Abstract
The nifH gene encodes the iron protein (component II) of the nitrogenase complex. We have previously shown the presence in Clostridium pasteurianum of two nifH-like sequences in addition to the nifH1 gene which codes for a protein identical to the isolated iron protein. In the present study, we report that there are at least five nifH-like sequences in C. pasteurianum. DNA sequencing data indicate that the six nifH (nifH1) and nifH-like (nifH2, nifH3, nifH4, nifH5 and nifH6) sequences are not identical and vary from each other to different extents with sequence identity ranging between 68 to 99.9% within the nifH coding regions. Under normal N2-fixing growth conditions (molybdenum-containing medium), transcripts of nifH1 and most of the nifH-like sequences accumulate. The above results suggest the functioning of more than one "nifH" gene under N2-fixing growth conditions for C. pasteurianum. A common sequence was found around the -100 regions of all nif or nif-like transcription units. Sequences identical to or very similar to the consensus Escherichia coli promoter were found in the -35 and -10 regions.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alam J., Whitaker R. A., Krogmann D. W., Curtis S. E. Isolation and sequence of the gene for ferredoxin I from the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1265–1271. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1265-1271.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausubel F. M. Regulation of nitrogen fixation genes. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90294-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. E., Premakumar R., Dean D. R., Jacobson M. R., Chisnell J. R., Rizzo T. M., Kopczynski J. Nitrogen Fixation by Azotobacter vinelandii Strains Having Deletions in Structural Genes for Nitrogenase. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):92–94. doi: 10.1126/science.232.4746.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan-Wollaston V., Cannon M. C., Cannon F. C. The use of cloned nif (nitrogen fixation) DNA to investigate transcriptional regulation of nif expression in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(1):102–106. doi: 10.1007/BF00271203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardenas J., Mortenson L. E. Role of molybdenum in dinitrogen fixation by Clostridium pasteurianum. J Bacteriol. 1975 Sep;123(3):978–984. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.3.978-984.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
