Abstract
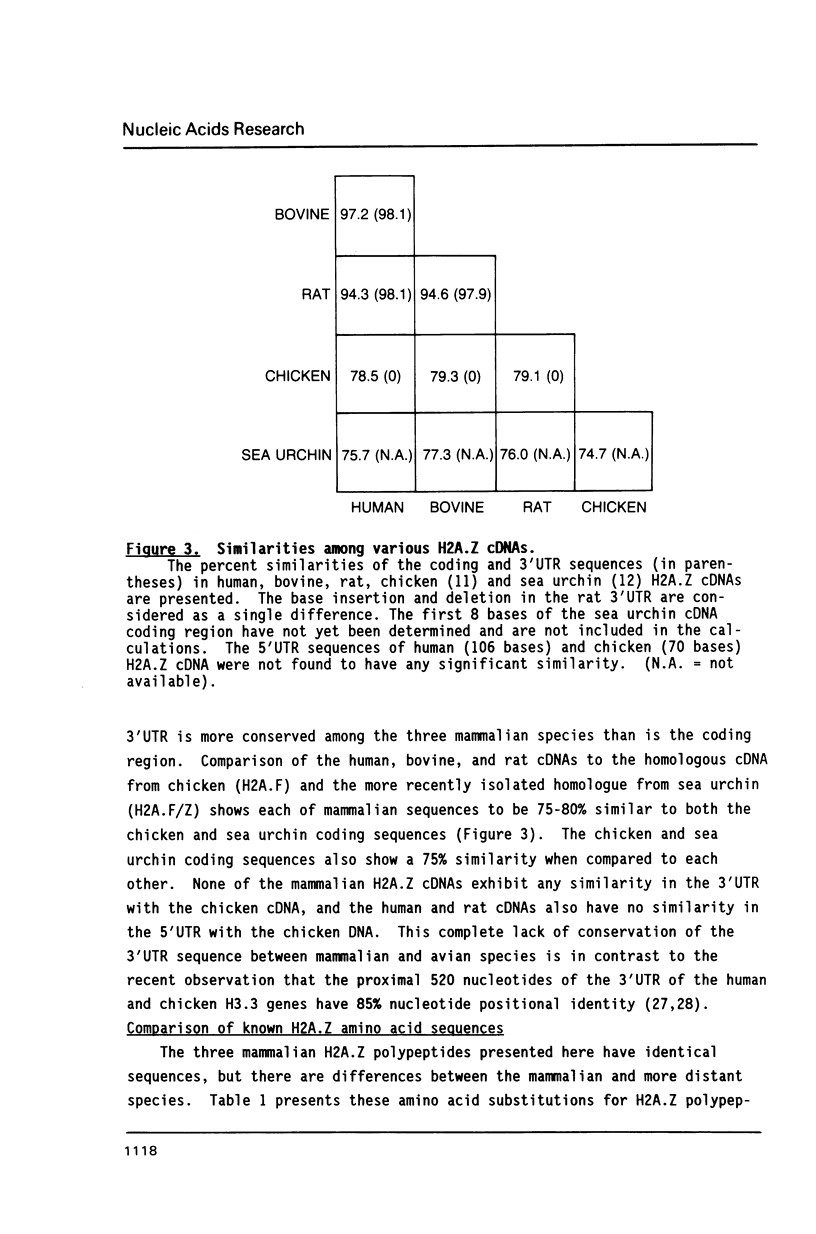
The nucleotide sequences of cDNAs for the evolutionarily diverged but highly conserved basal H2A isoprotein, H2A.Z, have been determined for the rat, cow, and human. As a basal histone, H2A.Z is synthesized throughout the cell cycle at a constant rate, unlinked to DNA replication, and at a much lower rate in quiescent cells. Each of the cDNA isolates encodes the entire H2A.Z polypeptide. The human isolate is about 1.0 kilobases long. It contains a coding region of 387 nucleotides flanked by 106 nucleotides of 5'UTR and 376 nucleotides of 3'UTR, which contains a polyadenylation signal followed by a poly A tail. The bovine and rat cDNAs have 97 and 94% nucleotide positional identity to the human cDNA in the coding region and 98% in the proximal 376 nucleotides of the 3'UTR which includes the polyadenylation signal. A potential stem-forming sequence imbedded in a direct repeat is found centered at 261 nucleotides into the 3'UTR. Each of the cDNA clones could be transcribed and translated in vitro to yield H2A.Z protein. The mammalian H2A.Z cDNA coding sequences are approximately 80% similar to those in chicken and 75% to those in sea urchin.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allis C. D., Richman R., Gorovsky M. A., Ziegler Y. S., Touchstone B., Bradley W. A., Cook R. G. hv1 is an evolutionarily conserved H2A variant that is preferentially associated with active genes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1941–1948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alterman R. B., Sprecher C., Graves R., Marzluff W. F., Skoultchi A. I. Regulated expression of a chimeric histone gene introduced into mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2316–2324. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artishevsky A., Grafsky A., Lee A. S. Isolation of a mammalian sequence capable of conferring cell cycle regulation to a heterologous gene. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1061–1063. doi: 10.1126/science.4059922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball D. J., Slaughter C. A., Hensley P., Garrard W. T. Amino acid sequence of the N-terminal domain of calf thymus histone H2A.Z. FEBS Lett. 1983 Apr 5;154(1):166–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80896-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Folk W., Birnstiel M. L. The terminal RNA stem-loop structure and 80 bp of spacer DNA are required for the formation of 3' termini of sea urchin H2A mRNA. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., West M. H., Stedman J. D. Two-dimensional gel analysis of histones in acid extracts of nuclei, cells, and tissues. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(1):17–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capasso O., Bleecker G. C., Heintz N. Sequences controlling histone H4 mRNA abundance. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1825–1831. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02437.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodgson J. B., Yamamoto M., Engel J. D. Chicken histone H3.3B cDNA sequence confirms unusual 3' UTR structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):6294–6294. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.6294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst S. G., Miller H., Brenner C. A., Nocente-McGrath C., Francis S., McIsaac R. Characterization of a cDNA clone coding for a sea urchin histone H2A variant related to the H2A.F/Z histone protein in vertebrates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4629–4644. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin S. G., Zweidler A. Non-allelic variants of histones 2a, 2b and 3 in mammals. Nature. 1977 Mar 17;266(5599):273–275. doi: 10.1038/266273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielli F., Hancock R., Faber A. J. Characterisation of a chromatin fraction bearing pulse-labelled RNA. 2. Quantification of histones and high-mobility-group proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(2):363–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves R. A., Pandey N. B., Chodchoy N., Marzluff W. F. Translation is required for regulation of histone mRNA degradation. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):615–626. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. P., Whiting J. A., Coles L. S., Krieg P. A., Wells J. R. H2A.F: an extremely variant histone H2A sequence expressed in the chicken embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2819–2823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch C. L., Bonner W. M., Moudrianakis E. N. Minor histone 2A variants and ubiquinated forms in the native H2A:H2B dimer. Science. 1983 Jul 29;221(4609):468–470. doi: 10.1126/science.6306766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchhausen T., Scarmato P., Harrison S. C., Monroe J. J., Chow E. P., Mattaliano R. J., Ramachandran K. L., Smart J. E., Ahn A. H., Brosius J. Clathrin light chains LCA and LCB are similar, polymorphic, and share repeated heptad motifs. Science. 