP50. Mol Gen Genet. 1967;100(1):39–55. doi: 10.1007/BF00425774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. L., Smith M. A general method for defining restriction enzyme cleavage and recognition sites. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):391–404. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chai S., Bravo A., Lüder G., Nedlin A., Trautner T. A., Alonso J. C. Molecular analysis of the Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SPP1 region encompassing genes 1 to 6. The products of gene 1 and gene 2 are required for pac cleavage. J Mol Biol. 1992 Mar 5;224(1):87–102. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90578-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchward G., Belin D., Nagamine Y. A pSC101-derived plasmid which shows no sequence homology to other commonly used cloning vectors. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90207-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobritsa A. P., Dobritsa S. V. DNA protection with the DNA methylase M . BbvI from Bacillus brevis var. GB against cleavage by the restriction endonucleases PstI and PvuII. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90128-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann D., Düsterhöft A., Kröger M. Cloning and molecular characterization of the HgiCI restriction/modification system from Herpetosiphon giganteus Hpg9 reveals high similarity to BanI. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Dec 18;202(3):1247–1256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürste J. P., Pansegrau W., Frank R., Blöcker H., Scholz P., Bagdasarian M., Lanka E. Molecular cloning of the plasmid RP4 primase region in a multi-host-range tacP expression vector. Gene. 1986;48(1):119–131. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90358-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günthert U., Freund M., Trautner T. A. Restriction and modification in Bacillus subtilis: two DNA methyltransferases with BsuRI specificity. I. Purification and physical properties. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9340–9345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günthert U., Reiners L., Lauster R. Cloning and expression of Bacillus subtilis phage DNA methyltransferase genes in Escherichia coli and B. subtilis. Gene. 1986;41(2-3):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90106-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haima P., Bron S., Venema G. The effect of restriction on shotgun cloning and plasmid stability in Bacillus subtilis Marburg. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Sep;209(2):335–342. doi: 10.1007/BF00329663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. E., Miceli S. M., Roberts R. J., Manley J. L. Sequence specificity of the human mRNA N6-adenosine methylase in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5735–5741. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Sadaoka A., Kotani H., Hiraoka N., Nakamura T. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of the HincII restriction-modification system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3903–3911. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Shimato H., Sadaoka A., Kotani H., Kimizuka F., Kato I. Cloning and expression of the HpaI restriction-modification genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 25;20(4):705–709. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.4.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapfer W., Walter J., Trautner T. A. Cloning, characterization and evolution of the BsuFI restriction endonuclease gene of Bacillus subtilis and purification of the enzyme. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6457–6463. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimasauskas S., Timinskas A., Menkevicius S., Butkienè D., Butkus V., Janulaitis A. Sequence motifs characteristic of DNA[cytosine-N4]methyltransferases: similarity to adenine and cytosine-C5 DNA-methylases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9823–9832. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIA S. E., BURROUS J. W. Hybridization between Escherichia coli and Shigella. J Bacteriol. 1957 Oct;74(4):461–476. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.4.461-476.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen J. E., Gerdes K., Light J., Molin S. Low-copy-number plasmid-cloning vectors amplifiable by derepression of an inserted foreign promoter. Gene. 1984 Apr;28(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauster R., Trautner T. A., Noyer-Weidner M. Cytosine-specific type II DNA methyltransferases. A conserved enzyme core with variable target-recognizing domains. J Mol Biol. 1989 Mar 20;206(2):305–312. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90480-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., LeGrice S. F., Lee G., Stephens M., Sonenshein A. L., Pero J., Losick R. Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00729452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noyer-Weidner M., Jentsch S., Pawlek B., Günthert U., Trautner T. A. Restriction and modification in Bacillus subtilis: DNA methylation potential of the related bacteriophages Z, SPR, SP beta, phi 3T, and rho 11. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):446–453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.446-453.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nölling J., de Vos W. M. Characterization of the archaeal, plasmid-encoded type II restriction-modification system MthTI from Methanobacterium thermoformicicum THF: homology to the bacterial NgoPII system from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(17):5719–5726. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.17.5719-5726.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posfai G., Kiss A., Venetianer P. Overproduction of the Bacillus sphaericus R modification methylase in Escherichia coli and its purification to homogeneity. Gene. 1986;50(1-3):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90310-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pósfai J., Bhagwat A. S., Pósfai G., Roberts R. J. Predictive motifs derived from cytosine methyltransferases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2421–2435. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata T., Ando T. Host controlled modification and restriction in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;131(4):275–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00264858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata T., Ikawa S., Komatsu Y., Ando T., Saito H. Introduction of host-controlled modification and restriction systems of Bacillus subtilis IAM1247 into Bacillus subtilis 168. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):308–310. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.308-310.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szomolányi E., Kiss A., Venetianer P. Cloning the modification methylase gene of Bacillus sphaericus R in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1980 Aug;10(3):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T. Restriction of plasmid-mediated transformation in Bacillus subtilis 168. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Sep;175(2):235–237. doi: 10.1007/BF00425542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautner T. A., Pawlek B., Bron S., Anagnostopoulos C. Restriction and modification in B. subtilis. Biological aspects. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;131(3):181–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00267958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walder R. Y., Hartley J. L., Donelson J. E., Walder J. A. Cloning and expression of the Pst I restriction-modification system in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1503–1507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walder R. Y., Walder J. A., Donelson J. E. The organization and complete nucleotide sequence of the PstI restriction-modification system. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):8015–8026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. G., Murray N. E. Restriction and modification systems. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:585–627. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.003101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. G. Organization of restriction-modification systems. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 25;19(10):2539–2566. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.10.2539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock D. M., Crowther P. J., Doherty J., Jefferson S., DeCruz E., Noyer-Weidner M., Smith S. S., Michael M. Z., Graham M. W. Quantitative evaluation of Escherichia coli host strains for tolerance to cytosine methylation in plasmid and phage recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3469–3478. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock D. M., Crowther P. J., Simmons D. L., Cooper I. A. Sequence specificity of cytosine methylation in the DNA of the Chinese hamster ovary (CHO-K1) cell line. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Dec 14;783(3):227–233. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasbin R. E., Fields P. I., Andersen B. J. Properties of Bacillus subtilis 168 derivatives freed of their natural prophages. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(1-2):155–159. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]