Abstract
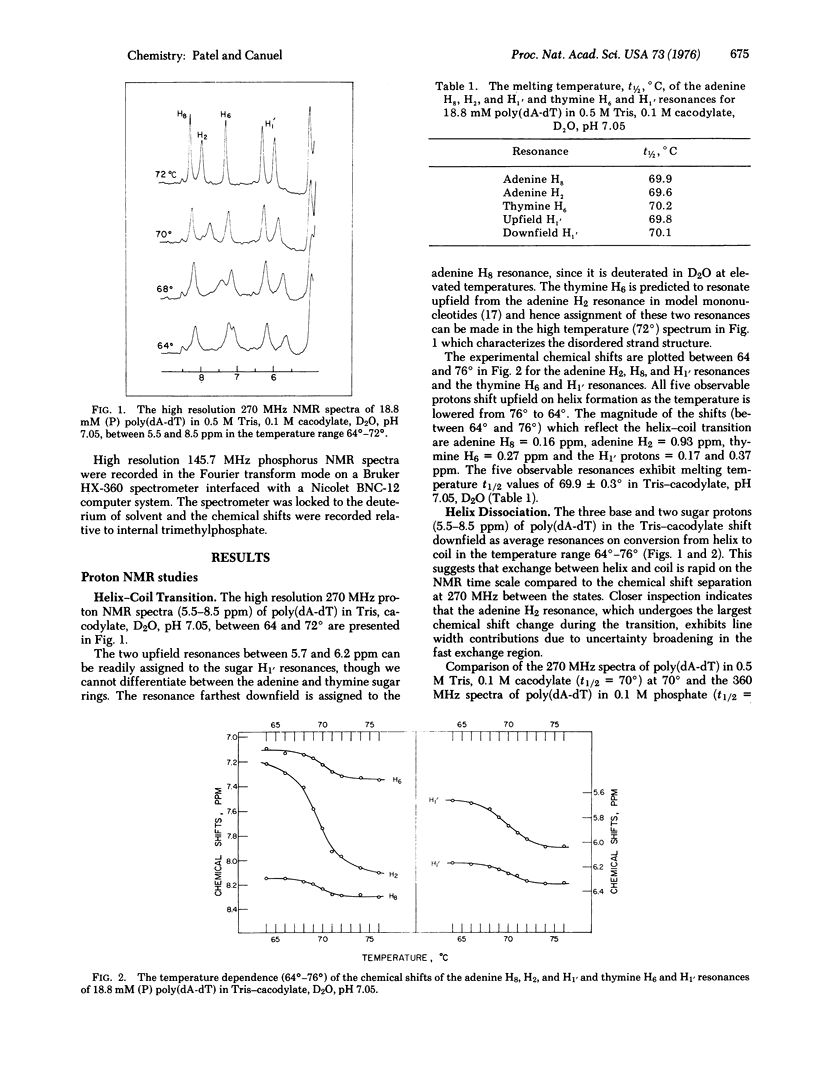
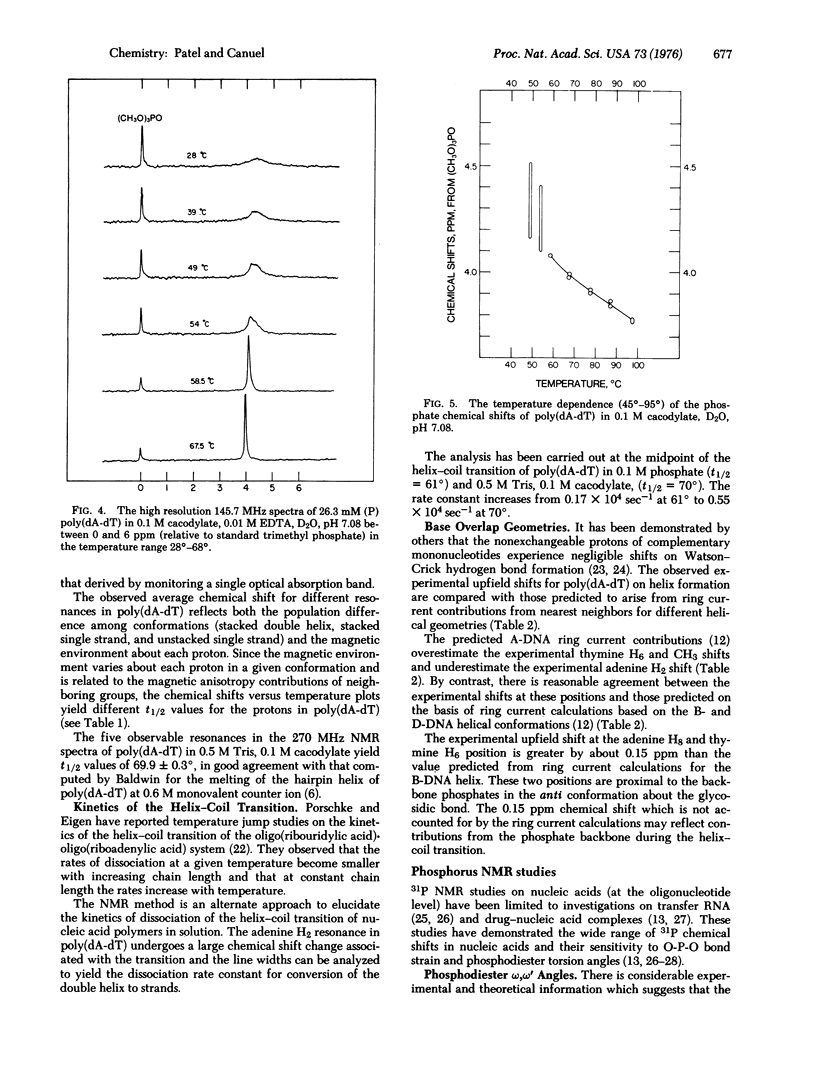
The well-resolved base and sugar proton resonances in the high resolution proton nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra of poly(dA-dT) can be monitored during the helix-coil transition. The observable resonances shift upfield on helix formation and the temperature-dependent chemical shifts exhibit a melting temperature t 1/2 = 69.9 +/- 0.3 degrees for 18.8 mM (with respect to phosphorus) poly(dA-dT) in 0.5 M Tris, 0.1 M cacodylate, D2O, pH 7.05. The observable protons are in fast exchange throughout the poly (dA-dT) helix-coil transition. The adenine H2 resonance that shifts upfield by about 1 ppm on helix formation exhibits uncertainty broadening in the fast exchange region...
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Hukins D. W., Smith P. J., Watts L. Structural details of double-helix observed for DNAs containing alternating purine and pyrimidine sequences. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):523–533. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90499-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arter D. B., Walker G. C., Uhlenbeck O. C., Schmidt P. G. PMR or the self-complementary oligoribonucleotide CpCpGpG. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 23;61(4):1089–1094. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80395-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borer P. N., Kan L. S., Ts'o P. O. Conformation and interaction of short nucleic acid double-stranded helices. I. Proton magnetic resonance studies on the nonexchangeable protons of ribosyl ApApGpCpUpU. Biochemistry. 1975 Nov 4;14(22):4847–4863. doi: 10.1021/bi00693a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calascibetta F. G., Dentini M., de Santis P., Morosetti S. Conformational analysis of polynucleotide chains. Double-stranded structures. Biopolymers. 1975 Aug;14(8):1667–1684. doi: 10.1002/bip.1975.360140810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. D., Crothers D. M. A proton magnetic resonance study of single-stranded and double-helical deoxyribooligonucleotides. Biochemistry. 1971 Oct 26;10(22):4015–4023. doi: 10.1021/bi00798a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES D. R., BALDWIN R. L. X-ray studies on two synthetic DNA copolymers. J Mol Biol. 1963 Apr;6:251–255. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giessner-Prettre C., Pullman B. Intermolecular nuclear shielding values for protons of purines and flavins. J Theor Biol. 1970 Apr;27(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(70)90130-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorenstein D. G., Kar D. 31-P chemical shifts in phosphate diester monoanions. Bond angle and torsional angle effects. