Abstract
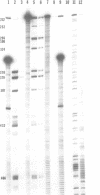
Preferential psoralen photobinding sites have been mapped in vitro on restriction fragments spanning the SV40 origin region and surrounding sequences by a new fine structure analysis technique. Purified DNA fragments were photoreacted with 3H-5-methylisopsoralen (3H-5-MIP), a psoralen derivative which forms only monoadducts. Fragments were then end-labeled and digested with lambda exonuclease, a 5' processive enzyme which we have determined pauses at 5-MIP monoadducts. When photobinding sites were mapped on denaturing sequencing gels, it was observed that 5-MIP binds preferentially to 5'-TA sites, and to a lesser degree to 5'-AT sites. Utilizing this approach, we have identified a psoralen hypersensitive region in which the binding sites were much stronger than those in the surrounding sequences. This region extends from 150 base pairs (bp) to the late side of the enhancers to the early enhancer/promoter boundary. We suggest that this region contains a sequence directed structural alteration of the DNA helix which can be detected by the psoralen mapping approach described.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker M. M., Wang J. C. Use of light for footprinting DNA in vivo. Nature. 1984 Jun 21;309(5970):682–687. doi: 10.1038/309682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T., Pardue M. L. Cross-linking of DNA with trimethylpsoralen is a probe for chromatin structure. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):631–640. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimino G. D., Gamper H. B., Isaacs S. T., Hearst J. E. Psoralens as photoactive probes of nucleic acid structure and function: organic chemistry, photochemistry, and biochemistry. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:1151–1193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke M. F., FitzGerald P. C., Brubaker J. M., Simpson R. T. Sequence-specific interaction of histones with the simian virus 40 enhancer region in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12394–12397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremisi C. The appearance of DNase I hypersensitive sites at the 5' end of the late SV40 genes is correlated with the transcriptional switch. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):5949–5964. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.5949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., DeLucia A. L., Koff A., Tsui S., Tegtmeyer P. The adenine-thymine domain of the simian virus 40 core origin directs DNA bending and coordinately regulates DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4578–4584. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamper H., Piette J., Hearst J. E. Efficient formation of a crosslinkable HMT monoadduct at the Kpn I recognition site. Photochem Photobiol. 1984 Jul;40(1):29–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1984.tb04549.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Dhar R., Khoury G. Simian virus 40 tandem repeated sequences as an element of the early promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):943–947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallick L. M., Yokota H. A., Bartholomew J. C., Hearst J. E. Photochemical addition of the cross-linking reagent 4,5', 8-trimethylpsoralen (trioxaslen) to intracellular and viral simian virus 40 DNA-histone complexes. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):127–135. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.127-135.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson C. V., Shen C. K., Hearst J. E. Cross-linking of DNA in situ as a probe for chromatin structure. Science. 1976 Jul 2;193(4247):62–64. doi: 10.1126/science.935855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiwasa T., Segawa M., Yamaguchi N., Oda K. Phasing of nucleosomes in SV40 chromatin reconstituted in vitro. J Biochem. 1981 May;89(5):1375–1389. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Bratosin S., Aloni Y. A nucleosome-free region in SV40 minichromosomes. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):263–265. doi: 10.1038/285263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongstra J., Reudelhuber T. L., Oudet P., Benoist C., Chae C. B., Jeltsch J. M., Mathis D. J., Chambon P. Induction of altered chromatin structures by simian virus 40 enhancer and promoter elements. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):708–714. doi: 10.1038/307708a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondoleon S. K., Robinson G. W., Hallick L. M. SV40 virus particles lack a psoralen-accessible origin and contain an altered nucleoprotein structure. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):261–273. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90166-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickol J., Behe M., Felsenfeld G. Effect of the B--Z transition in poly(dG-m5dC) . poly(dG-m5dC) on nucleosome formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1771–1775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Rich A. Negatively supercoiled simian virus 40 DNA contains Z-DNA segments within transcriptional enhancer sequences. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):674–679. doi: 10.1038/303674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrander E. A., Robinson G. W., Isaacs S. T., Tessman J., Hallick L. M. The site-specific inhibition of Bgl I cleavage by psoralen photoadducts. Photochem Photobiol. 1986 Jul;44(1):21–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1986.tb03559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J. G., Hearst J. E. Termination sites of the in vitro nick-translation reaction on DNA that had photoreacted with psoralen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5540–5544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson G. W., Hallick L. M. Mapping the in vivo arrangement of nucleosomes on simian virus 40 chromatin by the photoaddition of radioactive hydroxymethyltrimethylpsoralen. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):78–87. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.78-87.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Silver S., DeLucia A. L., Fanning E., Tegtmeyer P. An altered DNA conformation in origin region I is a determinant for the binding of SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):719–725. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90838-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saragosti S., Moyne G., Yaniv M. Absence of nucleosomes in a fraction of SV40 chromatin between the origin of replication and the region coding for the late leader RNA. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A., Wigmore D. J. Sites in simian virus 40 chromatin which are preferentially cleaved by endonucleases. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1511–1518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinden R. R., Carlson J. O., Pettijohn D. E. Torsional tension in the DNA double helix measured with trimethylpsoralen in living E. coli cells: analogous measurements in insect and human cells. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):773–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90440-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobell H. M., Sakore T. D., Jain S. C., Banerjee A., Bhandary K. K., Reddy B. S., Lozansky E. D. beta-kinked DNA--a structure that gives rise to drug intercalation and DNA breathing--and its wider significance in determining the premelting and melting behavior of DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):293–314. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundin O., Varshavsky A. Staphylococcal nuclease makes a single non-random cut in the simian virus 40 viral minichromosome. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 15;132(3):535–546. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Sundin O. H., Bohn M. J. SV40 viral minichromosome: preferential exposure of the origin of replication as probed by restriction endonucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3469–3477. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Sundin O., Bohn M. A stretch of "late" SV40 viral DNA about 400 bp long which includes the origin of replication is specifically exposed in SV40 minichromosomes. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):453–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldeck W., Föhring B., Chowdhury K., Gruss P., Sauer G. Origin of DNA replication in papovavirus chromatin is recognized by endogenous endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5964–5968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Oudet P., Chambon P. Preferential in vitro assembly of nucleosome cores on some AT-rich regions of SV40 DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Oct 10;7(3):705–713. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.3.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieshahn G. P., Hyde J. E., Hearst J. E. The photoaddition of trimethylpsoralen to Drosophila melanogaster nuclei: a probe for chromatin substructure. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):925–932. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhen W. P., Buchardt O., Nielsen H., Nielsen P. E. Site specificity of psoralen-DNA interstrand cross-linking determined by nuclease Bal31 digestion. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 21;25(21):6598–6603. doi: 10.1021/bi00369a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]