Abstract
The 5'-termini were precisely mapped for five constitutive and one UV-inducible transcript from the Sulfolobus virus-like particle SSV1. The comparison of the DNA sequences around these transcriptional initiation sites revealed the presence of two conserved sequence elements: a trinucleotide sequence close to the initiation site itself and an AT-rich hexanucleotide sequence centered about 26 nucleotides upstream of it. Similar DNA sequences were found upstream of the transcriptional start sites for the ribosomal RNA genes in Sulfolobus and upstream of transcriptional start sites in other archaebacteria, allowing the derivation of a general consensus sequence for archaebacterial promoters. This consensus sequence is unlike that found in eubacteria but it resembles promoters recognized by eukaryotic RNA polymerase II.
Full text
PDF
















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Betlach M., Friedman J., Boyer H. W., Pfeifer F. Characterization of a halobacterial gene affecting bacterio-opsin gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7949–7959. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanck A., Oesterhelt D. The halo-opsin gene. II. Sequence, primary structure of halorhodopsin and comparison with bacteriorhodopsin. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):265–273. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04749.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollschweiler C., Kühn R., Klein A. Non-repetitive AT-rich sequences are found in intergenic regions of Methanococcus voltae DNA. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):805–809. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03701.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher P., Trifonov E. N. Compilation and analysis of eukaryotic POL II promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):10009–10026. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.10009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Castagnoli L., Cortese R. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1983;18:59–88. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60579-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels C. J., Gupta R., Doolittle W. F. Transcription and excision of a large intron in the tRNATrp gene of an archaebacterium, Halobacterium volcanii. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):3132–3134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dassarma S., Rajbhandary U. L., Khorana H. G. Bacterio-opsin mRNA in wild-type and bacterio-opsin-deficient Halobacterium halobium strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):125–129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis P. P. Molecular biology of archaebacteria. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):471–478. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.471-478.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis P. P. Multiple promoters for the transcription of the ribosomal RNA gene cluster in Halobacterium cutirubrum. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 20;186(2):457–461. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90117-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi R. H., Wang L. F. Multiple procaryotic ribonucleic acid polymerase sigma factors. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Sep;50(3):227–243. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.3.227-243.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Schnabel R., Sentenac A., Zillig W. Archaebacteria and eukaryotes possess DNA-dependent RNA polymerases of a common type. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1291–1294. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01583.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
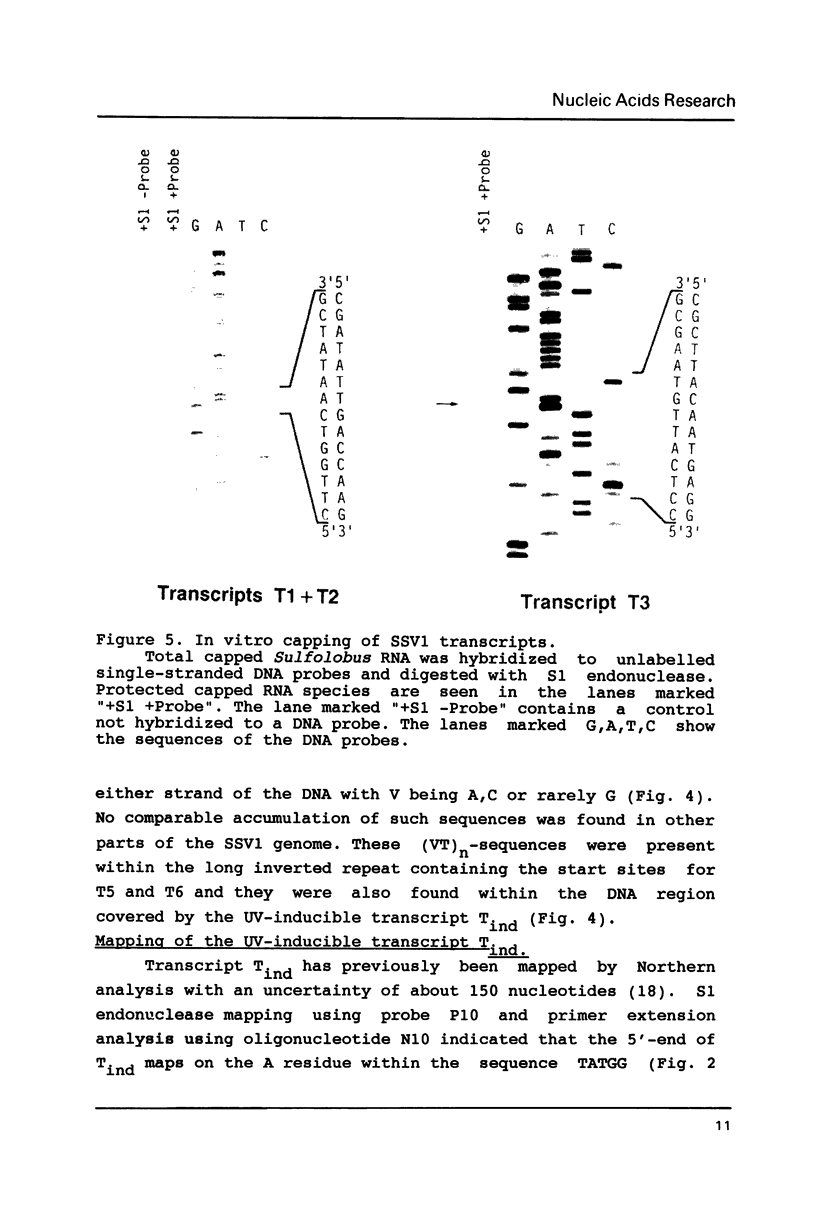
- Kaine B. P., Gupta R., Woese C. R. Putative introns in tRNA genes of prokaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3309–3312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel M., Klink F. Archaebacterial elongation factor is ADP-ribosylated by diphtheria toxin. Nature. 1980 Sep 18;287(5779):250–251. doi: 10.1038/287250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechner J., Sumper M. The primary structure of a procaryotic glycoprotein. Cloning and sequencing of the cell surface glycoprotein gene of halobacteria. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9724–9729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffers H., Kjems J., Ostergaard L., Larsen N., Garrett R. A. Evolutionary relationships amongst archaebacteria. A comparative study of 23 S ribosomal RNAs of a sulphur-dependent extreme thermophile, an extreme halophile and a thermophilic methanogen. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 5;195(1):43–61. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A., Yeats S., Janekovic D., Reiter W. D., Aicher W., Zillig W. SAV 1, a temperate u.v.-inducible DNA virus-like particle from the archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius isolate B12. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2165–2168. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02107.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Di Liegro C., Melli M. The in vitro transcription of the 7SK RNA gene by RNA polymerase III is dependent only on the presence of an upstream promoter. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
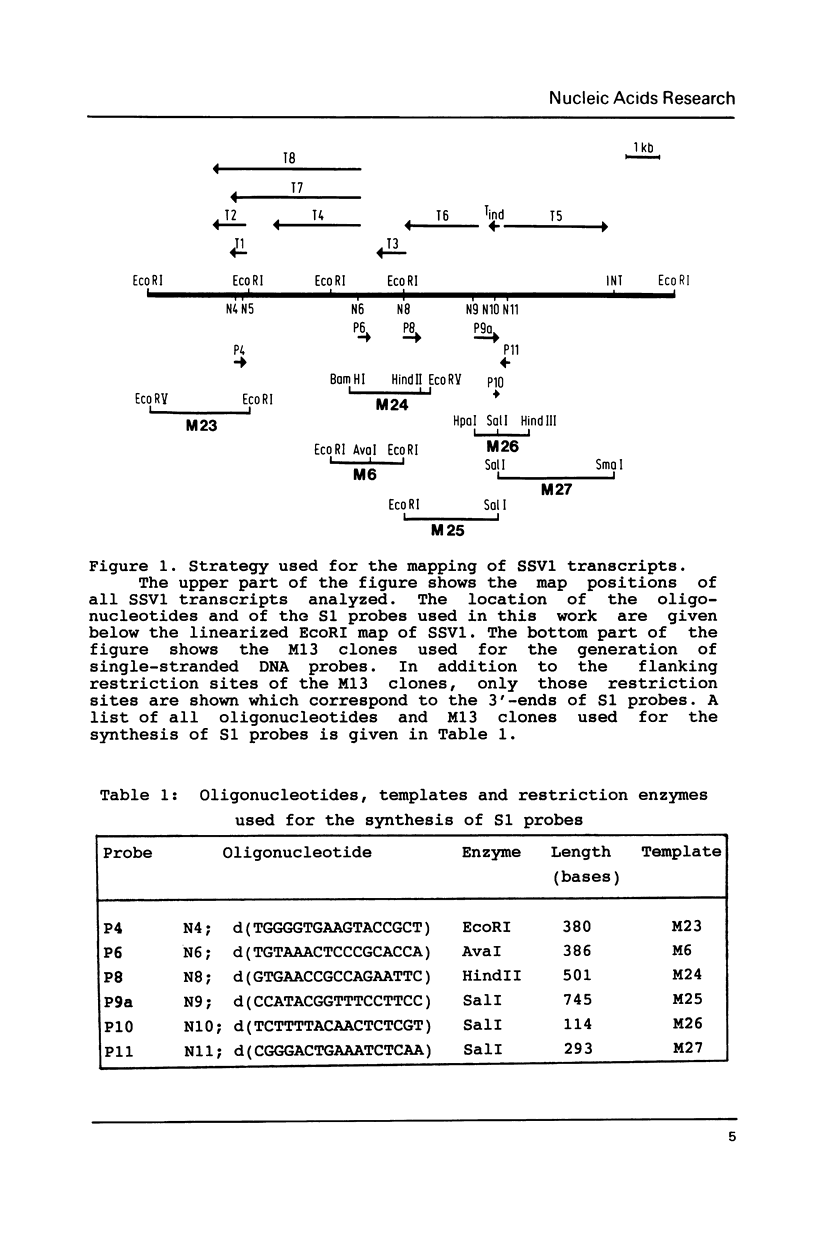