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Aug 4;65(3):1073–1080. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80495-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenwedel D. W. Salt effects on the denaturation of DNA. IV. A calorimetric study of the helix-coil conversion of the alternating copolymer poly[d(A-T)]. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 7;395(3):246–257. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90195-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guéron M. 31P magnetic resonance of purified tRNA. FEBS Lett. 1971 Dec 15;19(3):264–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80529-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guéron M., Shulman R. G. 31P magnetic resonance of tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3482–3485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilbers C. W., Patel D. J. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance investigations of the nucleation and propagation reactions associated with the helix-coil transition of d-ApTpGpCpApT in H2O solution. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 17;14(12):2656–2660. doi: 10.1021/bi00683a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INMAN R. B., BALDWIN R. L. Helix-random coil transitions in synthetic DNAs of alternating sequence. J Mol Biol. 1962 Aug;5:172–184. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroon P. A., Kreishman G. P., Nelson J. H., Chan S. I. The effects of chain length on the secondary structure of oligoadenylates. Biopolymers. 1974 Dec;13(12):2571–2592. doi: 10.1002/bip.1974.360131214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Hilbers C. W. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance investigations of fraying in double-stranded d-ApTpGpCpApT in H2O solution. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 17;14(12):2651–2656. doi: 10.1021/bi00683a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J. Peptide antibiotic-oligonucleotide interactions. Nuclear magnetic resonance investigations of complex formation between actinomycin D and d-ApTpGpCpApT in aqueous solution. Biochemistry. 1974 May 21;13(11):2396–2402. doi: 10.1021/bi00708a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Tonelli A. E. Assignment of the proton Nmr chemical shifts of the T-N3H and G-N1H proton resonances in isolated AT and GC Watson-Crick base pairs in double-stranded deoxy oligonucleotides in aqueous solution. Biopolymers. 1974;13(10):1943–1964. doi: 10.1002/bip.1974.360131003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pörschke D., Eigen M. Co-operative non-enzymic base recognition. 