Abstract
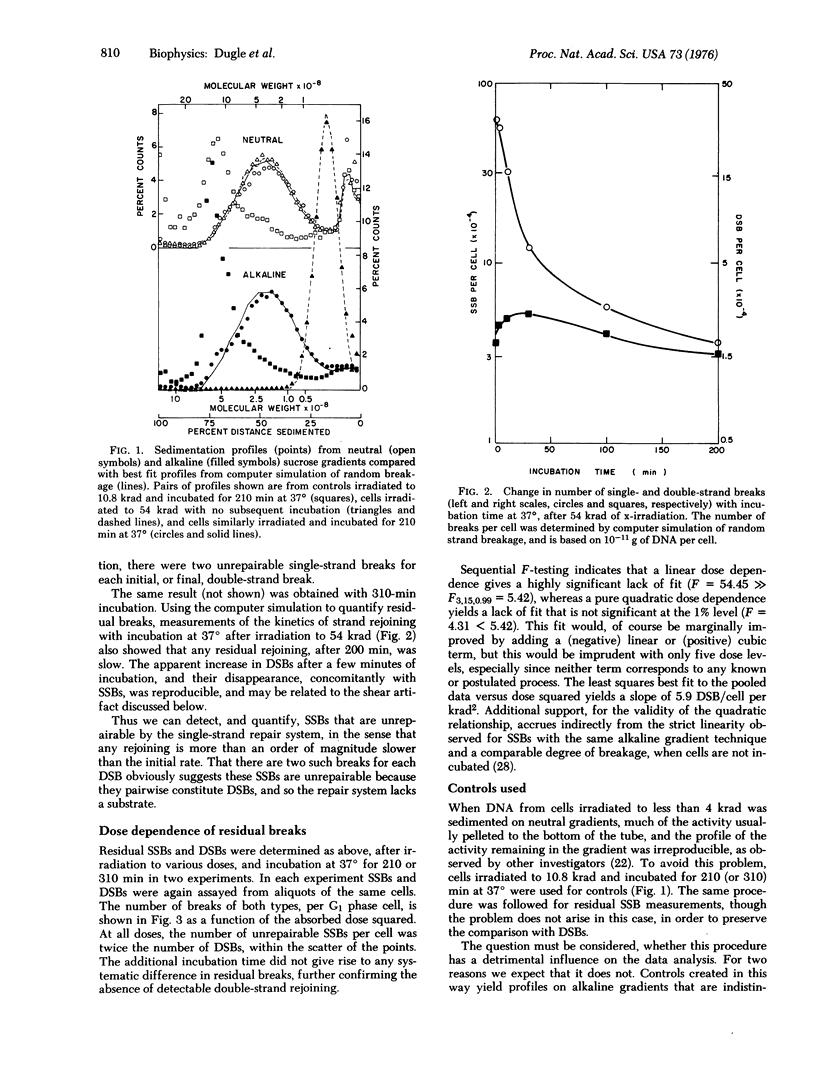
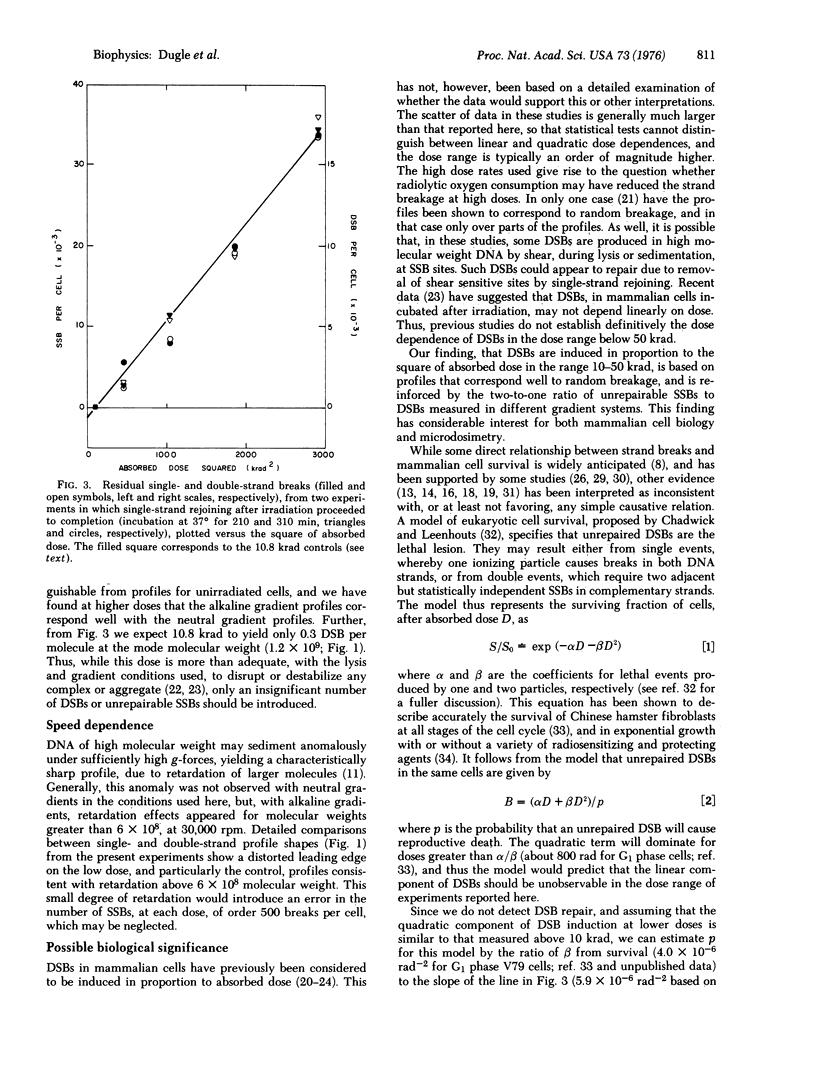
The yields of unrepairable single-and double-strand breaks in the DNA of x-irradiated Chinese hamster cells were measured by low-speed neutral and alkaline sucrose density gradient sedimentation in order to investigate the relation between these lesions and reproductive death. After maximal single-strand remoining, at all doses, the number of residual single-strand breaks was twice the number of residual double-strand breaks. Both double-strand and unrepairable single-strand breaks were proportional to the square of absorbed dose, in the range 10-50 krad. No rejoining of double-strand breaks was observed. These observations suggest that, in mammalian cells, most double-strand breaks are not repairable, while all single-strand breaks are repaired except those that are sufficiently close on complementary strands to constitute double-strand breaks. Comparison with cell survival measurements at much lower doses suggests that loss of reproductive capacity corresponds to induction of approximately one double-strand break.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chadwick K. H., Leenhouts H. P. A molecular theory of cell survival. Phys Med Biol. 1973 Jan;18(1):78–87. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/18/1/007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman J. D., Todd P., Sturrock J. X-ray survival of cultured Chinese hamster cells resuming growth after plateau phase. Radiat Res. 1970 Jun;42(3):590–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coquerelle T., Bopp A., Kessler B., Hagen U. Strand breaks and K' end-groups in DNA of irradiated thymocytes. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1973 Oct;24(4):397–404. doi: 10.1080/09553007314551251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corry P. M., Cole A. Double strand rejoining in mammalian DNA. Nat New Biol. 1973 Sep 26;245(143):100–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corry P. M., Cole A. Radiation-induced double-strand scission of the DNA of mammalian metaphase chromosomes. Radiat Res. 1968 Dec;36(3):528–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donlon T., Norman A. Kinetics of rejoining of single-strand breaks induced by ionizing radiation in DNA of human lymphocytes. Mutat Res. 1971 Oct;13(2):97–107. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(71)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkind M. M., Chang-Liu C. M. Repair of a DNA complex from x-irradiated Chinese hamster cells. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1972 Jul;22(1):75–90. doi: 10.1080/09553007214550801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkind M. M., Kamper C. Two forms of repair of DNA in mammalian cells following irradiation. Biophys J. 1970 Mar;10(3):237–245. