Abstract
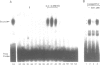
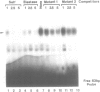
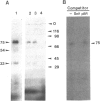
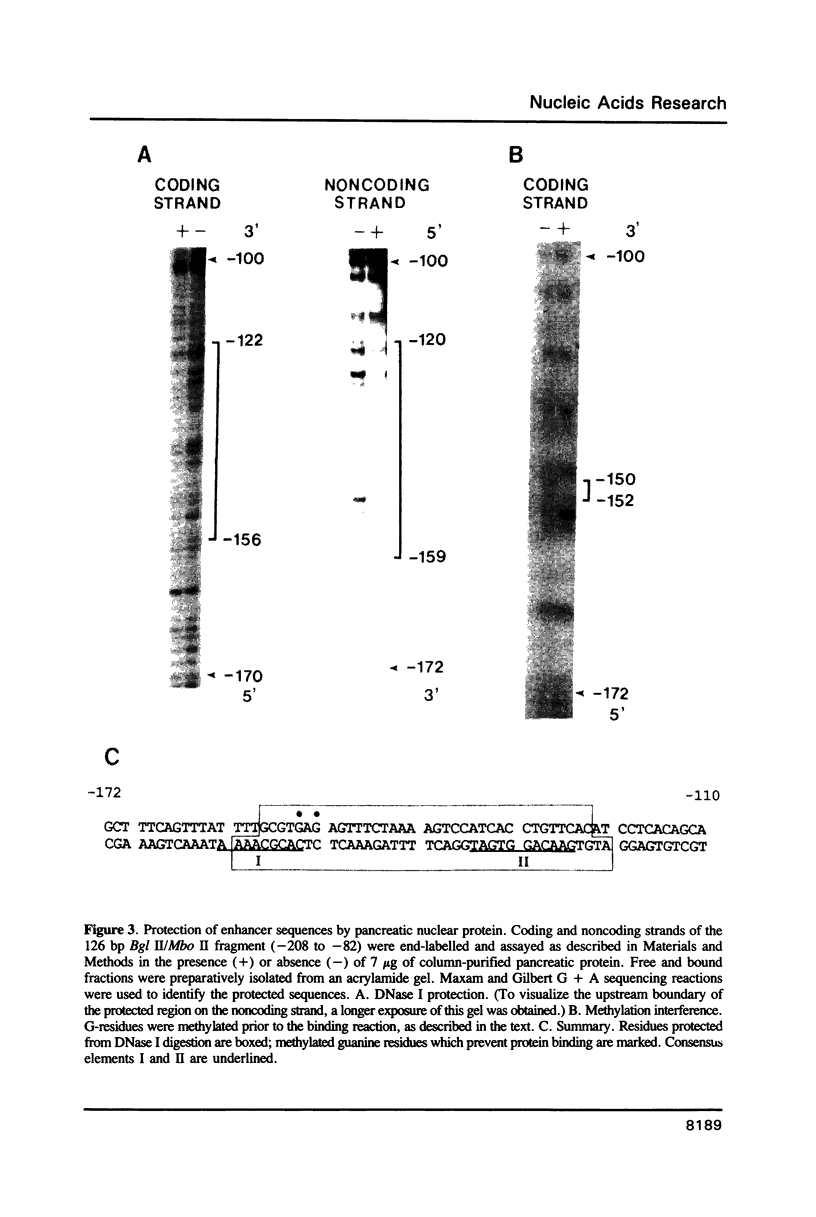
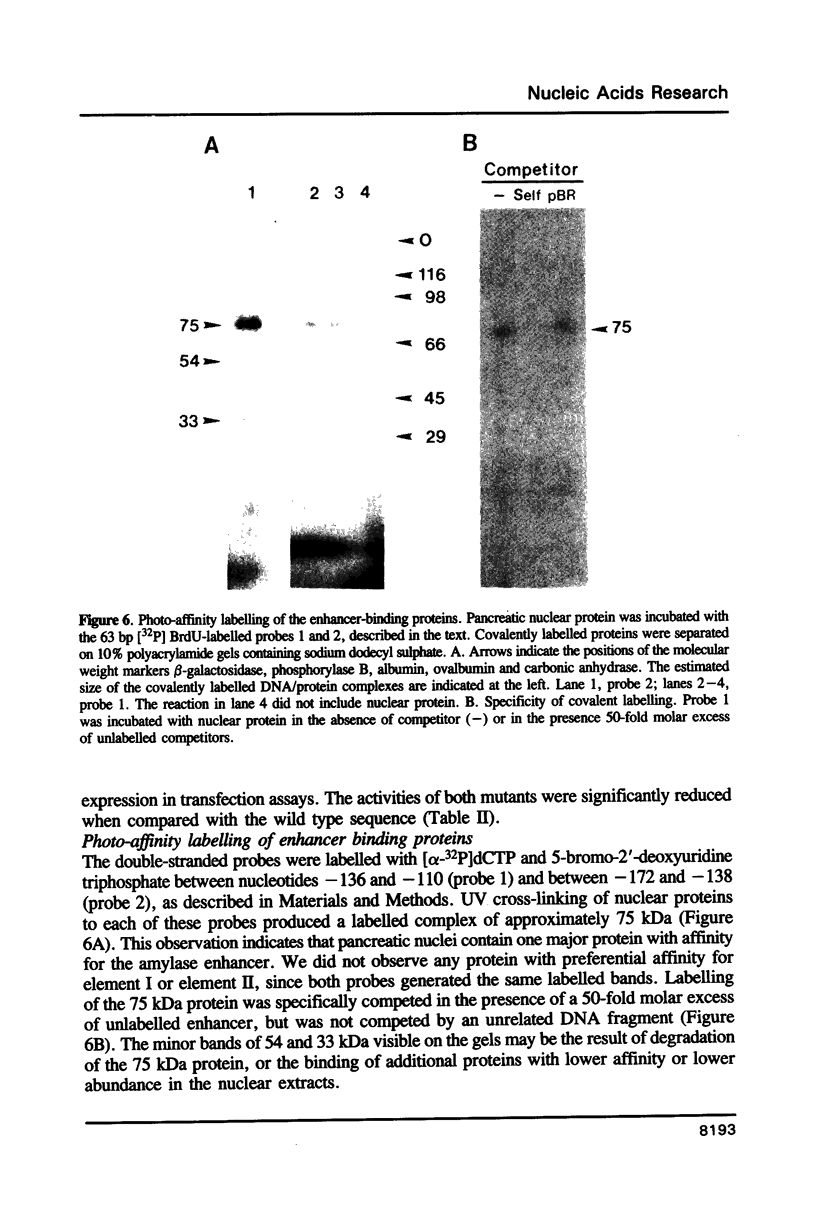
The mouse amylase gene Amy-2.2 is expressed at high levels specifically in the acinar cells of the pancreas. The region between -172 and -110 of this gene includes sequence elements common to pancreas-specific genes. Nuclear proteins with specific affinity for this region were partially purified from rat pancreas. The consensus element of another pancreas-specific gene, elastase 1, competes for protein binding to the amylase sequences. Binding was localized by DNase I protection to the sequence -156 to -122. Site-directed mutagenesis of this sequence resulted in concomitant loss of protein binding and enhancer activity. Photo-affinity labelling of pancreatic nuclear extracts identified one predominant binding protein with a molecular weight of approximately 75 kDa. The data indicate that binding of this nuclear protein is essential for the enhancer activity of this pancreas-specific element.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Nuclei from rat liver: isolation method that combines purity with high yield. Science. 1966 Dec 30;154(3757):1662–1665. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3757.1662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodner M., Castrillo J. L., Theill L. E., Deerinck T., Ellisman M., Karin M. The pituitary-specific transcription factor GHF-1 is a homeobox-containing protein. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):505–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulet A. M., Erwin C. R., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific enhancers in the rat exocrine pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3599–3603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. A single polypeptide possesses the binding and transcription activities of the adenovirus major late transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4723–4733. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockell M., Stevenson B. J., Strubin M., Hagenbüchle O., Wellauer P. K. Identification of a cell-specific DNA-binding activity that interacts with a transcriptional activator of genes expressed in the acinar pancreas. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2464–2476. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockell M., Stevenson B. J., Strubin M., Hagenbüchle O., Wellauer P. K. Identification of a cell-specific DNA-binding activity that interacts with a transcriptional activator of genes expressed in the acinar pancreas. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2464–2476. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Reitman M., Felsenfeld G. An erythrocyte-specific DNA-binding factor recognizes a regulatory sequence common to all chicken globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5976–5980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumucio D. L., Wiebauer K., Caldwell R. M., Samuelson L. C., Meisler M. H. Concerted evolution of human amylase genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1197–1205. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R. E., Swift G. H., Ornitz D. M., Quaife C. J., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., MacDonald R. J. The rat elastase I regulatory element is an enhancer that directs correct cell specificity and developmental onset of expression in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2956–2967. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham H. A., Chen R. P., Mangalam H. J., Elsholtz H. P., Flynn S. E., Lin C. R., Simmons D. M., Swanson L., Rosenfeld M. G. A tissue-specific transcription factor containing a homeodomain specifies a pituitary phenotype. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse F., Komro C. T., Michnoff C. H., MacDonald R. J. The cell-specific elastase I enhancer comprises two domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):893–902. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. J., Hammer R. E., Swift G. H., Ornitz D. M., Davis B. P., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Tissue-specific expression of pancreatic genes in transgenic mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;478:131–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb15527.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. J., Hammer R. E., Swift G. H., Ornitz D. M., Davis B. P., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Tissue-specific expression of pancreatic genes in transgenic mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;478:131–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb15527.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick A., Wu D., Castrillo J. L., Dana S., Strobl J., Thompson E. B., Karin M. Extinction of growth hormone expression in somatic cell hybrids involves repression of the specific trans-activator GHF-1. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):379–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornitz D. M., Palmiter R. D., Messing A., Hammer R. E., Pinkert C. A., Brinster R. L. Elastase I promoter directs expression of human growth hormone and SV40 T antigen genes to pancreatic acinar cells in transgenic mice. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:399–409. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Rosenberg M. P., Keller S. A., Meisler M. H. Tissue-specific and insulin-dependent expression of a pancreatic amylase gene in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):326–334. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Rosenberg M. P., Keller S. A., Ting C. N., Meisler M. H. Insulin response of a hybrid amylase/CAT gene in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16519–16522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift G. H., Craik C. S., Stary S. J., Quinto C., Lahaie R. G., Rutter W. J., MacDonald R. J. Structure of the two related elastase genes expressed in the rat pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14271–14278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift G. H., Craik C. S., Stary S. J., Quinto C., Lahaie R. G., Rutter W. J., MacDonald R. J. Structure of the two related elastase genes expressed in the rat pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14271–14278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall L., deBoer E., Grosveld F. The human beta-globin gene 3' enhancer contains multiple binding sites for an erythroid-specific protein. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1089–1100. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]