Abstract
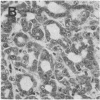
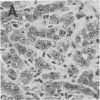
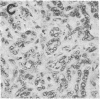
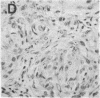
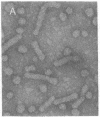
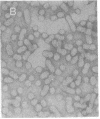
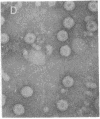
Particles with properties similar to those associated with human hepatitis B were found in serum from woodchucks with chronic hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. It is suggested that woodchuck hepatitis virus is a second member of a novel class of viruses represented by the human hepatitis B virus.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando T. A nuclease specific for heat-denatured DNA in isolated from a product of Aspergillus oryzae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 18;114(1):158–168. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Blumberg B. S., Werner B. Particles associated with Australia antigen in the sera of patients with leukaemia, Down's Syndrome and hepatitis. Nature. 1968 Jun 15;218(5146):1057–1059. doi: 10.1038/2181057a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B. S., Larouzé B., London W. T., Werner B., Hesser J. E., Millman I., Saimot G., Payet M. The relation of infection with the hepatitis B agent to primary hepatic carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 1975 Dec;81(3):669–682. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dane D. S., Cameron C. H., Briggs M. Virus-like particles in serum of patients with Australia-antigen-associated hepatitis. Lancet. 1970 Apr 4;1(7649):695–698. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90926-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDMONDSON H. A., STEINER P. E. Primary carcinoma of the liver: a study of 100 cases among 48,900 necropsies. Cancer. 1954 May;7(3):462–503. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195405)7:3<462::aid-cncr2820070308>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruska J. F., Clayton D. A., Rubenstein J. L., Robinson W. S. Structure of hepatitis B Dane particle DNA before and after the Dane particle DNA polymerase reaction. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):666–672. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.666-672.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. M., Greenman R. L., Gerin J. L., Purcell R. H., Robinson W. S. DNA polymerase associated with human hepatitis B antigen. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):995–1005. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.995-1005.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popper H. Clinical pathologic correlation in viral hepatitis. The effect of the virus on the liver. Am J Pathol. 1975 Dec;81(3):609–628. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. S., Clayton D. A., Greenman R. L. DNA of a human hepatitis B virus candidate. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):384–391. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.384-391.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder R. L., Ratcliffe H. L. Marmota monax: a model for studies of cardiovascular, cerebrovascular and neoplastic disease. Acta Zool Pathol Antverp. 1969 May;48:265–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., O'Connell A., Millman I. Genome of hepatitis B virus: restriction enzyme cleavage and structure of DNA extracted from Dane particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4597–4601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]