Abstract
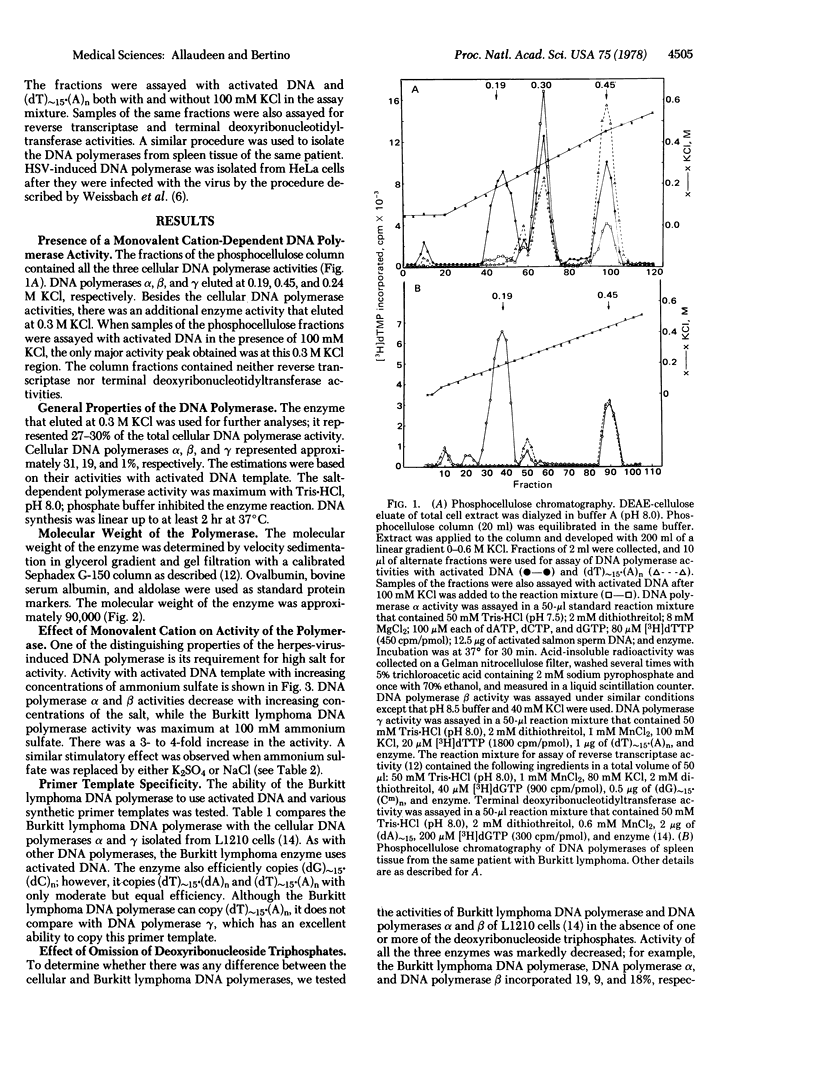
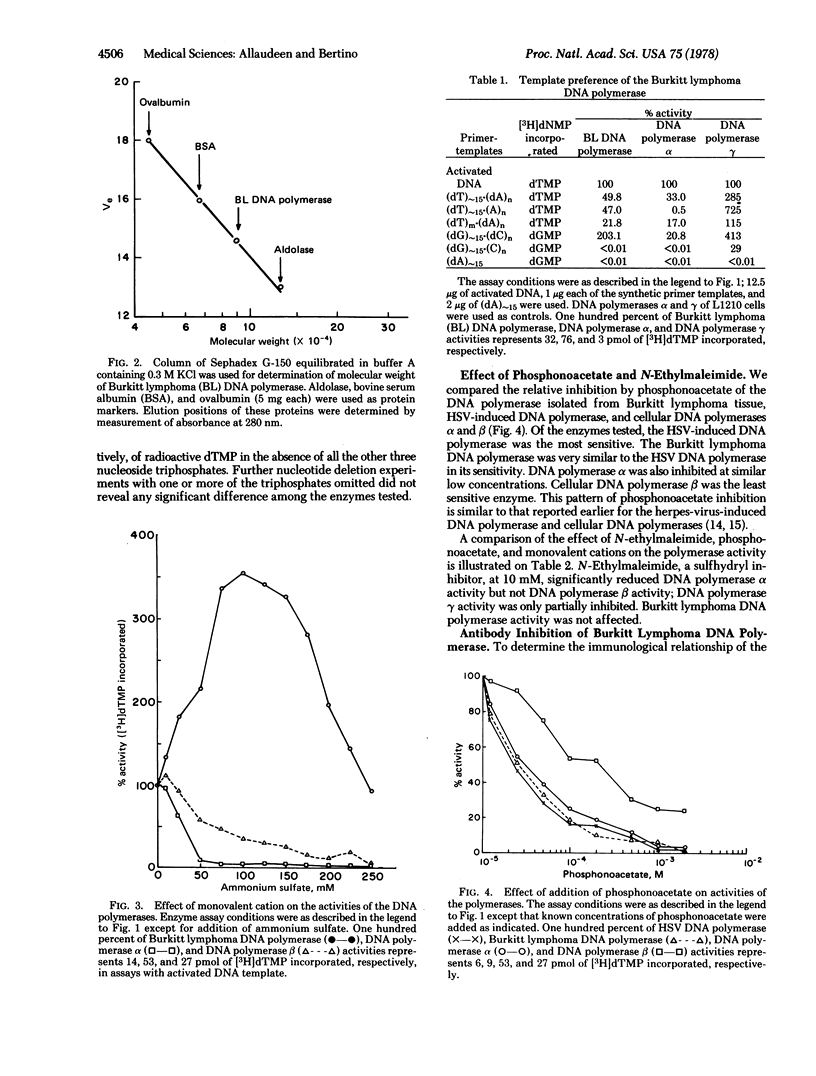
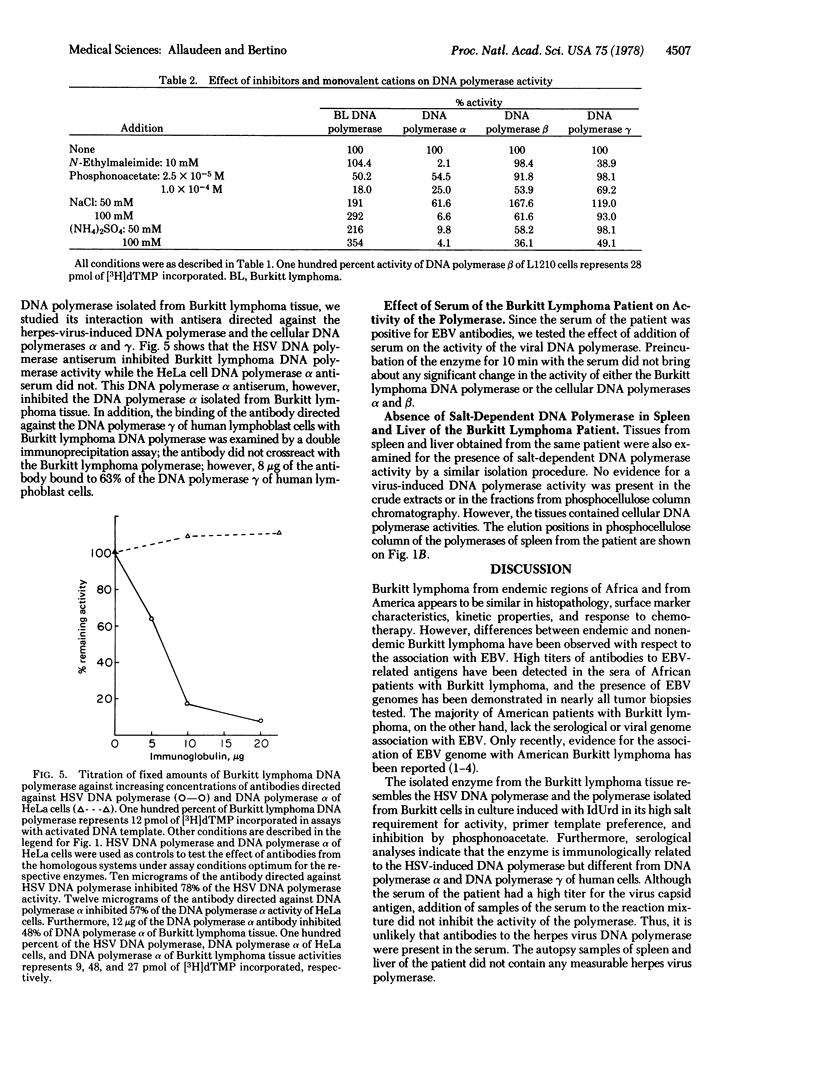
A DNA polymerase (DNA nucleotidyltransferase) has been partially purified from a neck mass of an American patient with Burkitt lymphoma and separated from the cellular DNA polymerases. The molecular weight of the enzyme was approximately 90,000. The enzyme differs from the cellular DNA polymerases, but resembles herpes-virus-induced DNA polymerase in its primer template preference, high monovalent cation requirement for activity, and sensitivity to phosphonoacetate. Enzyme activity was inhibited specifically by an antibody directed against herpes-simplex-virus-induced DNA polymerase but not by antibodies directed against DNA polymerase alpha of HeLa cells and DNA polymerase gamma of a normal human lymphoblast cell line, NC37. Although serum of the patient with Burkitt lymphoma contained high Epstein-Barr virus titer, addition of the serum to the assay mixture did not have any effect on the activity of Burkitt lymphoma DNA polymerase. Tissues from spleen and liver of the patient with Burkitt lymphoma did not contain the herpes-virus-induced DNA polymerase. Detection of the herpes virus polymerase in the Burkitt lymphoma tissue provides additional evidence for the association of Epstein-Barr virus with this malignancy.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allaudeen H. S., Bertino J. R. Presence of type C particles containing reverse transcriptase in L1210 leukemia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Jul;59(1):227–235. doi: 10.1093/jnci/59.1.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson M., Klein G., Zeigler J. L., Henle W. Association of Epstein-Barr viral genomes with American Burkitt lymphoma. Nature. 