Abstract
An HSV virion component, Vmw65, interacts with cellular transcription factors to transactivate TAATGARAT-containing viral genes and some cellular genes containing the related octamer element. We show that the octamer-containing histone H2B promoter can be trans-activated by transfection of Vmw65 but not by viral infection. The induction of H2B transcription by Vmw65 can be abolished by co-transfection of excess amounts of either a TAATGARAT element or a Vmw65 responsive octamer element. This effect cannot be overcome by addition of increasing amounts of Vmw65. The H2B promoter and TAATGARAT-containing viral promoters therefore compete for limiting cellular factors required for induction by Vmw65 resulting in repression of the H2B gene during lytic infection. The competitive effect of TAATGARAT elements on the H2B gene is not observed in the absence of Vmw65, but can be produced in the presence of a truncated form of Vmw65 lacking the acidic tail required for transcriptional activation. Hence a domain of Vmw65 distinct from that involved in transcriptional induction interacts with cellular octamer binding proteins favouring binding to the TAATGARAT motif.
Full text
PDF



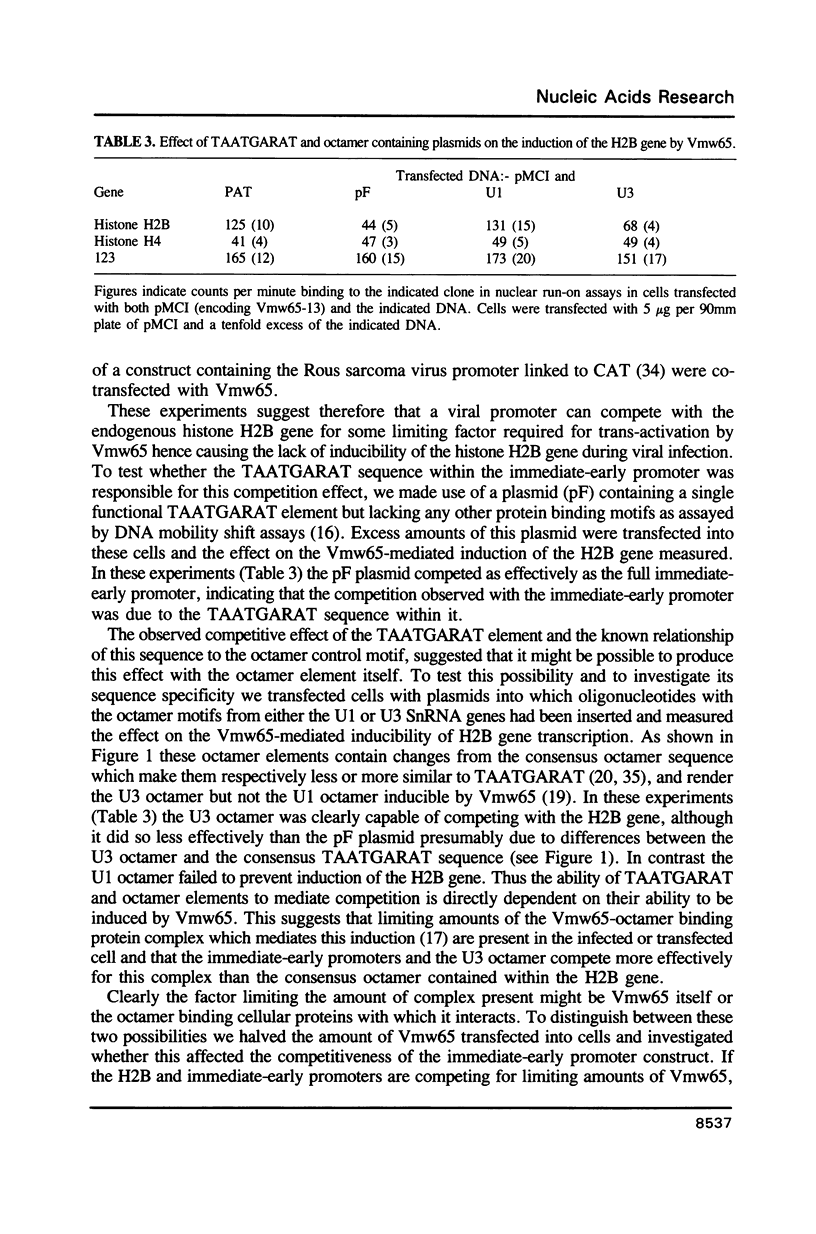



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batterson W., Roizman B. Characterization of the herpes simplex virion-associated factor responsible for the induction of alpha genes. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):371–377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.371-377.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumruker T., Sturm R., Herr W. OBP100 binds remarkably degenerate octamer motifs through specific interactions with flanking sequences. Genes Dev. 1988 Nov;2(11):1400–1413. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.11.1400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. E., Palfreyman J. W., Preston C. M. Identification of herpes simplex virus DNA sequences which encode a trans-acting polypeptide responsible for stimulation of immediate early transcription. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ejercito P. M., Kieff E. D., Roizman B. Characterization of herpes simplex virus strains differing in their effects on social behaviour of infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):357–364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher C., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Purification and characterization of OTF-1, a transcription factor regulating cell cycle expression of a human histone H2b gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., Triezenberg S. J., McKnight S. L. Expression of a truncated viral trans-activator selectively impedes lytic infection by its cognate virus. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):452–454. doi: 10.1038/335452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
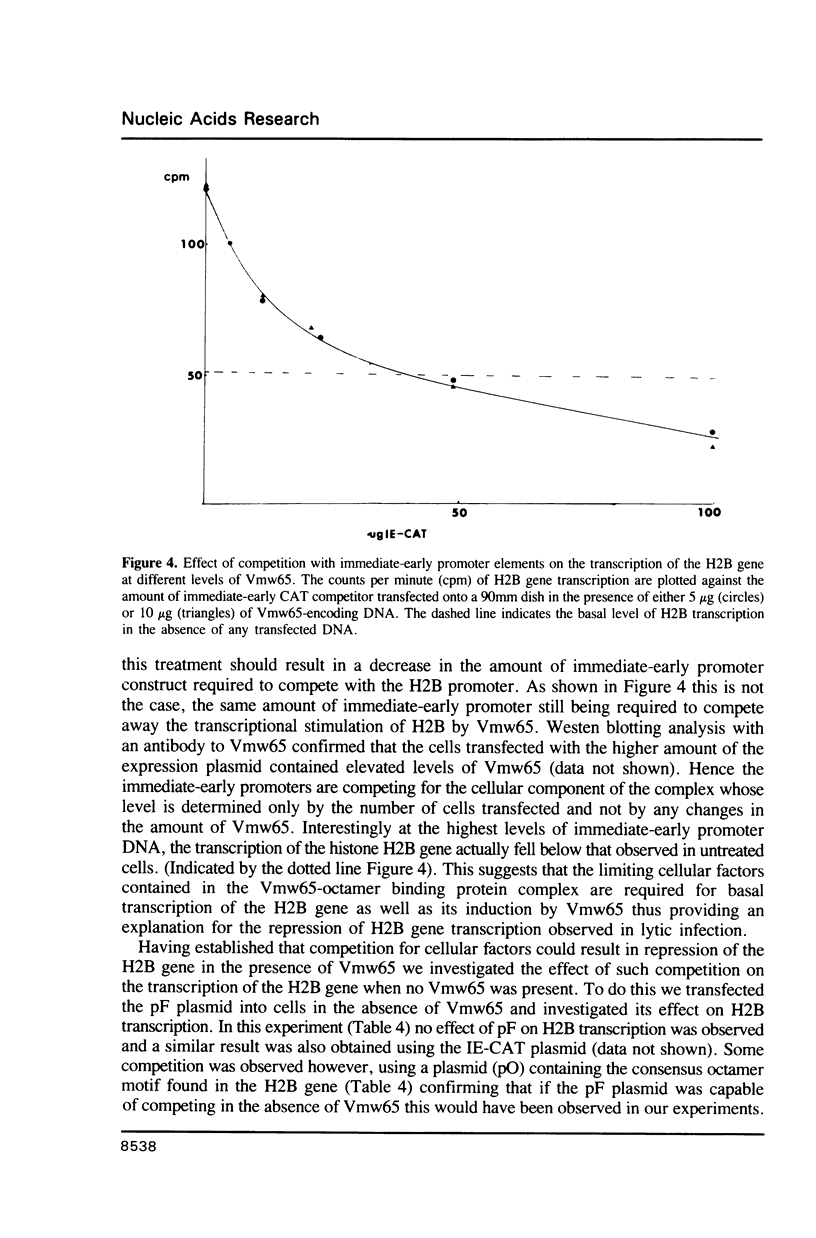