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86296-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkind M. M. Sedimentation of DNA released from Chinese hamster cells. Biophys J. 1971 Jun;11(6):502–520. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(71)86231-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox W., Fox M. DNA single-strand rejoining in two pairs of cell-lines showing the same and different sensitivities to x-rays. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1973 Aug;24(2):127–135. doi: 10.1080/09553007314550921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie C. J., Gislason G. S., Dugle D. L., Chapman J. D. Random break analysis of DNA sedimentation profiles. Radiat Res. 1972 Aug;51(2):272–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikawa M., Fukuhara M., Suzuki F., Nikaido O., Sugahara T. Comparative studies on induction and rejoining of DNA single-strand breaks by radiation and chemical carcinogen in mammalian cells in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Feb;70(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90146-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikawa M., Nikaido O., Tanaka T., Nagata H., Sugahara T. Comparative studies on rejoining of DNA-strand breaks induced by x-irradiation in mammalian cell lines in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Dec;63(2):325–332. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey R. M., Steward D. L., Sedita B. A. DNA-strand breaks and rejoining following exposure of synchronized Chinese hamster cells to ionizing radiations. Mutat Res. 1968 Nov-Dec;6(3):459–465. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(68)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellerer A. M., Rossi H. H. RBE and the primary mechanism of radiation action. Radiat Res. 1971 Jul;47(1):15–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn K. W., Grimek-Ewig R. A. Alkaline elution analysis, a new approach to the study of DNA single-strand interruptions in cells. Cancer Res. 1973 Aug;33(8):1849–1853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. C., Bennett L. R., Byfield J. E. Inhibition of repair of DNA single strand breaks in mouse leukemia cells by actinomycin D. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 1;49(3):758–765. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90476-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann A. R., Ormerod M. G. Double-strand breaks in the DNA of a mammalian cell after x-irradiation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Oct 15;217(2):268–277. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90526-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lett J. T., Caldwell I., Dean C. J., Alexander P. Rejoining of x-ray induced breaks in the DNA of leukaemia cells. Nature. 