1987 Apr 17;236(4799):320–324. doi: 10.1126/science.3563513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Stauber C., Schindler R., Schümperli D. Faithful cell-cycle regulation of a recombinant mouse histone H4 gene is controlled by sequences in the 3'-terminal part of the gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4389–4393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocchetti I., Einstein R., Brosius J. Putative diazepam binding inhibitor peptide: cDNA clones from rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7221–7225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Cary P. D., Abercrombie B. D., Crane-Robinson C., Bradbury E. M. A pH-dependent interaction between histones H2A and H2B involving secondary and tertiary folding. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Dec 11;71(2):337–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickel B. E., Roth S. Y., Cook R. G., Allis C. D., Davie J. R. Changes in the histone H2A variant H2A.Z and polyubiquitinated histone species in developing trout testis. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4417–4421. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):161–170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R., Elton T. S., Nissen M. S., Lehn D., Johnson K. R. Posttranscriptional gene regulation and specific binding of the nonhistone protein HMG-I by the 3' untranslated region of bovine interleukin 2 cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6531–6535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Kobs G. H4 histone messenger RNA decay in cell-free extracts initiates at or near the 3' terminus and proceeds 3' to 5'. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 20;188(4):579–593. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(86)80008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Peltz S. W., Kobs G., Brewer G. Histone mRNA degradation in vivo: the first detectable step occurs at or near the 3' terminus. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4362–4371. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler-Tuyns A., Paterson B. M. A chimeric mouse histone H4 gene containing either an intron or poly(A) addition signal behaves like a basal histone. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):8845–8862. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.8845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherbany A. A., Parent A. S., Brosius J. Rat calmodulin cDNA. DNA. 1987 Jun;6(3):267–272. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Strauss F., Varshavsky A. A mammalian high mobility group protein recognizes any stretch of six A.T base pairs in duplex DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauber C., Lüscher B., Eckner R., Lötscher E., Schümperli D. A signal regulating mouse histone H4 mRNA levels in a mammalian cell cycle mutant and sequences controlling RNA 3' processing are both contained within the same 80-bp fragment. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3297–3303. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04643.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells D., Hoffman D., Kedes L. Unusual structure, evolutionary conservation of non-coding sequences and numerous pseudogenes characterize the human H3.3 histone multigene family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):2871–2889. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.2871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West M. H., Bonner W. M. Histone 2A, a heteromorphous family of eight protein species. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 8;19(14):3238–3245. doi: 10.1021/bi00555a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West M. H., Bonner W. M. Structural comparisons of mouse histones 2A.X and 2A.Z with 2A.1 and 2A.2. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1983;76(3):455–464. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(83)90275-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M., Stephenson P. Role of the conserved AAUAAA sequence: four AAUAAA point mutants prevent messenger RNA 3' end formation. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1045–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.6208611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R. S., Bonner W. M. Separation of basal histone synthesis from S-phase histone synthesis in dividing cells. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90415-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R. S., Nishioka D., Bonner W. M. Differential conservation of histone 2A variants between mammals and sea urchins. J Cell Biol. 1982 May;93(2):426–431. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.2.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R. S., Panusz H. T., Hatch C. L., Bonner W. M. Histones and their modifications. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;20(2):201–263. doi: 10.3109/10409238609083735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R. S., Tsai S., Bonner W. M. Patterns of histone variant synthesis can distinguish G0 from G1 cells. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90130-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