3. Kinetics of the helix-coil transition of the oligoribouridylic--oligoriboadenylic acid system and of oligoriboadenylic acid alone at acidic pH. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 14;62(2):361–381. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90433-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raszka M., Kaplan N. O. Association by hydrogen bonding of mononucleotides in aqueous solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2025–2029. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffler I. E., Elson E. L., Baldwin R. L. Helix formation by d(TA) oligomers. II. Analysis of the helix-coli transitions of linear and circular oligomers. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 28;48(1):145–171. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90225-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffler I. E., Elson E. L., Baldwin R. L. Helix formation by dAT oligomers. I. Hairpin and straight-chain helices. J Mol Biol. 1968 Sep 28;36(3):291–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90156-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffler I. E., Sturtevant J. M. Thermodynamics of the helix-coil transition of the alternating copolymer of deoxyadenylic acid and deoxythymidylic acid. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jun 28;42(3):577–580. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90244-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoup R. R., Miles H. T., Becker E. D. NMR evidence of specific base-pairing between purines and pyrimidines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Apr 19;23(2):194–201. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90527-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman R. G., Hilbers C. W., Wong Y. P., Wong K. L., Lightfoot D. R., Reid B. R., Kearns D. R. Determination of secondary and tertiary structural features of transfer RNA molecules in solution by nuclear magnetic resonance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2042–2045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari R., Nanda R. K., Govil G. Spatial configuration of single-stranded polynucleotides. Calculations of average dimensions and Nmr coupling constants. Biopolymers. 1974;13(10):2015–2035. doi: 10.1002/bip.1974.360131007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yathindra N., Sundaralingam M. Backbone conformations in secondary and tertiary structural units of nucleic acids. Constraint in the phosphodiester conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3325–3328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


