Abstract
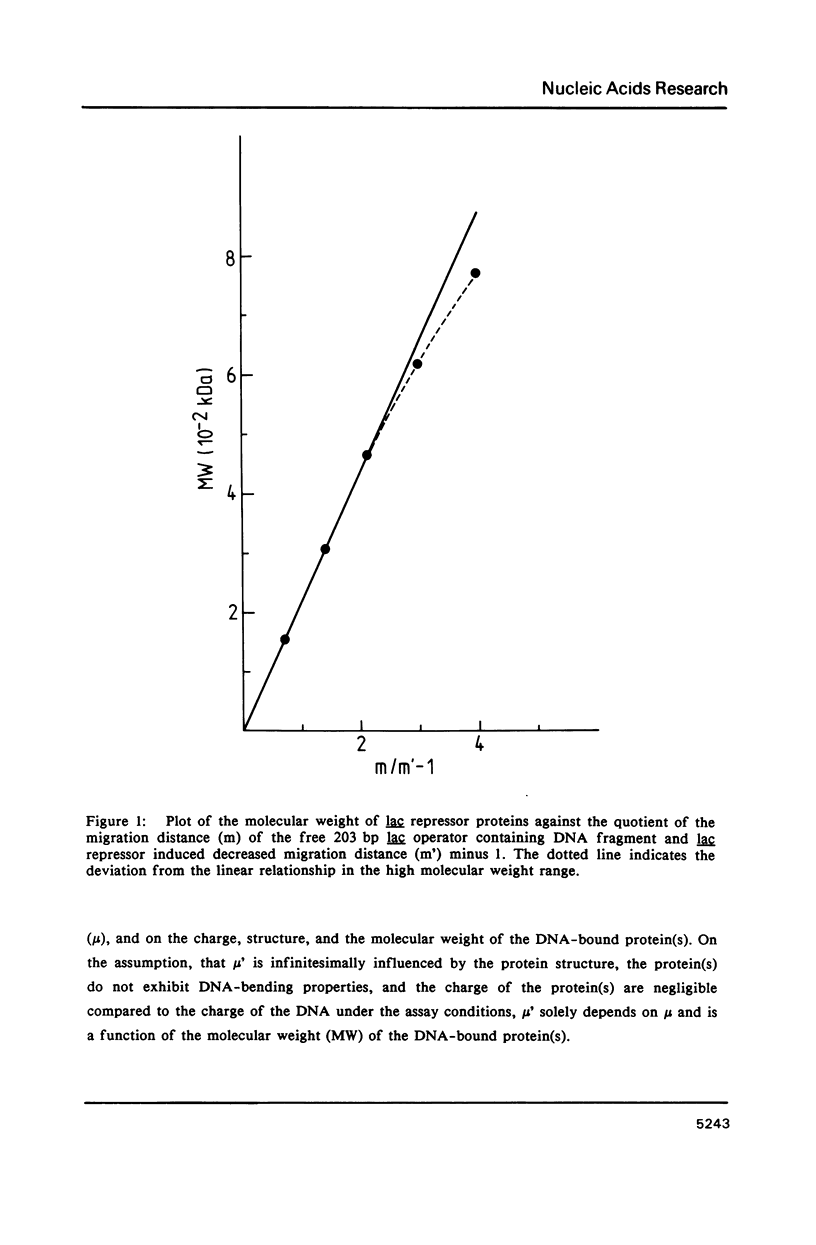
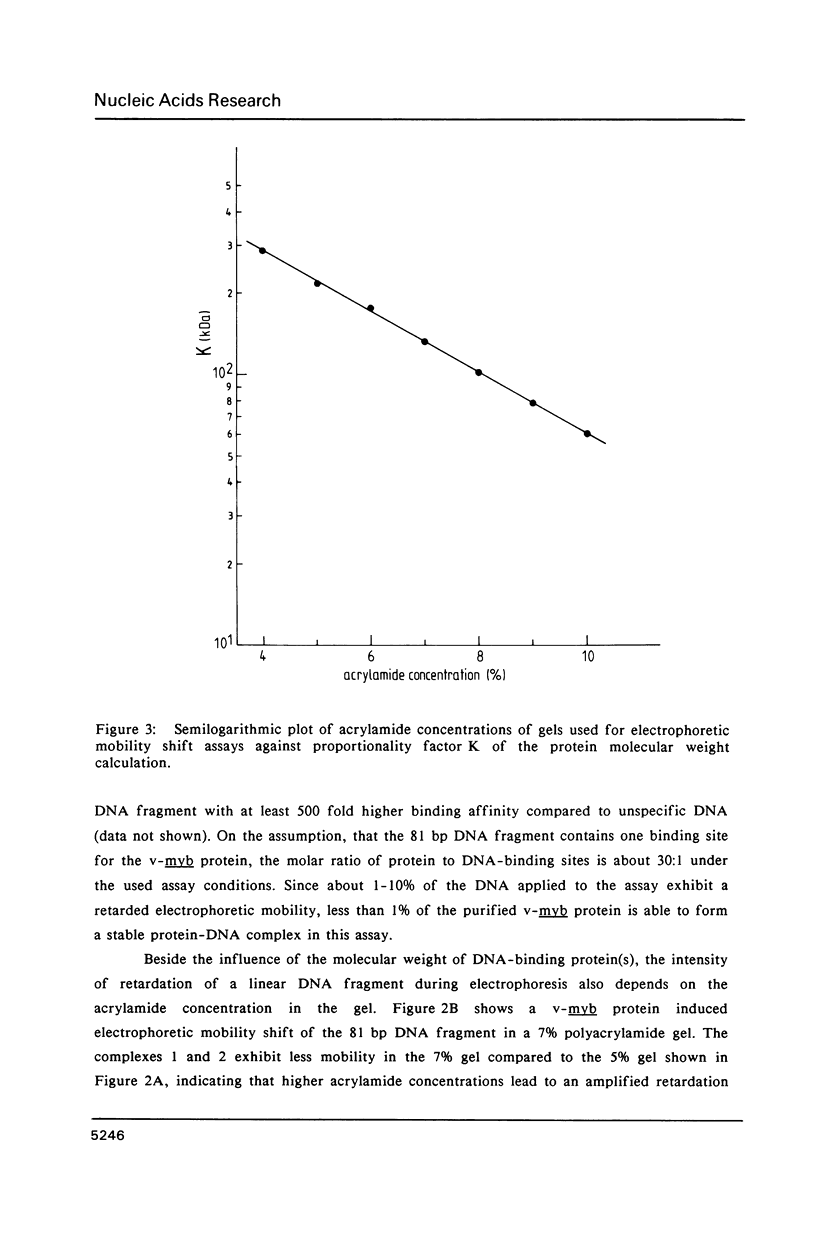
A protein-DNA complex has less gel electrophoretic mobility than the free DNA fragment. One parameter for the degree of retardation of a linear DNA fragment in a protein-DNA complex is the molecular weight of the bound protein(s). The quotient of the migration distances of free DNA (m) and protein-DNA complex (m') is a function of the molecular weight (MW) of the bound protein(s). Based on the evaluation of the lac repressor induced mobility shift of a 203 bp DNA fragment containing the lac operator in a 5% non-denaturating polyacrylamide gel a direct proportionality could be shown between (m/m'-1) and MW with the proportionality factor K = 215 kDa. The factor K depends on the acrylamide concentration in the gel, getting lower values with increasing acrylamide concentrations. A calculation is given to determine the molecular weight of DNA-binding factors responsible for the decreased electrophoretic mobility of a linear DNA fragment. As an example this calculation was used in order to analyse DNA-binding of the isolated viral myb protein. It could be demonstrated that the viral myb protein binds to DNA as a monomer and as a dimer.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bading H., Hansen J., Moelling K. Selective DNA binding of the human cellular myb protein isolated by immunoaffinity chromatography using a monoclonal antibody. Oncogene. 1987;1(4):395–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey J. Gel retardation at low pH resolves trp repressor-DNA complexes for quantitative study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):975–979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M., Moscovici M. G., Moscovici C., McGrath J. P., Levinson A. D. The product of the retroviral transforming gene v-myb is a truncated version of the protein encoded by the cellular oncogene c-myb. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):345–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90416-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Sippel A. E. Subnuclear localization of proteins encoded by the oncogene v-myb and its cellular homolog c-myb. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):62–69. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Sippel A. E. The highly conserved amino-terminal region of the protein encoded by the v-myb oncogene functions as a DNA-binding domain. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2719–2725. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02565.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. DNA-binding site of major regulatory protein alpha 4 specifically associated with promoter-regulatory domains of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4700–4704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moelling K., Pfaff E., Beug H., Beimling P., Bunte T., Schaller H. E., Graf T. DNA-binding activity is associated with purified myb proteins from AMV and E26 viruses and is temperature-sensitive for E26 ts mutants. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):983–990. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90358-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C. Leukemic transformation with avian myeloblastosis virus: present status. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1975;71:79–101. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66193-8_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Hong G. F., Hill D. F., Petersen G. B. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 25;162(4):729–773. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90546-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]