Abstract
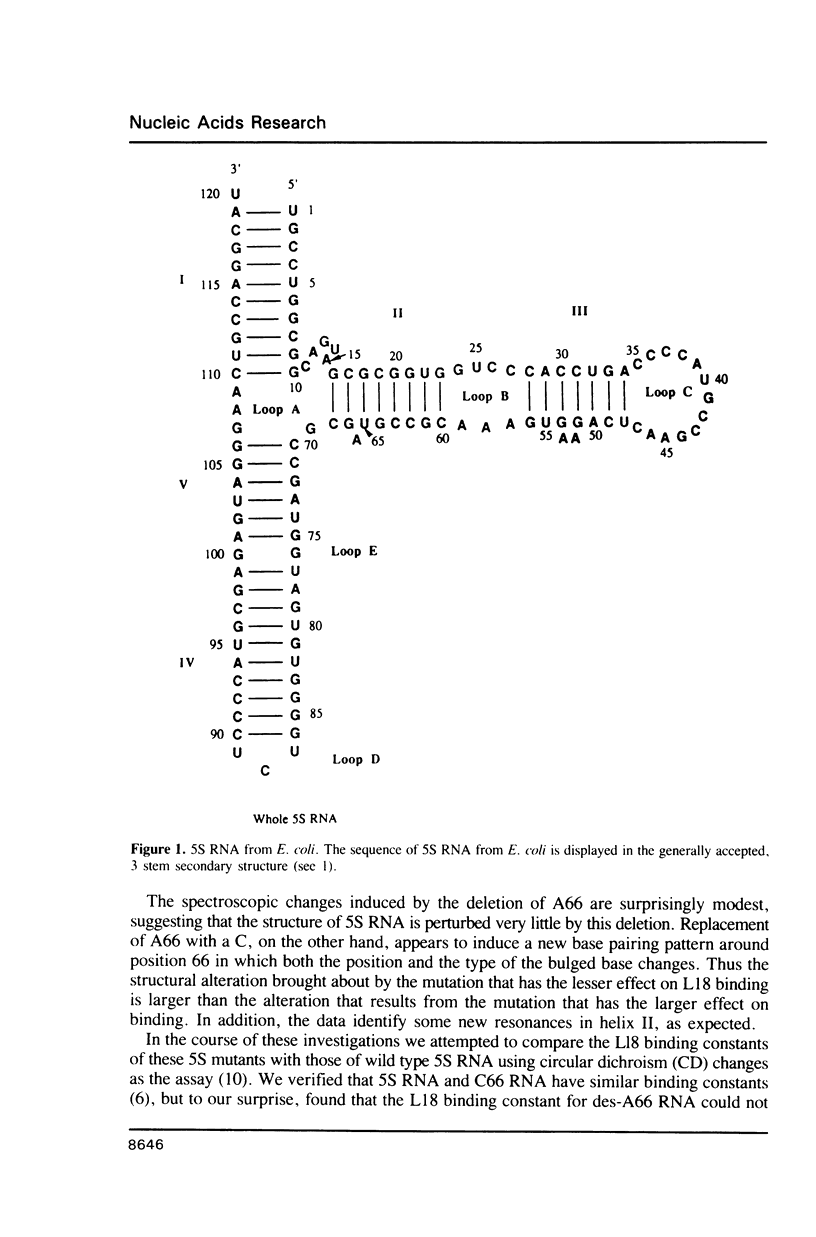
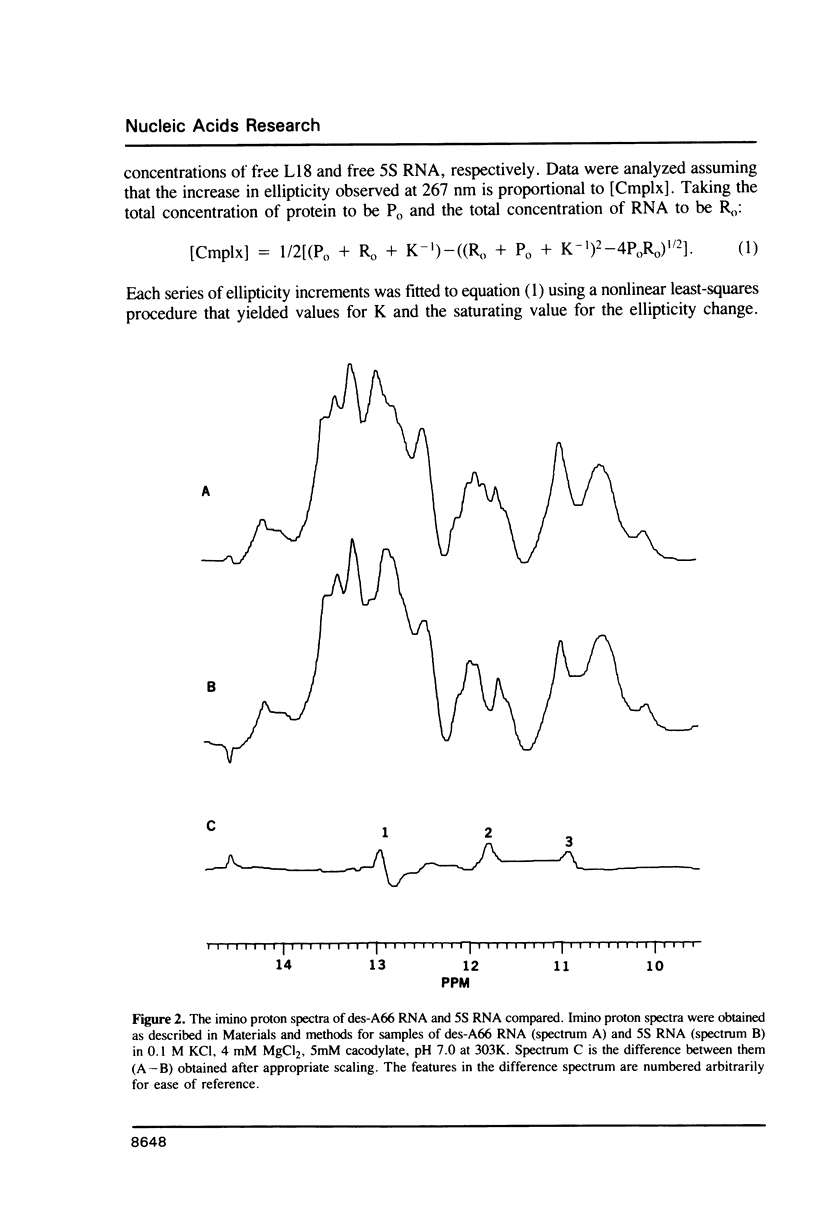
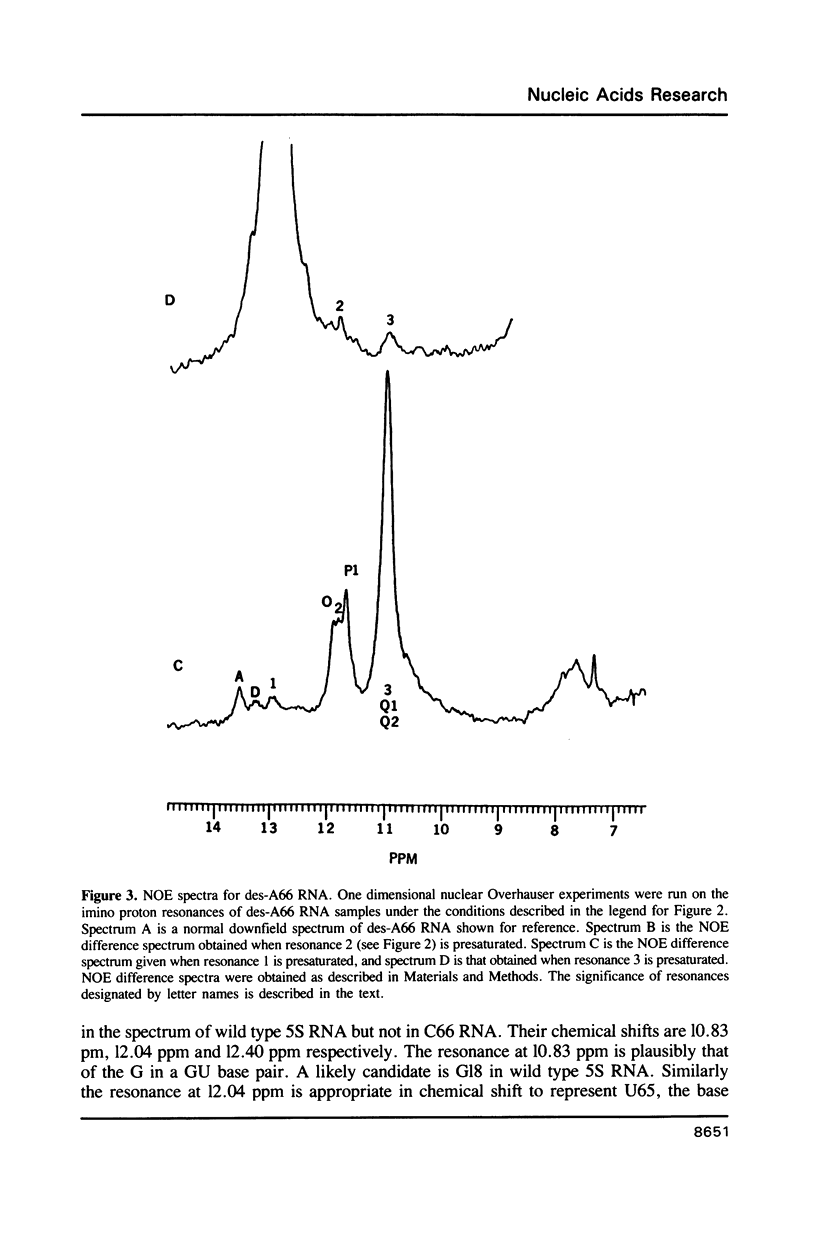
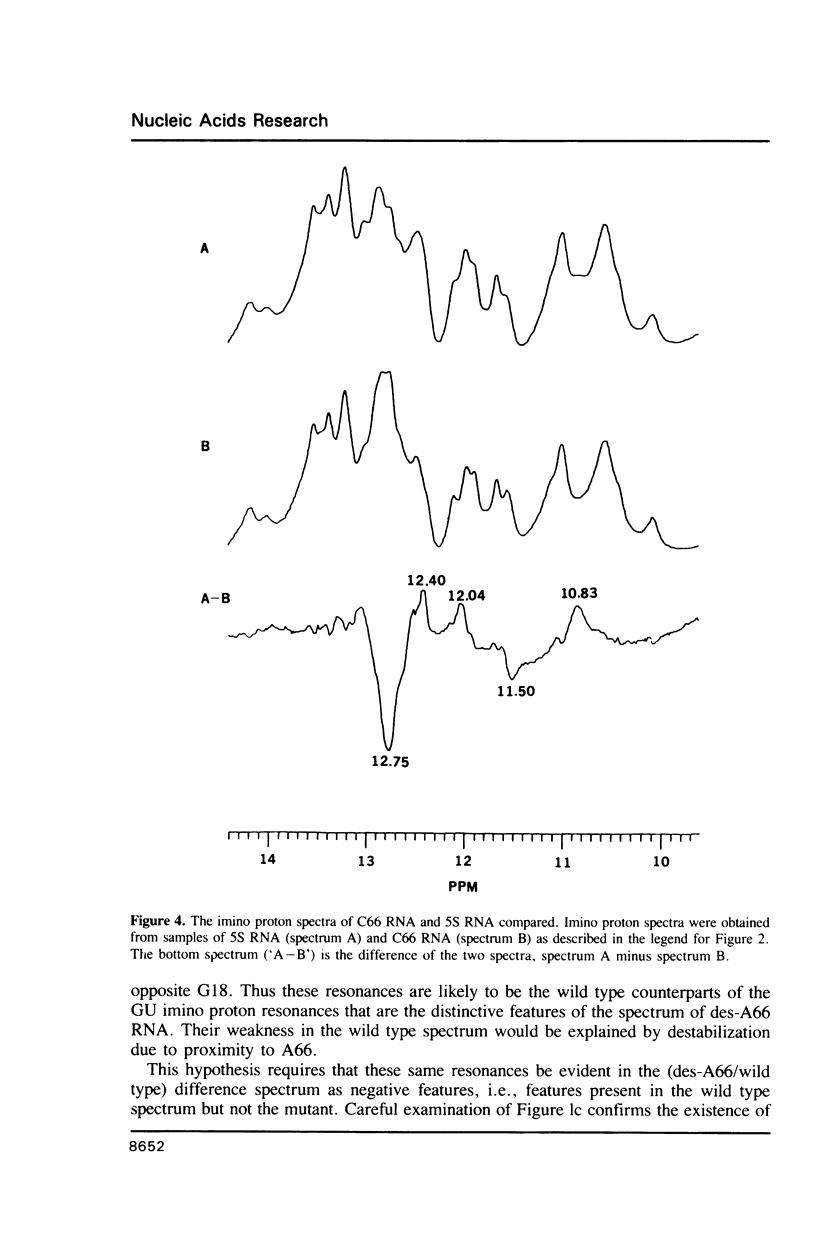
Two variants of the 5S RNA of E. coli have been examined by imino proton NMR spectroscopy, one of them a deletion of A66 (Christiansen, J., Douthwaite, S.R., Christensen, A. and Garrett, R.A. (1985) EMBO J. 4, 1019-1024) and the other a replacement of A66 with a C (Goringer, H.U. and Wagner, R. (1986) Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler 367, 769-780). Both are of interest because the role the bulged A in helix II of 5S RNA is supposed to play in interactions with ribosomal protein L18. The data show that the structural perturbations that result from these mutations are minimal, and assign the resonances of some of the imino protons around position 66. Some mutations at or near position 66 greatly reduce the L18-dependent increase in the circular dichroism of 5S RNA at 267 nm first observed by Bear and coworkers (Bear, D.G., Schleich, T., Noller, H.F. and Garrett, R.A. (1977) Nucl. Acids Res. 4, 2511-2526).