1967 May 20;214(5090):790–792. doi: 10.1038/214790a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lett J. T., Sun C. The production of strand breaks in mammalian DNA by X-rays: at different stages in the cell cycle. Radiat Res. 1970 Dec;44(3):771–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohman P. H. Induction and rejoining of breaks in the deoxyribonucleic acid of human cells irradiated at various phases of the cell cycle. Mutat Res. 1968 Nov-Dec;6(3):449–458. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(68)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira H., Nakagawa C., Bannai S. Rejoining of x-ray-induced breaks in the DNA of Ehrlich ascites-tumour cells in vitro. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1969;15(6):575–581. doi: 10.1080/09553006914550881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira H., Nakagawa C., Hishizawa T. Rejoining of X-ray induced breaks in the DNA of Ehrlich ascites tumour cells in vivo. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1969 Feb 20;15(1):95–100. doi: 10.1080/09553006914550181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss A. J., Jr, Dalrymple G. V., Sanders J. L., Wilkinson K. P., Nash J. C. Dinitrophenol inhibits the rejoining of radiation-induced DNA breaks by L-cells. Biophys J. 1971 Feb;11(2):158–174. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(71)86205-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono T., Okada S. Estimation in vivo of DNA strand breaks and their rejoining in thymus and liver of mouse. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1974 Mar;25(3):291–301. doi: 10.1080/09553007414550341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormerod M. G., Stevens U. The rejoining of x-ray-induced strand breaks in the DNA of a murine lymphoma cell (L5178Y). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 25;232(1):72–82. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90492-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A. R., Fox B. W. Toxicity of tritiated thymidine in P388F lymphoma cells. II. Effects of DNA molecular weight. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1971;19(3):237–246. doi: 10.1080/09553007114550341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada S., Okada S. Rejoining of single-strand breaks of DNA in cultured mammalian cells. Radiat Res. 1970 Jan;41(1):145–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuboi A., Terasima T. Rejoining of single breaks of DNA induced by x-rays in mammalian cells: effects of metabolic inhibitors. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;108(2):117–128. doi: 10.1007/BF02430518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veatch W., Okada S. Radiation-induced breaks of DNA in cultured mammalian cells. Biophys J. 1969 Mar;9(3):330–346. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86390-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


