Abstract
The equilibrium for the binding reaction between the 30 S and 50 S ribosomal subunits of E. coli is shifted towards formation of 70 S ribosomes in the presence of a variety of polymers. The polymers also increase a further interaction between 70 S particles to form the 100 S dimer. The requirement for relatively high concentrations of non-specific polymers indicates that the shifts in equilibria arise from excluded volume effects. Analysis using scaled particle theory is consistent with this mechanism. The effects of high concentrations of polymers on the interactions between ribosomal species may make important changes in the function of ribosomes under the crowded conditions which occur in vivo.
Full text
PDF





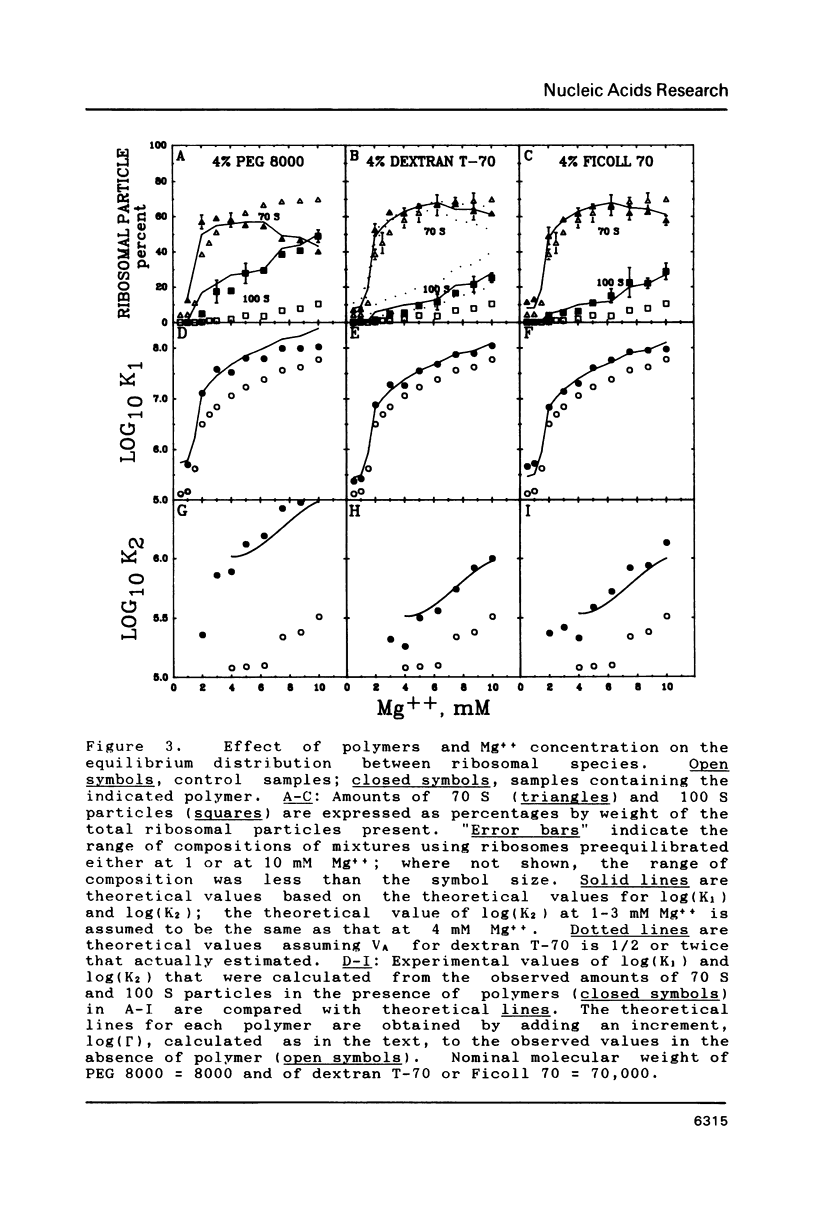
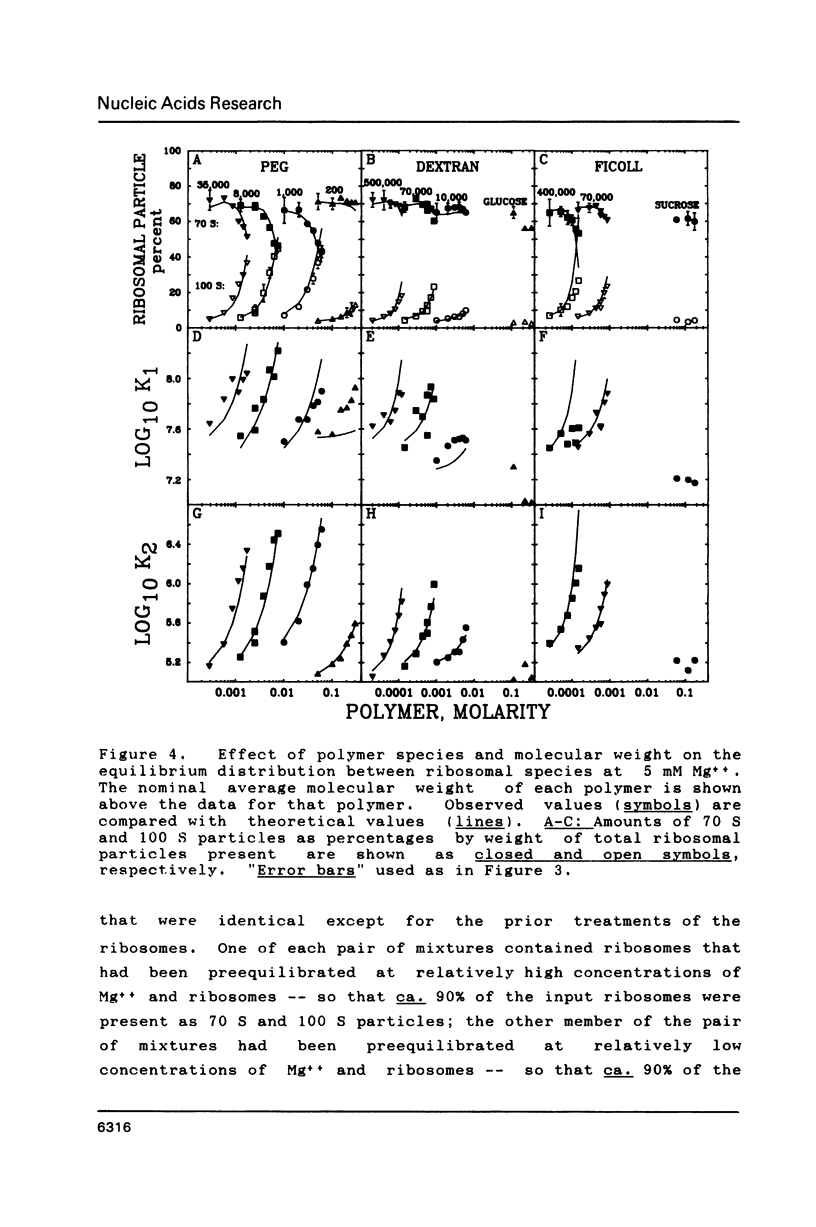








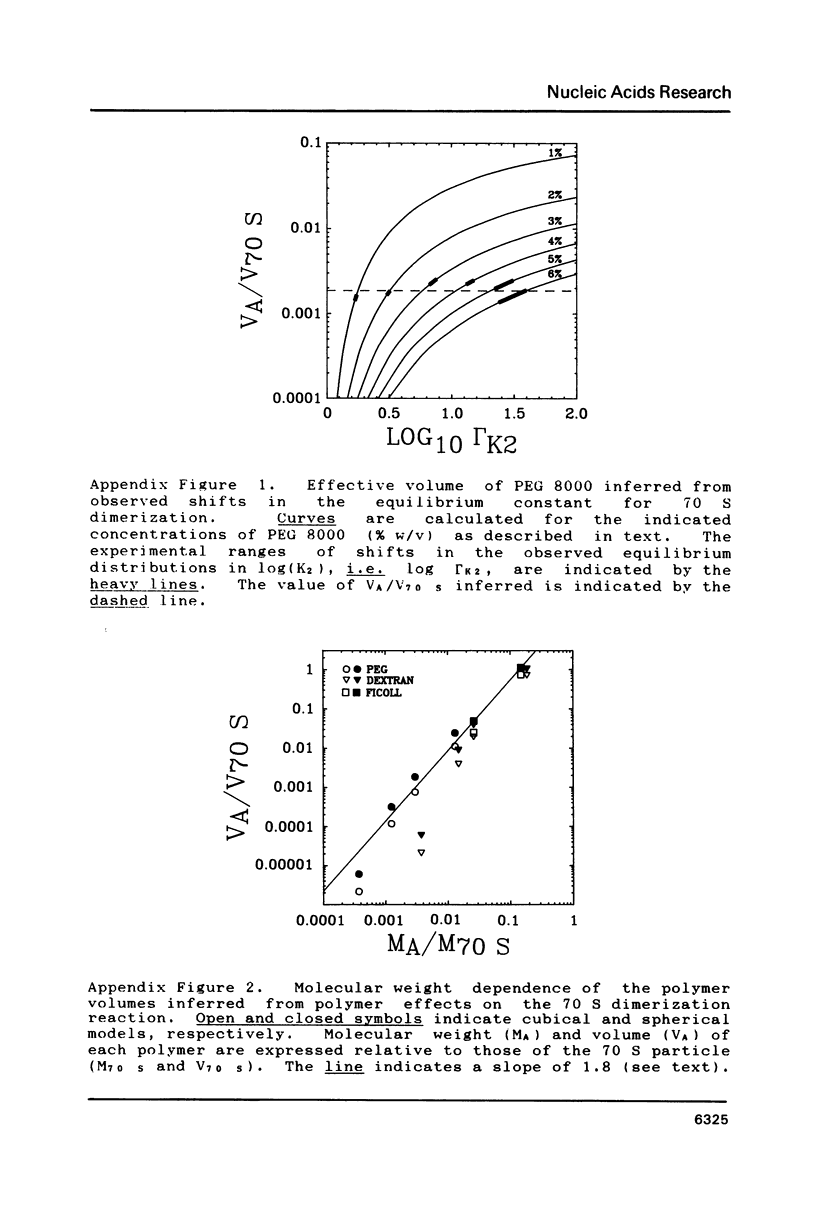

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernabeu C., Lake J. A. Packing of 70 S Ribosomes in dimers formed at low ionic strength. Images of an unusual ribosome projection. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 15;160(2):369–373. