Abstract
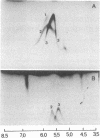
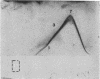
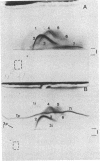
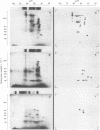
Highly purified Plasmodium knowlesi schizonts were used to produce a hyperimmune anti-parasite serum in a rhesus monkey. Proteins of membranes from normal and P. knowlesi-infected erythrocytes, as well as purified schizonts, were solubilized in 1% Triton X-100 and analyzed by bidimensional electrophoretic techniques. Of seven parasite-specific antigens identified in membranes of parasitized erythrocytes by crossed immune electrophoresis against monkey anti-parasite serum, only three could be detected in the purified schizonts. Bidimensional focusing-dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of membranes from parasitized cells revealed three proteins, in the 55,000-90,000 molecular weight region, with isoelectric points between pH 4.5 and pH 5.2, that could not be detected in normal membranes or purified schizonts. Membranes of normal erythrocytes and uninfected erythrocytes that had been incubated with sera from monkeys with 25-50% parasitemia did not react with the monkey anti-parasite serum.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown K. N., Brown I. N., Hills L. A. Immunity to malaria. I. Protection against Plasmodium knowlesi shown by monkeys sensitized with drug-suppressed infections or by dead parasites in Freund's adjuvant. Exp Parasitol. 1970 Oct;28(2):304–317. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(70)90101-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins W. E., Contacos P. G., Harrison A. J., Stanfill P. S., Skinner J. C. Attempts to immunize monkeys against Plasmodium knowlesi by using heat-stable, serum-soluble antigens. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 May;26(3):373–376. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilejian A., Abati A., Trager W. Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium coatneyi: immunogenicity of "knob-like protrusions" on infected erythrocyte membranes. Exp Parasitol. 1977 Jun;42(1):157–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(77)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McColm A. A., Shakespeare P. G., Trigg P. I. Release of protein by erythrocytic stages of Plasmodium knowlesi during cultivation in vitro. Bull World Health Organ. 1977;55(2-3):277–283. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell G. H., Butcher G. A., Langhorne J., Cohen S. A freeze-dried merozoite vaccine effective against Plasmodium knowlesi malaria. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 May;28(2):276–279. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Ullrich R., Thompson W. S., Lin P. S., Wallach D. F. Simian virus 40-specific proteins in the membranes of simian virus 40-transformed hamster and mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5069–5072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Ullrich R., Thompson W. S., Wallach D. F. Antigenic distinctions of glycoproteins in plasma and mitochondrial membranes of lymphoid cells neoplastically transformed by simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):643–647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Ullrich R., Wallach D. F., Davis F. D., 2nd Membranes of normal hamster lymphocytes and lymphoid cells neoplastically transformed by simian virus 40. II. Plasma membrane proteins analyzed by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and two-dimensional immune electrophoresis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Nov;57(5):1117–1126. doi: 10.1093/jnci/57.5.1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui W. A. An effective immunization of experimental monkeys against a human malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum. Science. 1977 Jul 22;197(4301):388–389. doi: 10.1126/science.406671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]