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bear D. G., Schleich T., Noller H. F., Garrett R. A. Alteration of 5S RNA conformation by ribosomal proteins L18 and L25. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jul;4(7):2511–2526. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.7.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J. Toxicity of an overproduced foreign gene product in Escherichia coli and its use in plasmid vectors for the selection of transcription terminators. Gene. 1984 Feb;27(2):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen J., Douthwaite S. R., Christensen A., Garrett R. A. Does unpaired adenosine-66 from helix II of Escherichia coli 5S RNA bind to protein L18? EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):1019–1024. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03733.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delihas N., Andersen J., Singhal R. P. Structure, function and evolution of 5-S ribosomal RNAs. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1984;31:161–190. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60377-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egebjerg J., Christiansen J., Brown R. S., Larsen N., Garrett R. A. Protein L18 binds primarily at the junctions of helix II and internal loops A and B in Escherichia coli 5 S RNA. Implications for 5 S RNA structure. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):651–668. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90573-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewirth D. T., Moore P. B. Effects of mutation on the downfield proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of the 5S RNA of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 8;26(18):5657–5665. doi: 10.1021/bi00392a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewirth D. T., Moore P. B. Exploration of the L18 binding site on 5S RNA by deletion mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10717–10732. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göringer H. U., Wagner R. Construction and functional analysis of ribosomal 5S RNA from Escherichia coli with single base changes in the ribosomal protein binding sites. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1986 Aug;367(8):769–780. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1986.367.2.769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann R. K., Vogel D. W., Walker R. T., Erdmann V. A. In vitro incorporation of eubacterial, archaebacterial and eukaryotic 5S rRNAs into large ribosomal subunits of Bacillus stearothermophilus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3511–3524. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kime M. J., Moore P. B. Nuclear Overhauser experiments at 500 MHz on the downfield proton spectrum of a ribonuclease-resistant fragment of 5S ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1983 May 24;22(11):2615–2622. doi: 10.1021/bi00280a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kime M. J., Moore P. B. Physical evidence for a domain structure in Escherichia coli 5 S RNA. FEBS Lett. 1983 Mar 7;153(1):199–203. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80147-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J., Kimura M. The complete amino acid sequences of the 5 S rRNA binding proteins L5 and L18 from the moderate thermophile Bacillus stearothermophilus ribosome. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 1;210(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81303-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leontis N. B., Moore P. B. NMR evidence for dynamic secondary structure in helices II and III of the RNA of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 1;25(13):3916–3925. doi: 10.1021/bi00361a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. J., Wu J. J., Marshall A. G. 500-MHz proton homonuclear Overhauser evidence for additional base pair in the common arm of eukaryotic ribosomal 5S RNA: wheat germ. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 24;26(6):1578–1585. doi: 10.1021/bi00380a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier N., Göringer H. U., Kleuvers B., Scheibe U., Eberle J., Szymkowiak C., Zacharias M., Wagner R. The importance of individual nucleotides for the structure and function of rRNA molecules in E. coli. A mutagenesis study. FEBS Lett. 1986 Aug 11;204(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81392-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Kozlowski S. A., Marky L. A., Rice J. A., Broka C., Itakura K., Breslauer K. J. Extra adenosine stacks into the self-complementary d(CGCAGAATTCGCG) duplex in solution. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 2;21(3):445–451. doi: 10.1021/bi00532a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A., Douthwaite S., Garrett R. A., Noller H. F. A "bulged" double helix in a RNA-protein contact site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7331–7335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang P., Moore P. B. An NMR study of the helix V-loop E region of the 5S RNA from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4607–4615. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


