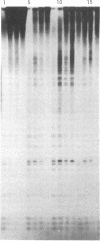
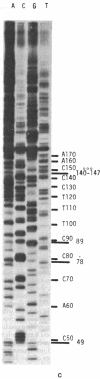
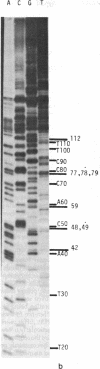
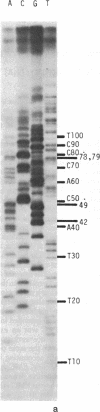
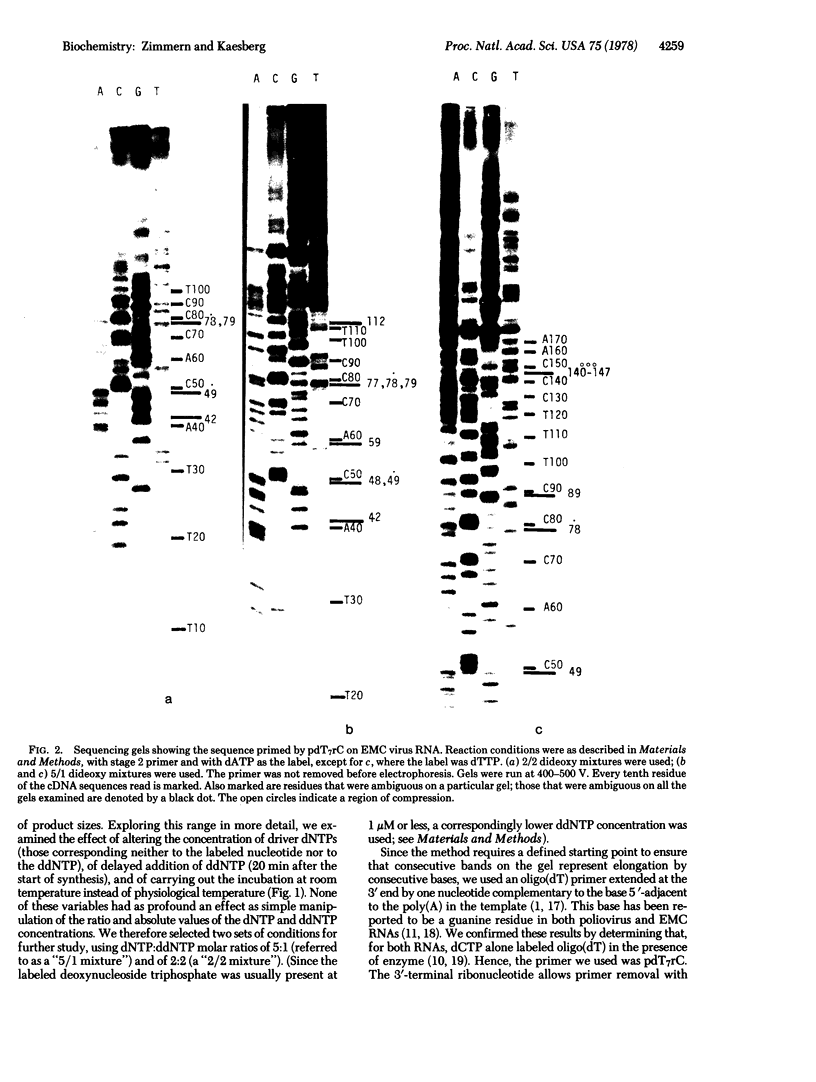
Abstract
We have adapted the chain-termination method for determining the nucleotide sequence of DNA of Sanger, Nicklen, and Coulson [(1977) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74, 5463--5467] for use with reverse transcriptase (RNA-directed DNA nucleotidyltransferase) on RNA templates. With this method and using a primer (the octanucleotide pdT7rC) directed at the 3'-terminal poly(A), we have determined a sequence of 166 residues in the genomic RNA of the picornavirus encephalomyocarditis virus.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brownlee G. G., Cartwright E. M. Rapid gel sequencing of RNA by primed synthesis with reverse transcriptase. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul;114(1):93–117. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burness A. T. Ribonucleic acid content of encephalomyocarditis virus. J Gen Virol. 1970 Mar;6(3):373–380. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-6-3-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Kafatos F. C., Maniatis T. The primary structure of rabbit beta-globin mRNA as determined from cloned DNA. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):571–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L., Rueckert R. R. Infection of mouse fibroblasts by cardioviruses: premature uncoating and its prevention by elevated pH and magnesium chloride. Virology. 1971 Jan;43(1):152–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Rous sarcoma virus genome is terminally redundant: the 5' sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):989–993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merregaert J., van Emmelo J., Devos R., Porter A., Fellner P., Fiers W. The 3'-Terminal nucleotide sequence of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jan 2;82(1):55–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb11996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Molecular weight estimation and separation of ribonucleic acid by electrophoresis in agarose-acrylamide composite gels. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):668–674. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J. Sequence analysis of the 3' non-coding regions of rabbit alpha- and beta-globin messenger RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov 15;107(4):491–525. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. E., Zamecnik P. C., Weith H. L. Rous sarcoma virus genome is terminally redundant: the 3' sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):994–998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H., Shine J., Martial J. A., Ullrich A., Baxter J. D., Goodman H. M. Nucleotide sequence of part of the gene for human chorionic somatomammotropin: purification of DNA complementary to predominant mRNA species. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90193-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoncsits A., Brownlee G. G., Brown R. S., Rubin J. R., Guilley H. New rapid gel sequencing method for RNA. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):833–836. doi: 10.1038/269833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smoler D., Molineux I., Baltimore D. Direction of polymerization by the avian myeloblastosis virus deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 25;246(24):7697–7700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Garfin D. E., Levinson W. E., Bishop J. M., Goodman H. M. Tumor virus ribonucleic acid directed deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis: nucleotide sequence at the 5' terminus of nascent deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 16;13(15):3159–3163. doi: 10.1021/bi00712a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Polyadenylic acid at the 3'-terminus of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1877–1882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]