- Reiter W D, Palm P, Yeats S, Zillig W. Gene expression in archaebacteria: physical mapping of constitutive and UV-inducible transcripts from the Sulfolobus virus-like particle SSV1. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Sep;209(2):270–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00329653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. D., Palm P., Voos W., Kaniecki J., Grampp B., Schulz W., Zillig W. Putative promoter elements for the ribosomal RNA genes of the thermoacidophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus sp. strain B12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5581–5595. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. R. Regulation of plasmid replication. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):1–23. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-048850-6.50006-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Promoters, activator proteins, and the mechanism of transcriptional initiation in yeast. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):295–297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler B. M. Transcription of Neurospora crassa 5 S rRNA genes requires a TATA box and three internal elements. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):801–811. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90406-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wich G., Hummel H., Jarsch M., Bär U., Böck A. Transcription signals for stable RNA genes in Methanococcus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2459–2479. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wich G., Leinfelder W., Böck A. Genes for stable RNA in the extreme thermophile Thermoproteus tenax: introns and transcription signals. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):523–528. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04784.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Fox G. E. Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: the primary kingdoms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5088–5090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Magrum L. J., Fox G. E. Archaebacteria. J Mol Evol. 1978 Aug 2;11(3):245–251. doi: 10.1007/BF01734485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Olsen G. J. Archaebacterial phylogeny: perspectives on the urkingdoms. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1986;7:161–177. doi: 10.1016/s0723-2020(86)80001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeats S., McWilliam P., Zillig W. A plasmid in the archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1035–1038. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01292.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zillig W., Schnabel R., Stetter K. O. Archaebacteria and the origin of the eukaryotic cytoplasm. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;114:1–18. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70227-3_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]