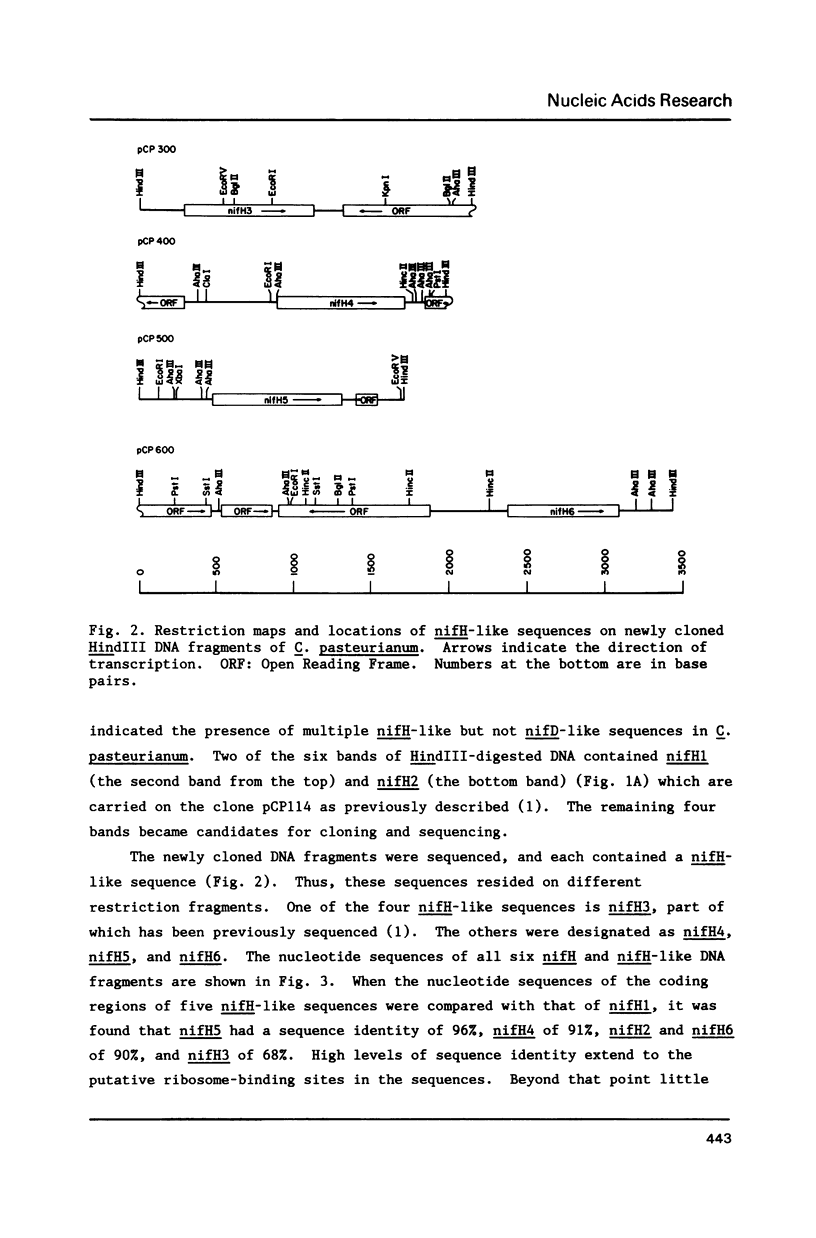
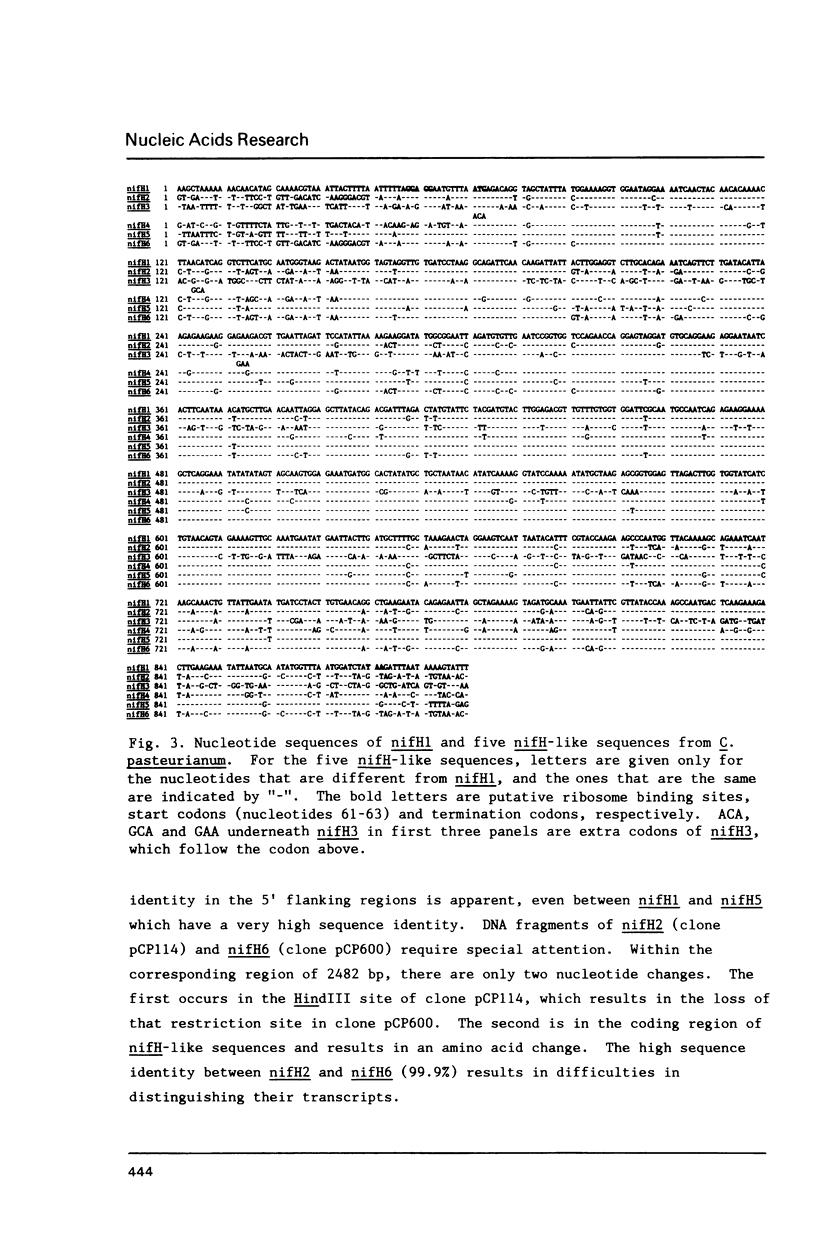
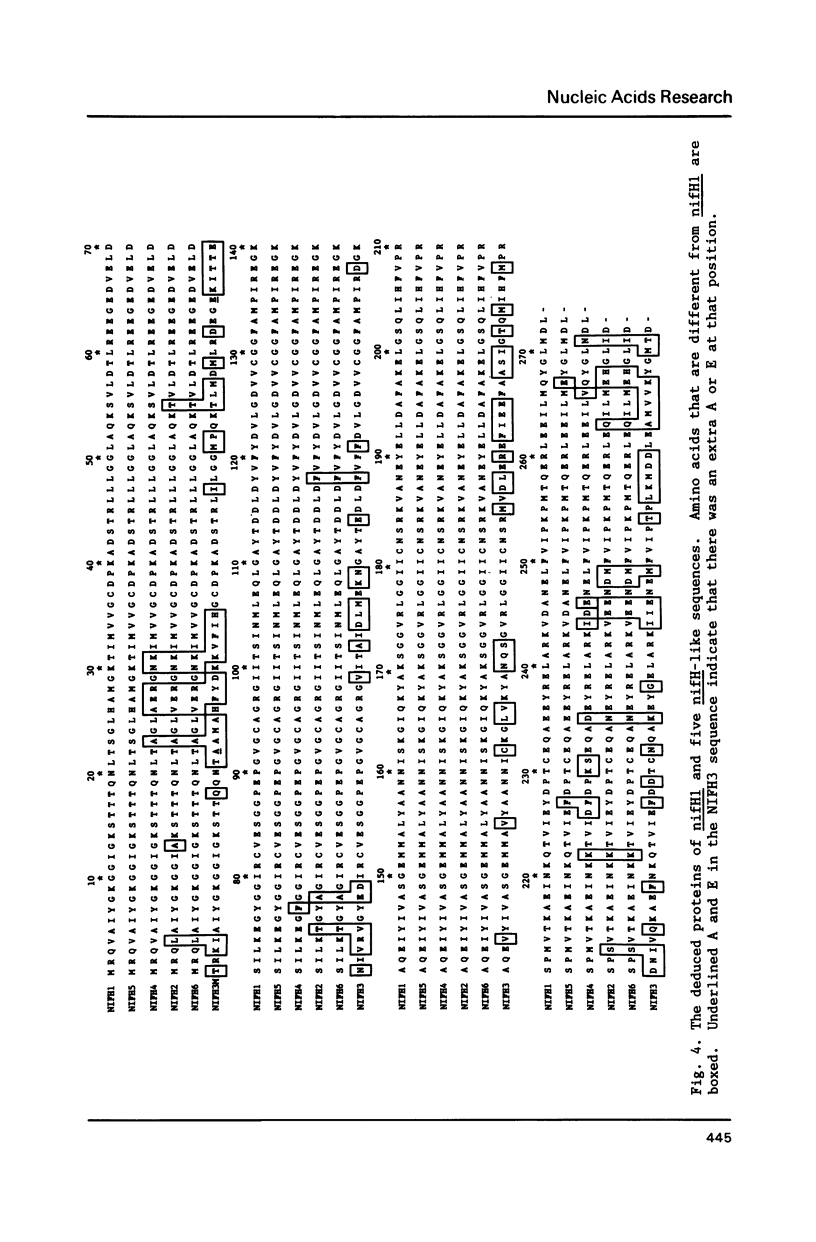
- Chen K. C., Chen J. S., Johnson J. L. Structural features of multiple nifH-like sequences and very biased codon usage in nitrogenase genes of Clostridium pasteurianum. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):162–172. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.162-172.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A. The genetic complexity of nitrogen fixation. The ninth Fleming lecture. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Nov;130(11):2745–2755. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-11-2745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond M., Whitty P., Wootton J. Sequence and domain relationships of ntrC and nifA from Klebsiella pneumoniae: homologies to other regulatory proteins. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):441–447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04230.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerich D. W., Ljones T., Burris R. H. Nitrogenase: properties of the catalytically inactive complex between the Azotobacter vinelandii MoFe protein and the Clostridium pasteurianum Fe protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 8;527(2):359–369. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90350-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George H. A., Johnson J. L., Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V., Chen J. S. Acetone, Isopropanol, and Butanol Production by Clostridium beijerinckii (syn. Clostridium butylicum) and Clostridium aurantibutyricum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1160–1163. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.1160-1163.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves M. C., Rabinowitz J. C. In vivo and in vitro transcription of the Clostridium pasteurianum ferredoxin gene. Evidence for "extended" promoter elements in gram-positive organisms. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11409–11415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton S. M., Slaughter C., Eisner W., Fisher T. The molybdenum-pterin binding protein is encoded by a multigene family in Clostridium pasteurianum. Gene. 1987;54(2-3):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90489-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. R., Premakumar R., Bishop P. E. Transcriptional regulation of nitrogen fixation by molybdenum in Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):480–486. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.480-486.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeng D. Y., Devanathan T., Mortenson L. E. Components of cell-free extracts of clostridium pasteurianum W5 required for acetylene reduction and N2 fixation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jun 6;35(5):625–633. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90450-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pretorius I. M., Rawlings D. E., O'Neill E. G., Jones W. A., Kirby R., Woods D. R. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the nitrogenase iron protein of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):367–370. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.367-370.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinto C., De La Vega H., Flores M., Leemans J., Cevallos M. A., Pardo M. A., Azpiroz R., De Lourdes Girard M., Calva E., Palacios R. Nitrogenase reductase: A functional multigene family in Rhizobium phaseoli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1170–1174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. C., Dean D. R., Burgess B. K. Iron-molybdenum cofactor biosynthesis in Azotobacter vinelandii requires the iron protein of nitrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14327–14332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson R., Woodley P., Jones R. Second gene (nifH*) coding for a nitrogenase iron protein in Azotobacter chroococcum is adjacent to a gene coding for a ferredoxin-like protein. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1159–1163. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04341.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto B., Mortenson L. E. In vivo kinetics of nitrogenase formation in Clostridium pasteurianum. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):822–830. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.822-830.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. E., Thorneley R. N., Eady R. R., Mortenson L. E. Nitrogenases from Klebsiella pneumoniae and Clostridium pasteurianum. Kinetic investigations of cross-reactions as a probe of the enzyme mechanism. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 1;157(2):439–447. doi: 10.1042/bj1570439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Haniu M., Yasunobu K. T. The amino acid sequence of Clostridium pasteurianum iron protein, a component of nitrogenase. I. Tryptic peptides. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7081–7088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Haniu M., Yasunobu K. T. The amino acid sequence of Clostridium pasteurianum iron protein, a component of nitrogenase. II. Cyanogen bromide peptides. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7089–7092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Haniu M., Yasunobu K. T. The amino acid sequence of Clostridium pasteurianum iron protein, a component of nitrogenase. III. The NH2-terminal and COOH-terminal sequences, tryptic peptides of large cyanogen bromide peptides, and the complete sequence. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7093–7100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. B. The enzymology of nitrogen fixation in cell-free extracts of Clostridium pasteurianum. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 10;244(1):171–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugalde R. A., Imperial J., Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Biosynthesis of iron-molybdenum cofactor in the absence of nitrogenase. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):888–893. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.888-893.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. Z., Chen J. S., Johnson J. L. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of nifD encoding the alpha-subunit of nitrogenase MoFe protein of Clostridium pasteurianum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 11;15(9):3935–3935. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.9.3935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]