Abstract
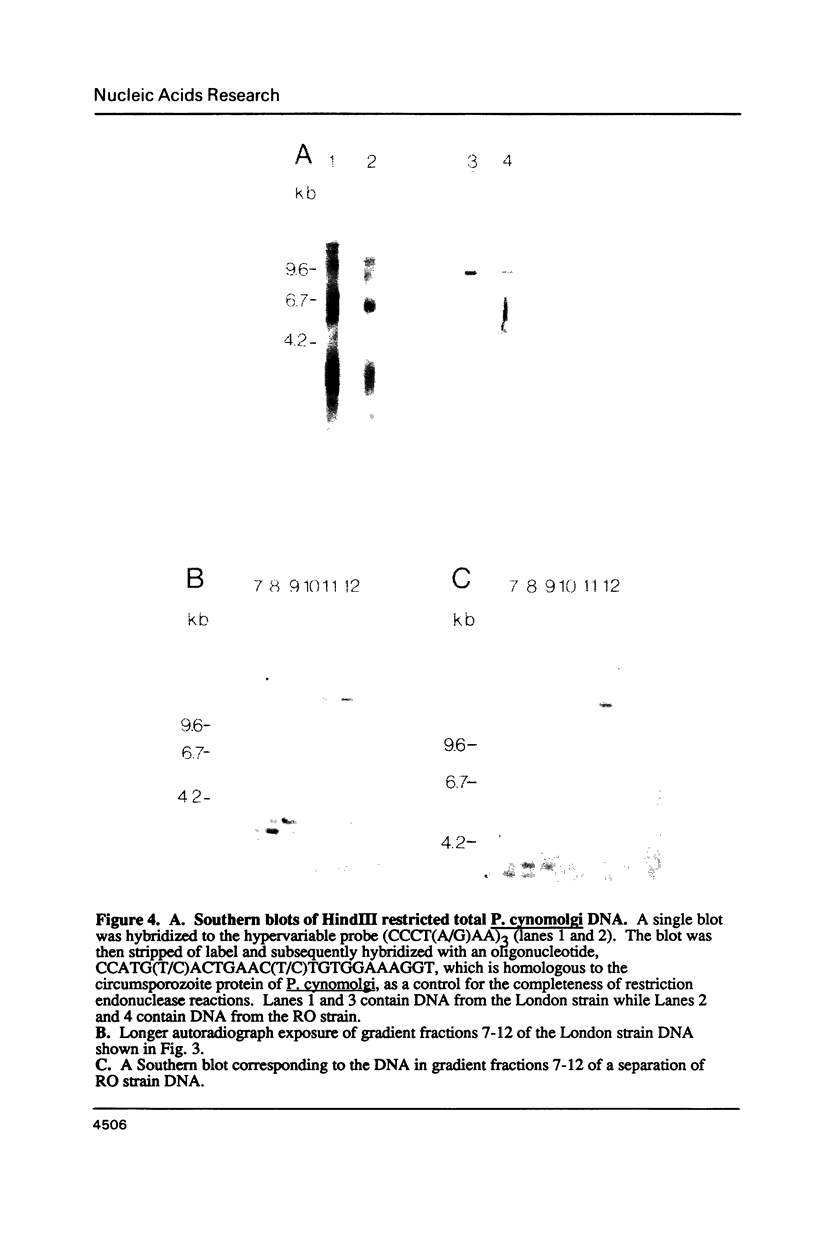
The genome of Plasmodium cynomolgi is partitioned into at least 7 distinct genetic domains. Each domain is apparently uniform in DNA density and is separable from the others by CsCl density centrifugation in the presence of Hoechst dye. The protein-encoding genes that were tested are localized in the two heaviest density domains (isochores). The ribosomal genes are in two lighter isochores as well as in one of the isochores that contains protein encoding genes. Telomeric sequences are mainly, if not exclusively, in the lightest isochores, indicating that position with regard to chromosome ends may correlate with density. Blocks of a tandemly-repeating sequence which mark genetically hypervariable chromosome regions in malaria parasites are located in all isochores. However, the rate of change associated with the blocks of sequence is much slower in some isochores than in others. This indicates that the rate of genetic change in these parasites may differ with isochore and chromosomal position. These results may also have more general biological implications since they suggest that the genetic instability often noted for tandem repeat sequences in the eukaryotic genome may be limited to only a distinct subset of the genomic complement of such sequence blocks.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernardi G., Olofsson B., Filipski J., Zerial M., Salinas J., Cuny G., Meunier-Rotival M., Rodier F. The mosaic genome of warm-blooded vertebrates. Science. 1985 May 24;228(4702):953–958. doi: 10.1126/science.4001930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. The molecular structure of centromeres and telomeres. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:163–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dame J. B., McCutchan T. F. Cloning and characterization of a ribosomal RNA gene from Plasmodium berghei. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1983 Jul;8(3):263–279. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(83)90048-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dame J. B., McCutchan T. F. The four ribosomal DNA units of the malaria parasite Plasmodium berghei. Identification, restriction map, and copy number analysis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6984–6990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dame J. B., Williams J. L., McCutchan T. F., Weber J. L., Wirtz R. A., Hockmeyer W. T., Maloy W. L., Haynes J. D., Schneider I., Roberts D. Structure of the gene encoding the immunodominant surface antigen on the sporozoite of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):593–599. doi: 10.1126/science.6204383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M. A., Holmquist G. P., Gray M. C., Caston L. A., Nag A. Replication timing of genes and middle repetitive sequences. Science. 1984 May 18;224(4650):686–692. doi: 10.1126/science.6719109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. L., McCutchan T. F. Isolation of a gene segment expressed by mature schizonts of Plasmodium knowlesi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986 Apr;19(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(86)90060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist G., Gray M., Porter T., Jordan J. Characterization of Giemsa dark- and light-band DNA. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):121–129. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90411-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan T. F., Dame J. B., Miller L. H., Barnwell J. Evolutionary relatedness of Plasmodium species as determined by the structure of DNA. Science. 1984 Aug 24;225(4664):808–811. doi: 10.1126/science.6382604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan T. F., Lal A. A., de la Cruz V. F., Miller L. H., Maloy W. L., Charoenvit Y., Beaudoin R. L., Guerry P., Wistar R., Jr, Hoffman S. L. Sequence of the immunodominant epitope for the surface protein on sporozoites of Plasmodium vivax. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1381–1383. doi: 10.1126/science.2416057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki L. S., Svec P., Nussenzweig R. S., Nussenzweig V., Godson G. N. Structure of the plasmodium knowlesi gene coding for the circumsporozoite protein. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):815–822. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90538-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pologe L. G., Ravetch J. V. A chromosomal rearrangement in a P. falciparum histidine-rich protein gene is associated with the knobless phenotype. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):474–477. doi: 10.1038/322474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silflow C. D., Rosenbaum J. L. Multiple alpha- and beta-tubulin genes in Chlamydomonas and regulation of tubulin mRNA levels after deflagellation. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90503-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L. Isolation of maxicircle component of kinetoplast DNA from hemoflagellate protozoa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernick K. D., McCutchan T. F. Sequence and structure of a Plasmodium falciparum telomere. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Mar;28(2):85–94. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellems T. E., Walliker D., Smith C. L., do Rosario V. E., Maloy W. L., Howard R. J., Carter R., McCutchan T. F. A histidine-rich protein gene marks a linkage group favored strongly in a genetic cross of Plasmodium falciparum. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):633–642. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90539-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]