Abstract
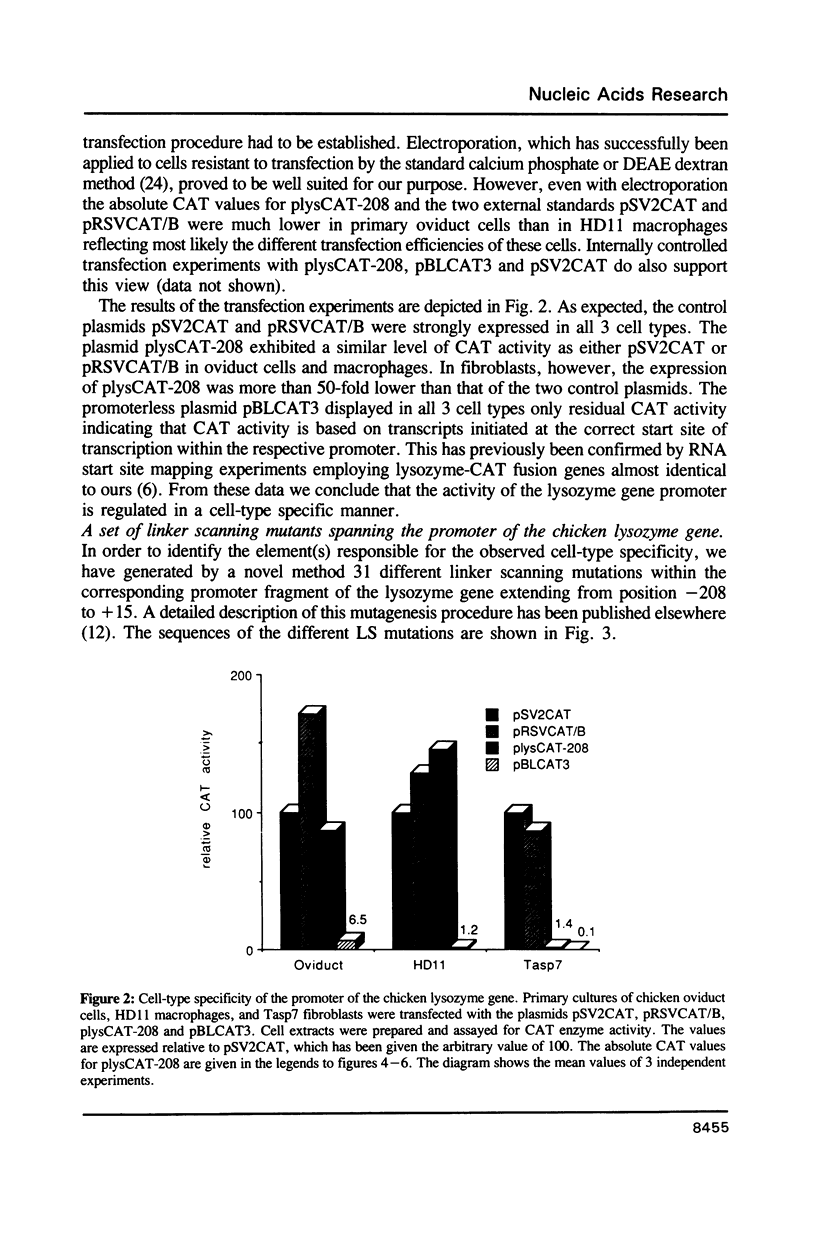
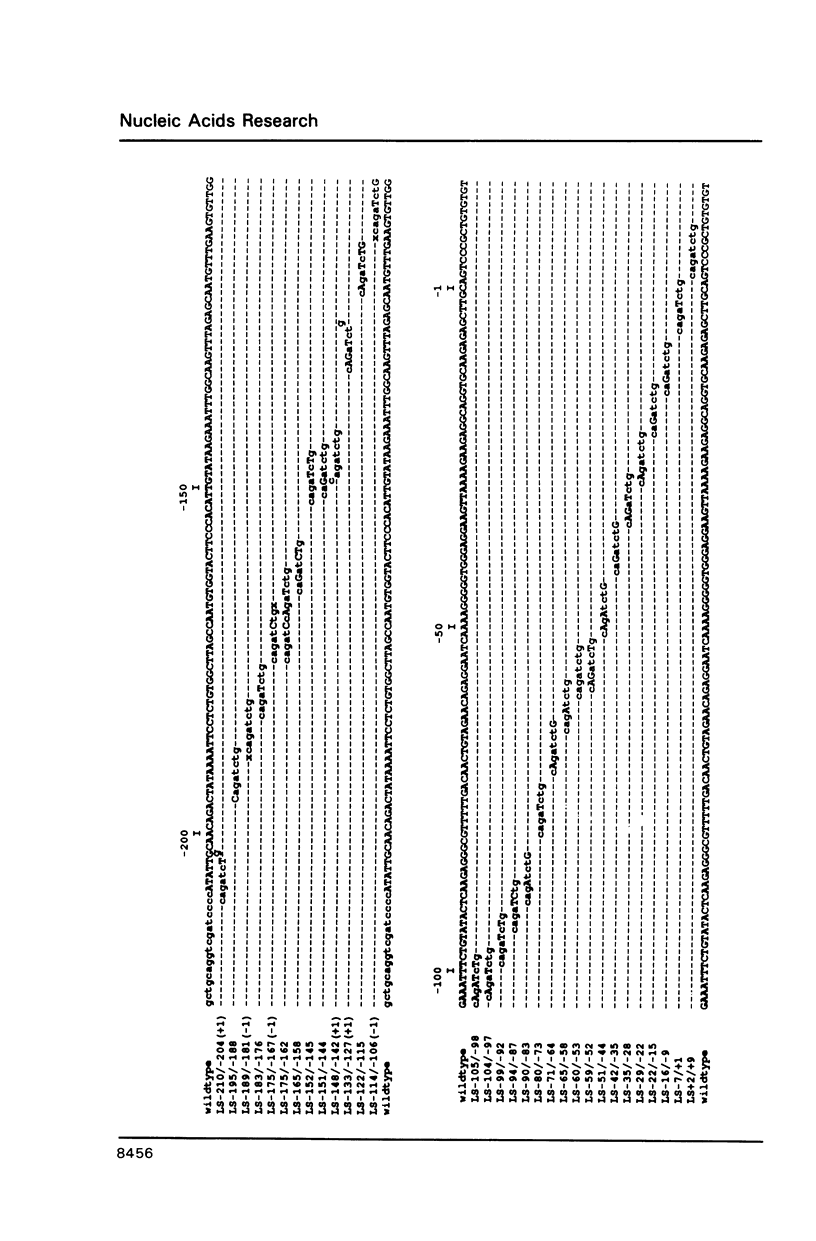
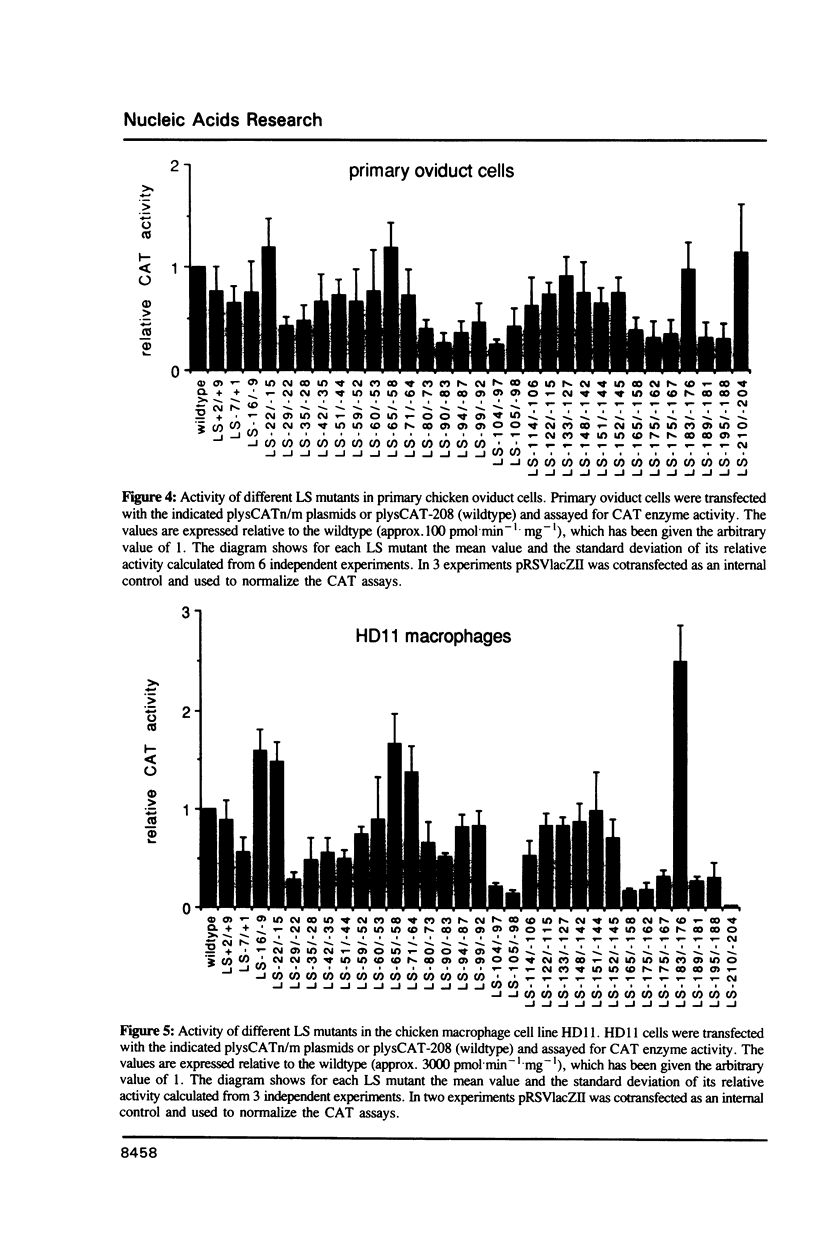
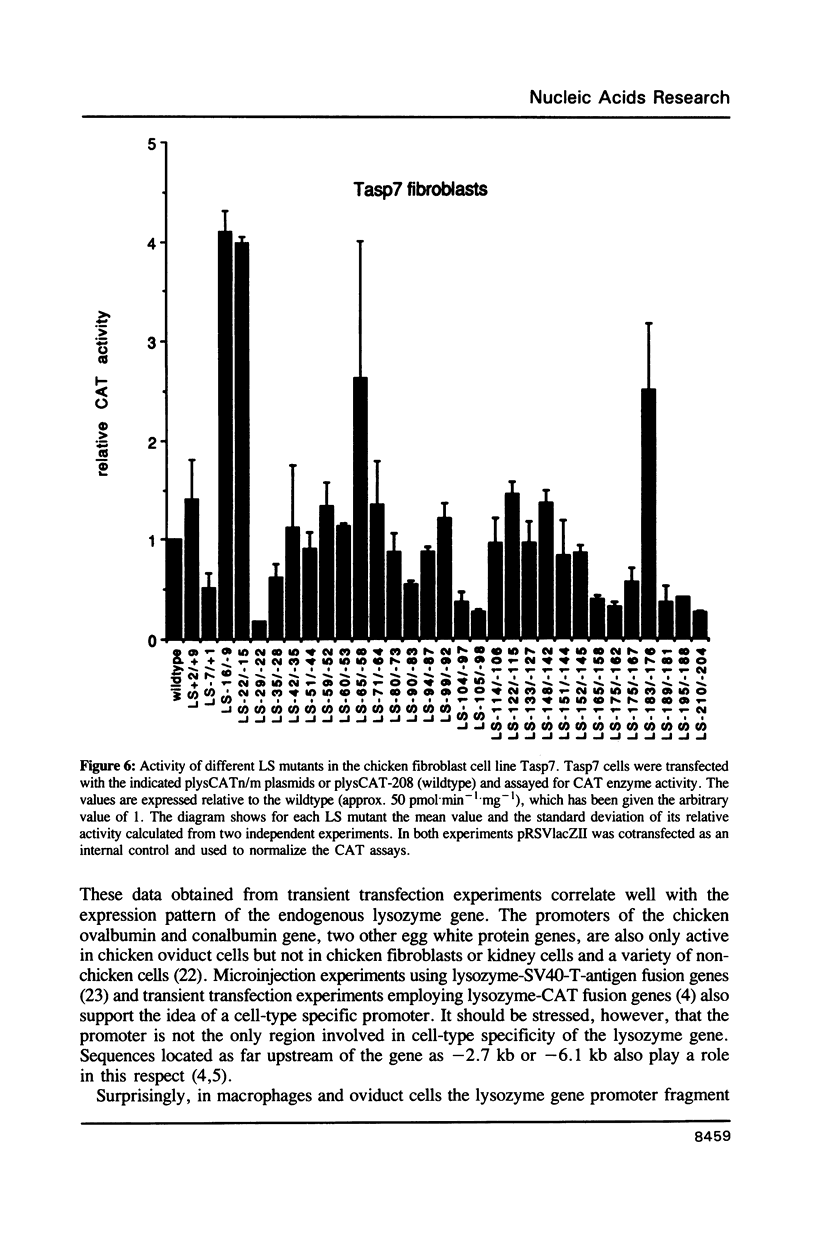
The chicken lysozyme gene is constitutively expressed in macrophages, in oviduct cells its expression is controlled by steroid hormones, and in fibroblasts the gene is not expressed. A fusion gene consisting of promoter sequences of the lysozyme gene from -208 to +15 in front of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) coding region was more than 50 times less active in non-expressing cells as compared to expressing cells. In order to identify the element(s) responsible for this cell-type specificity 31 different linker scanning mutations were generated within this promoter fragment and analyzed by transient transfections in the three types of chicken cells mentioned above. Three mutation sensitive regions located around position -25, -100 and between -158 and -208 were detected in each cell type, however, several LS mutations displayed clear cell-type specific differences in their phenotypic effects. Interestingly, a few LS mutations led to an increase in promoter activity in fibroblasts suggesting that the corresponding wildtype sequences represent binding sites for negatively acting transcription factors.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerblom I. E., Slater E. P., Beato M., Baxter J. D., Mellon P. L. Negative regulation by glucocorticoids through interference with a cAMP responsive enhancer. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):350–353. doi: 10.1126/science.2838908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschmied J., Muller M., Baniahmad A., Steiner C., Renkawitz R. Cooperative interaction of chicken lysozyme enhancer sub-domains partially overlapping with a steroid receptor binding site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):4975–4991. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.4975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baniahmad A., Muller M., Steiner C., Renkawitz R. Activity of two different silencer elements of the chicken lysozyme gene can be compensated by enhancer elements. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2297–2303. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02504.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barberis A., Superti-Furga G., Busslinger M. Mutually exclusive interaction of the CCAAT-binding factor and of a displacement protein with overlapping sequences of a histone gene promoter. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):347–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90489-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., von Kirchbach A., Döderlein G., Conscience J. F., Graf T. Chicken hematopoietic cells transformed by seven strains of defective avian leukemia viruses display three distinct phenotypes of differentiation. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):375–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Hayakawa H., Berg P. Electroporation for the efficient transfection of mammalian cells with DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1311–1326. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierich A., Gaub M. P., LePennec J. P., Astinotti D., Chambon P. Cell-specificity of the chicken ovalbumin and conalbumin promoters. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2305–2312. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02505.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritton H. P., Igo-Kemenes T., Nowock J., Strech-Jurk U., Theisen M., Sippel A. E. Alternative sets of DNase I-hypersensitive sites characterize the various functional states of the chicken lysozyme gene. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):163–165. doi: 10.1038/311163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaub M. P., Dierich A., Astinotti D., Touitou I., Chambon P. The chicken ovalbumin promoter is under negative control which is relieved by steroid hormones. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2313–2320. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02506.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Burstein H., Maniatis T. The human beta-interferon gene enhancer is under negative control. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):601–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Maniatis T. Overlapping positive and negative regulatory domains of the human beta-interferon gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1447–1451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C., Padmanabhan R., Howard B. H. High efficiency DNA-mediated transformation of primate cells. Science. 1983 Aug 5;221(4610):551–553. doi: 10.1126/science.6306768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grez M., Land H., Giesecke K., Schütz G., Jung A., Sippel A. E. Multiple mRNAs are generated from the chicken lysozyme gene. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):743–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90182-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. V., Jacob P. E., Ringold G. M., Lee F. Expression and regulation of Escherichia coli lacZ gene fusions in mammalian cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):101–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht A., Berkenstam A., Strömstedt P. E., Gustafsson J. A., Sippel A. E. A progesterone responsive element maps to the far upstream steroid dependent DNase hypersensitive site of chicken lysozyme chromatin. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2063–2073. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03046.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes N. E., Groner B., Sippel A. E., Jeep S., Wurtz T., Nguyen-Huu M. C., Giesecke K., Schütz G. Control of cellular content of chicken egg white protein specific RNA during estrogen administration and withdrawal. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):616–624. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Renkawitz R., Schütz G. A new method for constructing linker scanning mutants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):417–429. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tilly K., Maniatis T. Fine structure genetic analysis of a beta-globin promoter. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):613–618. doi: 10.1126/science.3457470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Náray A., Arányi P., Quiroga V. Comparative study of glucocorticoid sensitivity and receptors in lymphoid tissues. J Steroid Biochem. 1980 Apr;13(4):415–421. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(80)90348-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oro A. E., Hollenberg S. M., Evans R. M. Transcriptional inhibition by a glucocorticoid receptor-beta-galactosidase fusion protein. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1109–1114. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90255-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter H., Weir L., Leder P. Enhancer-dependent expression of human kappa immunoglobulin genes introduced into mouse pre-B lymphocytes by electroporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7161–7165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. Gene regulation by proteins acting nearby and at a distance. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):697–701. doi: 10.1038/322697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz R., Beug H., Graf T., Matthias P., Grez M., Schütz G. Expression of a chicken lysozyme recombinant gene is regulated by progesterone and dexamethasone after microinjection into oviduct cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90416-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz R., Schütz G., von der Ahe D., Beato M. Sequences in the promoter region of the chicken lysozyme gene required for steroid regulation and receptor binding. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):503–510. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90380-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirm S., Jiricny J., Schaffner W. The SV40 enhancer can be dissected into multiple segments, each with a different cell type specificity. Genes Dev. 1987 Mar;1(1):65–74. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütz G., Nguyen-Huu M. C., Giesecke K., Hynes N. E., Groner B., Wurtz T., Sippel A. E. Hormonal control of egg white protein messenger RNA synthesis in the chicken oviduct. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):617–624. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner C., Muller M., Baniahmad A., Renkawitz R. Lysozyme gene activity in chicken macrophages is controlled by positive and negative regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4163–4178. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theisen M., Stief A., Sippel A. E. The lysozyme enhancer: cell-specific activation of the chicken lysozyme gene by a far-upstream DNA element. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):719–724. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04273.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Foley R., Munck A. Interaction of glucocorticoids with macrophages. Identification of glucocorticoid receptors in monocytes and macrophages. J Exp Med. 1978 Jun 1;147(6):1684–1694. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.6.1684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenke M., Grundström T., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Schatz C., Wildeman A., Chambon P. Multiple sequence motifs are involved in SV40 enhancer function. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):387–397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Ahe D., Renoir J. M., Buchou T., Baulieu E. E., Beato M. Receptors for glucocorticosteroid and progesterone recognize distinct features of a DNA regulatory element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2817–2821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