- Gerster T., Roeder R. G. A herpesvirus trans-activating protein interacts with transcription factor OTF-1 and other cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6347–6351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves R., O'Hare P. Separation of requirements for protein-DNA complex assembly from those for functional activity in the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein Vmw65. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1641–1650. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1641-1650.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
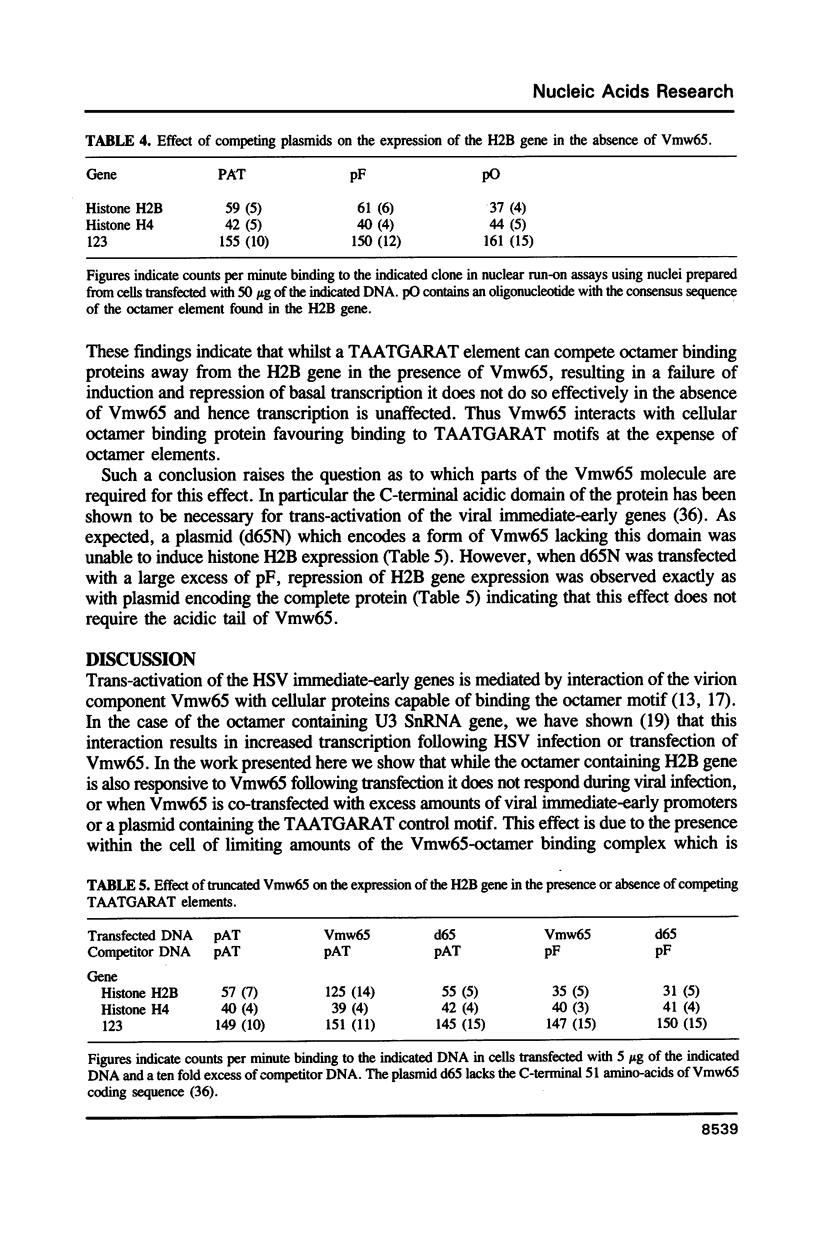
- Hanly S. M., Bleecker G. C., Heintz N. Identification of promoter elements necessary for transcriptional regulation of a human histone H4 gene in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):380–389. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X., Treacy M. N., Simmons D. M., Ingraham H. A., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Expression of a large family of POU-domain regulatory genes in mammalian brain development. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):35–41. doi: 10.1038/340035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Honess R. W., Cassai E., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XII. The virion polypeptides of type 1 strains. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):640–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.640-651.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay R., McPherson J. Hybrid pUC vectors for addition of new restriction enzyme sites to the ends of DNA fragments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2778–2778. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp L. M., Brickell P. M., La Thangue N. B., Latchman D. S. Transcriptional induction of cellular gene expression during lytic infection with herpes simplex virus. Biosci Rep. 1986 Nov;6(11):945–951. doi: 10.1007/BF01114970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp L. M., Latchman D. S. Differential regulation of octamer-containing cellular genes by the herpes simplex virus virion protein Vmw65 is mediated by sequence differences in the octamer element. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4239–4244. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03321.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp L. M., Preston C. M., Preston V. G., Latchman D. S. Cellular gene induction during herpes simplex virus infection can occur without viral protein synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 9;14(23):9261–9270. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.23.9261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaBella F., Sive H. L., Roeder R. G., Heintz N. Cell-cycle regulation of a human histone H2b gene is mediated by the H2b subtype-specific consensus element. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):32–39. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. True genes for human U1 small nuclear RNA. Copy number, polymorphism, and methylation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):2013–2021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I., STOKER M. Polyoma transformation of hamster cell clones--an investigation of genetic factors affecting cell competence. Virology. 1962 Feb;16:147–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marashi F., Prokopp K., Stein J., Stein G. Evidence for a human histone gene cluster containing H2B and H2A pseudogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1936–1940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Goding C. R. Herpes simplex virus regulatory elements and the immunoglobulin octamer domain bind a common factor and are both targets for virion transactivation. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):435–445. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel R., Chan W. L., Kemp L. M., La Thangue N. B., Latchman D. S. Isolation of cDNA clones derived from a cellular gene transcriptionally induced by herpes simplex virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5629–5640. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. Control of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA synthesis in cells infected with wild-type virus or the temperature-sensitive mutant tsK. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):275–284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.275-284.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Frame M. C., Campbell M. E. A complex formed between cell components and an HSV structural polypeptide binds to a viral immediate early gene regulatory DNA sequence. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):425–434. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W. How do different transcription factors binding the same DNA sequence sort out their jobs? Trends Genet. 1989 Feb;5(2):37–39. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Heguy A., Roeder R. G. Identification and purification of a human lymphoid-specific octamer-binding protein (OTF-2) that activates transcription of an immunoglobulin promoter in vitro. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):783–793. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90101-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sive H. L., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Multiple sequence elements are required for maximal in vitro transcription of a human histone H2B gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3329–3340. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sive H. L., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a common factor with conserved promoter and enhancer sequences in histone H2B, immunoglobulin, and U2 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6382–6386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skuzeski J. M., Lund E., Murphy J. T., Steinberg T. H., Burgess R. R., Dahlberg J. E. Synthesis of human U1 RNA. II. Identification of two regions of the promoter essential for transcription initiation at position +1. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8345–8352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh D., Busch H., Reddy R. Isolation and characterization of a human U3 small nucleolar RNA gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jun 30;137(3):1133–1140. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90343-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Grossniklaus U., Herr W., Hernandez N. Activation of the U2 snRNA promoter by the octamer motif defines a new class of RNA polymerase II enhancer elements. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1764–1778. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triezenberg S. J., Kingsbury R. C., McKnight S. L. Functional dissection of VP16, the trans-activator of herpes simplex virus immediate early gene expression. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):718–729. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Clements J. B. A herpes simplex virus type 1 function continuously required for early and late virus RNA synthesis. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):329–330. doi: 10.1038/285329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin G., Lund E., Murphy J. T., Pettersson U., Dahlberg J. E. Human U2 and U1 RNA genes use similar transcription signals. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3295–3301. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02293.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. Replication origins and a sequence involved in coordinate induction of the immediate-early gene family are conserved in an intergenic region of herpes simplex virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 24;12(4):2061–2079. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.4.2061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth T., Staudt L., Baltimore D. An octamer oligonucleotide upstream of a TATA motif is sufficient for lymphoid-specific promoter activity. Nature. 1987 Sep 10;329(6135):174–178. doi: 10.1038/329174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong R., Roeder R. G., Heintz N. The primary structure and expression of four cloned human histone genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7409–7425. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- apRhys C. M., Ciufo D. M., O'Neill E. A., Kelly T. J., Hayward G. S. Overlapping octamer and TAATGARAT motifs in the VF65-response elements in herpes simplex virus immediate-early promoters represent independent binding sites for cellular nuclear factor III. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2798–2812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2798-2812.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]