Abstract
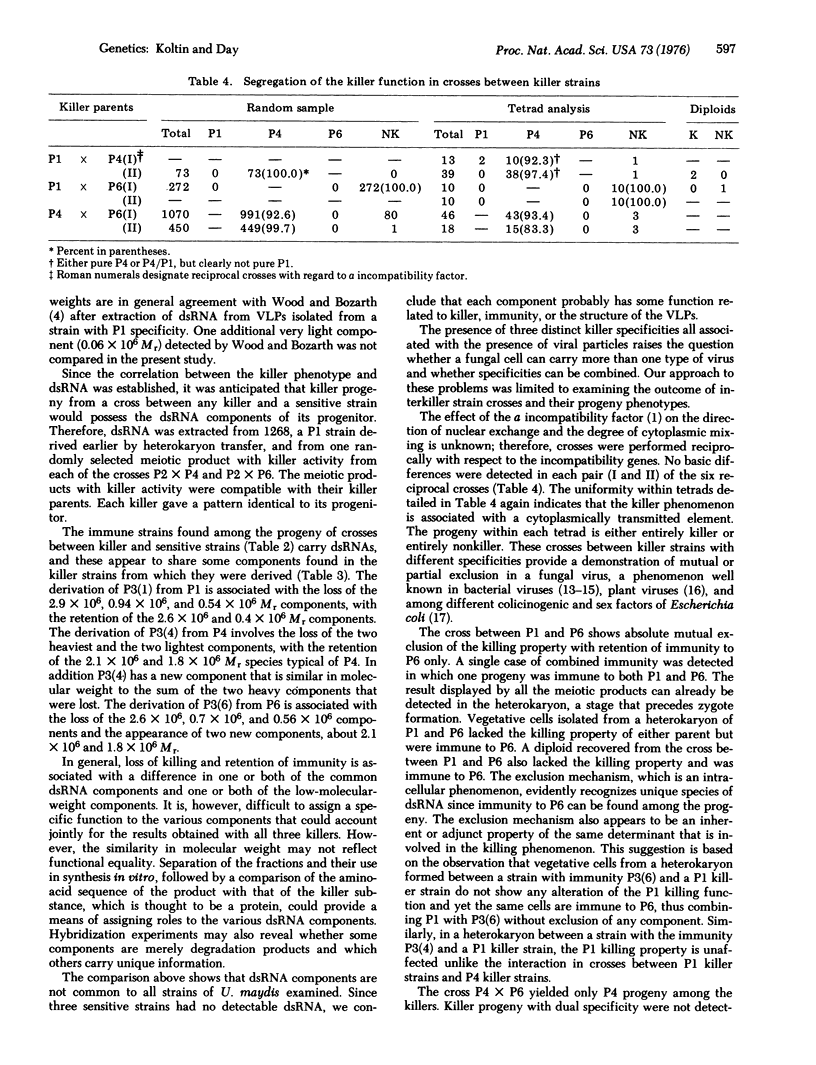
Three different killer specificities in U. maydis are inherited cytoplasmically and transmitted by cell fusion. Each killer generates low frequencies of specifically immune forms in crosses with sensitive strains. The properties of immunity to each killer are also inherited cytoplasmically and transmitted by cell fusion. Killer strains carry virus-like particles about 41 nm in diameter. Each killer possesses distinct double-stranded RNA components that range in molecular weight from 0.46 X 10(6) to 2.9 X 10(6). Two components are shared by all three killers. Immune strains possess new forms. Crosses and heterokaryons between different killers revealed unilateral or mutual restrictions that prevent inclusion of two killer specificities in the same cell.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bevan E. A., Herring A. J., Mitchell D. J. Preliminary characterization of two species of dsRNA in yeast and their relationship to the "killer" character. Nature. 1973 Sep 14;245(5420):81–86. doi: 10.1038/245081b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delbrück M. Interference Between Bacterial Viruses: III. The Mutual Exclusion Effect and the Depressor Effect. J Bacteriol. 1945 Aug;50(2):151–170. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii-Kawata I., Miura K. I. Segments of genome of viruses containing double-stranded ribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 28;51(2):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90140-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemke P. A., Nash C. H. Fungal viruses. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):29–56. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.29-56.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puhalla J. E. Compatibility reactions on solid medium and interstrain inhibition in Ustilago maydis. Genetics. 1968 Nov;60(3):461–474. doi: 10.1093/genetics/60.3.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. L., Huskey R. J. Partial exclusion between T-even bacteriophages: an incipient genetic isolation mechanism. Genetics. 1974 Dec;78(4):989–1014. doi: 10.1093/genetics/78.4.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., Sipe J. D., Loh P. Separation of ten reovirus genome segments by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):986–991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.986-991.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somers J. M., Bevan E. A. The inheritance of the killer character in yeast. Genet Res. 1969 Feb;13(1):71–83. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300002743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streisinger G., Weigle J. PROPERTIES OF BACTERIOPHAGES T2 AND T4 WITH UNUSUAL INHERITANCE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Aug;42(8):504–510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.8.504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]