Abstract
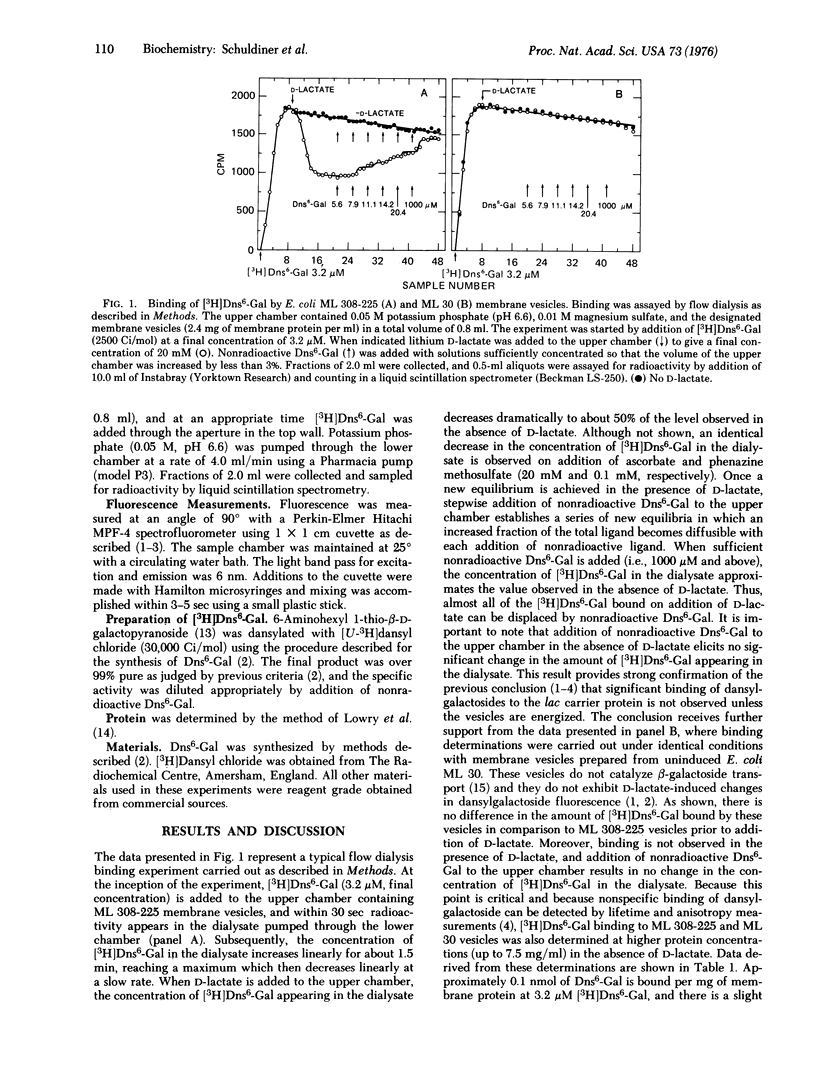
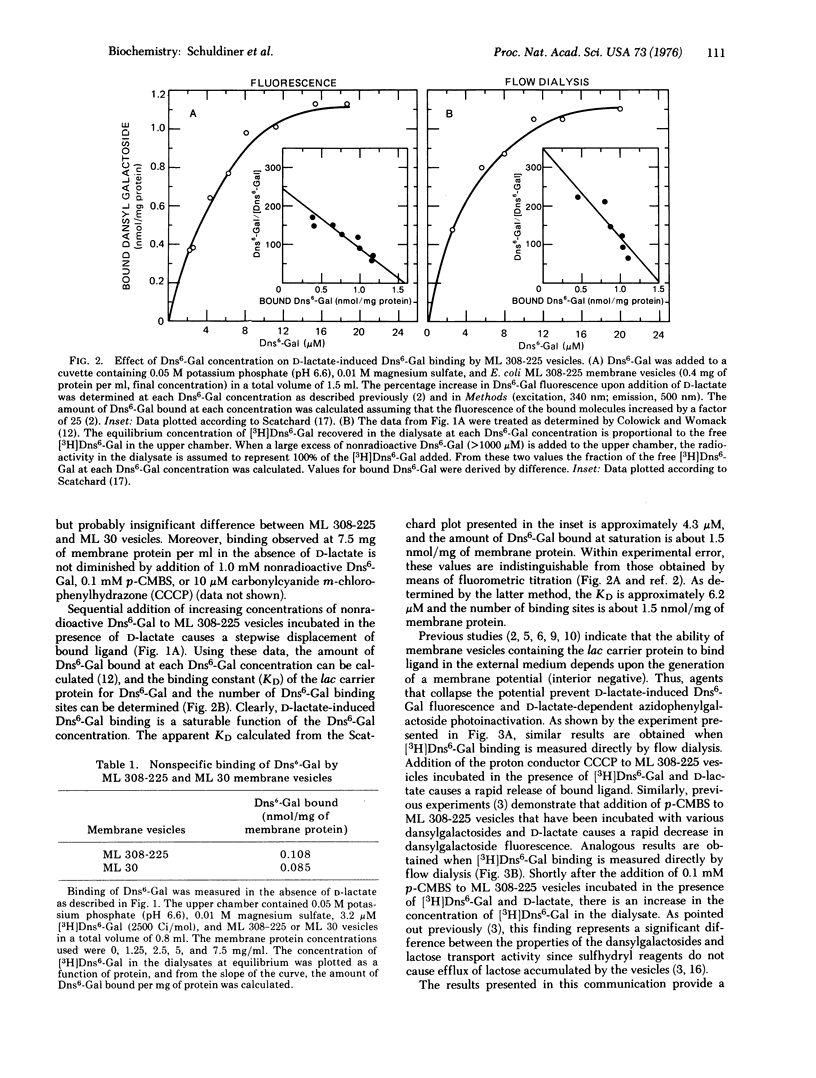
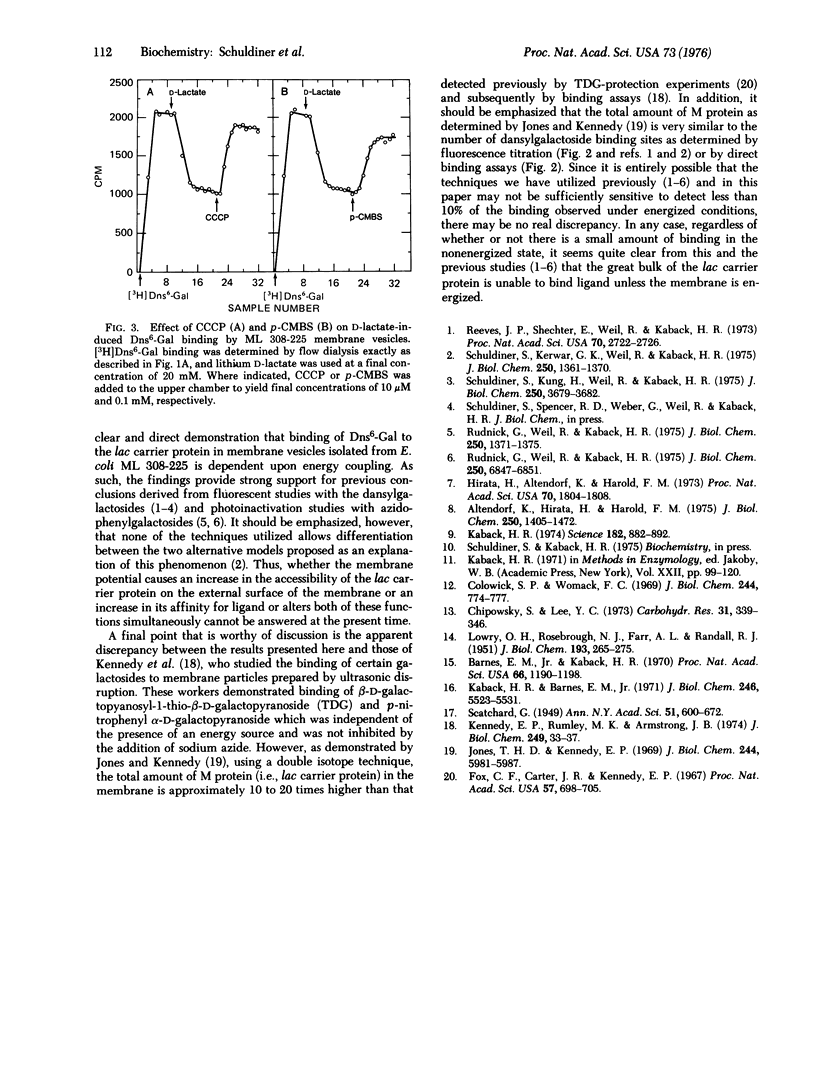
High specific activity 6'-N-[3H]dansyl)aminohexyl 1-thio-beta-D-galactopyranoside (Dns6-Gal) has been synthesized, and its binding to Escherichia coli membrane vesicles measured directly by flow dialysis. With ML 308-225 vesicles containing the lac carrier protein, specific binding is not detected in the absence of D-lactate or reduced phenazine methosulfate. In the presence of these electron donors, binding is observed, and the binding constant and number of binding sites are approximately 4 muM and 1.5 nmol/mg of membrane protein, respectively. These values are in excellent agreement with those obtained by fluorescence titration. p-Chloromercuribenzenesulfonate, which directly inactivates the lac carrier protein, and carbonylcyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone, which collapses the membrane potential, cause release of bound Dns6-Gal. Moreover, significant binding is not observed with membrane vesicles that are devoid of the lac carrier protein. The results provide qualitative and quantitative confirmation of previous studies which indicate that changes in dansylgalactoside fluorescence observed on "energization" of membrane vesicles reflect binding of the probe to the lac carrier protein.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altendorf K., Hirata H., Harold F. M. Accumulation of lipid-soluble ions and of rubidium as indicators of the electrical potential in membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1405–1412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes E. M., Jr, Kaback