1976 Mar 25;260(5549):357–359. doi: 10.1038/260357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolden A., Aucker J., Weissbach A. Synthesis of herpes simplex virus, vaccinia virus, and adenovirus DNA in isolated HeLa cell nuclei. I. Effect of viral-specific antisera and phosphonoacetic acid. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1584–1592. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1584-1592.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadman E. C., Lunberg W. B., Bertino J. R. Hyperphosphatermia and hypocalcemia accompanying rapid cell lysis in a patient with Burkitt's lymphoma and Burkitt cell leukemia. Am J Med. 1977 Feb;62(2):283–290. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90324-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jofre J. T., Schaffer P. A., Parris D. S. Genetics of resistance to phosphonoacetic acid in strain KOS of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):833–836. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.833-836.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. F., Boezi J. A., Blakesley R. W., Koenig M., Towle H. C. Marek's disease herpesvirus-induced DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1974 Nov;14(5):1209–1219. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.5.1209-1219.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. L., Glaser R., Rapp F. Studies of an Epstein-Barr virus-induced DNA polymerase. Virology. 1977 Feb;76(2):494–502. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90232-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoyama M., Huang C. H., Pagano J. S., Klein G., Singh S. DNA of Epstein-Barr virus detected in tissue of Burkitt's lymphoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3265–3268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Purifoy D. J. Nonstructural proteins of herpes simplex virus. I. Purification of the induced DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):618–626. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.618-626.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G., Pope J. H., Walters M. K., Hilgers J., Singh S., Johansson B. Epstein-Barr virus-associated complement-fixing and nuclear antigens in Burkitt lymphoma biopsies. Int J Cancer. 1974 Jun 15;13(6):755–763. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910130604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert-Guroff M., Gallo R. C. Serological analysis of cellular and viral DNA polymerases by an antiserum to DNA polymerase gamma of human lymphoblasts. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 28;16(13):2874–2880. doi: 10.1021/bi00632a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman S., Kufe D., Hehlmann R., Peters W. P. Evidence for RNA tumor viruses in human lymphomas including Burkitt's disease. Cancer Res. 1973 Jun;33(6):1515–1526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach A. Eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:25–47. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach A., Hong S. C., Aucker J., Muller R. Characterization of herpes simplex virus-induced deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6270–6277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler J. L., AnderssonM, Klein G., Henle W. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in American Burkitt's lymphoma. Int J Cancer. 1976 Jun 15;17(6):701–706. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


