Abstract
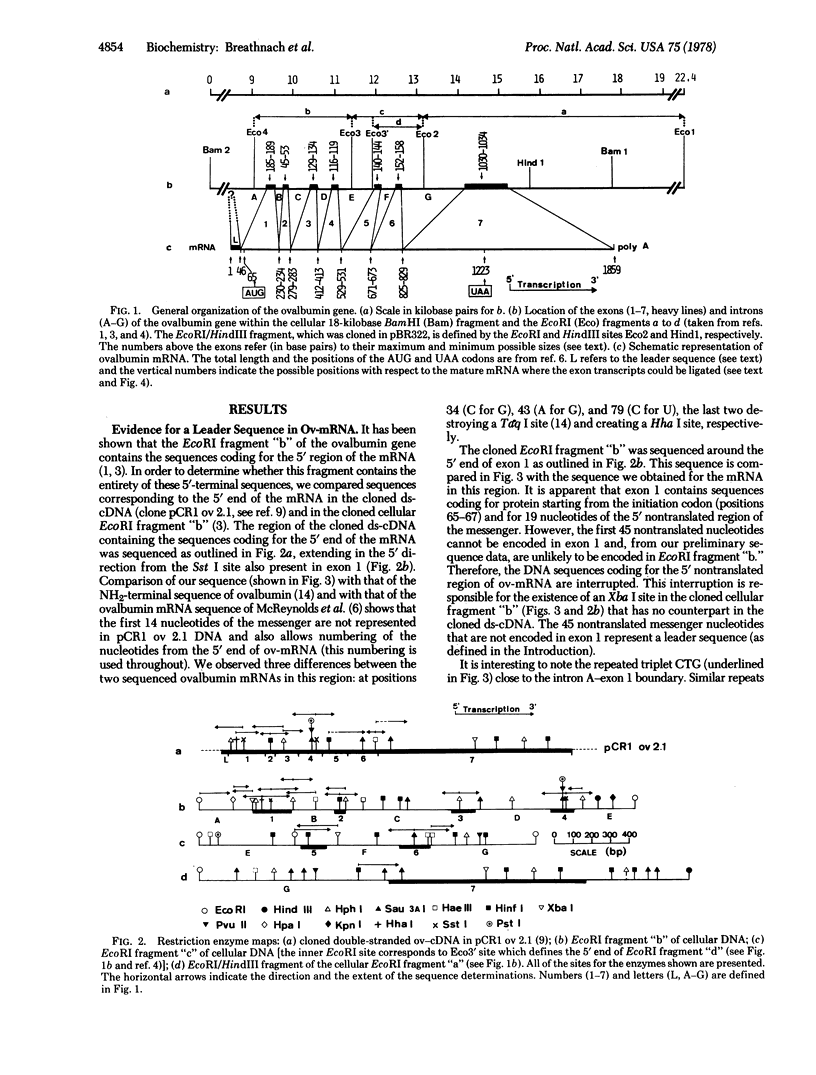
Selected regions of cloned EcoRI fragments of the chicken ovalbumin gene have been sequenced. The positions where the sequences coding for ovalbumin mRNA (ov-mRNA) are interrupted in the genome have been determined, and a previously unreported interruption in the DNA sequences coding for the 5' nontranslated region of the messenger has been discovered. Because directly repeated sequences are found at exon-intron boundaries, the nucleotide sequence alone cannot define unique excision-ligation points for the processing of a possible ov-mRNA precursor. However, the sequences in these boundary regions share common features; this leads to the proposal that there are, in fact, unique excision-ligation points common to all boundaries.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berget S. M., Moore C., Sharp P. A. Spliced segments at the 5' terminus of adenovirus 2 late mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3171–3175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Mandel J. L., Chambon P. Ovalbumin gene is split in chicken DNA. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):314–319. doi: 10.1038/270314a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calos M. P., Johnsrud L., Miller J. H. DNA sequence at the integration sites of the insertion element IS1. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):411–418. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90315-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Gelinas R. E., Broker T. R., Roberts R. J. An amazing sequence arrangement at the 5' ends of adenovirus 2 messenger RNA. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Vournakis J. N., Donis-Keller H., Chaconas G., Dougall D. K., Kafatos F. C. End labeling of enzymatically decapped mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Dec;4(12):4165–4174. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.12.4165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garapin A. C., Cami B., Roskam W., Kourilsky P., Le Pennec J. P., Perrin F., Gerlinger P., Cochet M., Chambon P. Electron microscopy and restriction enzyme mapping reveal additional intervening sequences in the chicken ovalbumin split gene. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):629–639. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90247-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garapin A. C., Lepennec J. P., Roskam W., Perrin F., Cami B., Krust A., Breathnach R., Chambon P., Kourilsky P. Isolation by molecular cloning of a fragment in the split ovalbumin gene. Nature. 1978 Jun 1;273(5661):349–354. doi: 10.1038/273349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman H. M., Olson M. V., Hall B. D. Nucleotide sequence of a mutant eukaryotic gene: the yeast tyrosine-inserting ochre suppressor SUP4-o. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5453–5457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindley N. D. IS1 insertion generates duplication of a nine base pair sequence at its target site. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):419–426. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90316-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hozumi N., Tonegawa S. Evidence for somatic rearrangement of immunoglobulin genes coding for variable and constant regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3628–3632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries P., Cochet M., Krust A., Gerlinger P., Kourilsky P., Chambon P. Molecular cloning of extensive sequences of the in vitro synthesized chicken ovalbumin structural gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jul;4(7):2389–2406. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.7.2389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F. Two adenovirus mRNAs have a common 5' terminal leader sequence encoded at least 10 kb upstream from their main coding regions. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):9–21. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90181-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. B., Anderson C. W., Atkins J. F. Further mapping of late adenovirus genes by cell-free translation of RNA selected by hybridization to specific DNA fragments. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90183-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel J. L., Breathnach R., Gerlinger P., Le Meur M., Gannon F., Chambon P. Organization of coding and intervening sequences in the chicken ovalbumin split gene. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):641–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90248-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Kee S. G., Efstratiadis A., Kafatos F. C. Amplification and characterization of a beta-globin gene synthesized in vitro. Cell. 1976 Jun;8(2):163–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McReynolds L., O'Malley B. W., Nisbet A. D., Fothergill J. E., Givol D., Fields S., Robertson M., Brownlee G. G. Sequence of chicken ovalbumin mRNA. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):723–728. doi: 10.1038/273723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Gagnon J., Walsh K. A. Ovalbumin: a secreted protein without a transient hydrophobic leader sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):94–98. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Forster A. Evidence for noncontiguous variable and constant region genes in both germ line and myeloma DNA. Cell. 1978 Feb;13(2):319–327. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Thimmappaya B., Dhar R., Subramanian K. N., Zain B. S., Pan J., Ghosh P. K., Celma M. L., Weissman S. M. The genome of simian virus 40. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):494–502. doi: 10.1126/science.205947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J. Adenovirus amazes at Cold Spring Harbor. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):101–104. doi: 10.1038/268101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilghman S. M., Curtis P. J., Tiemeier D. C., Leder P., Weissmann C. The intervening sequence of a mouse beta-globin gene is transcribed within the 15S beta-globin mRNA precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1309–1313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S., Maxam A. M., Tizard R., Bernard O., Gilbert W. Sequence of a mouse germ-line gene for a variable region of an immunoglobulin light chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1485–1489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela P., Venegas A., Weinberg F., Bishop R., Rutter W. J. Structure of yeast phenylalanine-tRNA genes: an intervening DNA segment within the region coding for the tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):190–194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