H. R. Beta-galactoside transport in bacterial membrane preparations: energy coupling via membrane-bounded D-lactic dehydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1190–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colowick S. P., Womack F. C. Binding of diffusible molecules by macromolecules: rapid measurement by rate of dialysis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 25;244(4):774–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. F., Carter J. R., Kennedy E. P. GENETIC CONTROL OF THE MEMBRANE PROTEIN COMPONENT OF THE LACTOSE TRANSPORT SYSTEM OF Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Mar;57(3):698–705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.3.698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata H., Altendorf K., Harold F. M. Role of an electrical potential in the coupling of metabolic energy to active transport by membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1804–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. H., Kennedy E. P. Characterization of the membrane protein component of the lactose transport system of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 10;244(21):5981–5987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R., Barnes E. M., Jr Mechanisms of active transport in isolated membrane vesicles. II. The mechanism of energy coupling between D-lactic dehydrogenase and beta-galactoside transport in membrane preparations from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 10;246(17):5523–5531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Transport studies in bacterial membrane vesicles. Science. 1974 Dec 6;186(4167):882–892. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4167.882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy E. P., Rumley M. K., Armstrong J. B. Dierect measurement of the binding of labeled sugars to the lactose permease M protein. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):33–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves J. P., Shechter E., Weil R., Kaback H. R. Dansyl-galactoside, a fluorescent probe of active transport in bacterial membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2722–2726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudnick G., Kaback H. R. Photoinactivation of the beta-galactoside transport system in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles with an impermeant azidophenylgalactoside. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6847–6851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudnick G., Kaback H. R., Weil R. Photoinactivation of the beta-galactoside transport system in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles with 2-nitro-4-azidophenyl-1-thio-beta-D-galactopyranoside. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1371–1375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuldiner S., Kerwar G. K., Kaback H. R., Weil R. Energy-dependent binding of dansylgalactosides to the beta-galactoside carrier protein. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1361–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuldiner S., Kung H., Kaback H. R., Weil R. Differentiation between binding and transport of dansylgalactosides in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):3679–3682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