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90182-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakesley R. W., Boezi J. A. A new staining technique for proteins in polyacrylamide gels using coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(2):580–582. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatelier R. C., Minton A. P. Sedimentation equilibrium in macromolecular solutions of arbitrary concentration. I. Self-associating proteins. Biopolymers. 1987 Apr;26(4):507–524. doi: 10.1002/bip.360260405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg A. E., Dingman C. W., Peacock A. C. Electrophoretic characterization of bacterial polyribosomes in agarose-acrylamide composite gels. J Mol Biol. 1969 Apr 14;41(1):139–147. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debey P., Hui Bon Hoa G., Douzou P., Godefroy-Colburn T., Graffe M., Grunberg-Manago M. Ribosomal subunit interaction as studied by light scattering. Evidence of different classes of ribosome preparations. Biochemistry. 1975 Apr 22;14(8):1553–1559. doi: 10.1021/bi00679a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghysen A., Bollen A., Herzog A. Ionic effects on the ribosomal quaternary structure. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Mar 1;13(1):132–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00908.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hapke B., Noll H. Structural dynamics of bacterial ribosomes. IV. Classification of ribosomes by subunit interaction. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 25;105(1):97–109. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90196-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison B., Zimmerman S. B. Stabilization of T4 polynucleotide kinase by macromolecular crowding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1863–1870. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Infante A. A., Baierlein R. Pressure-induced dissociation of sedimenting ribosomes: effect on sedimentation patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1780–1785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Infante A. A., Krauss M. Dissociation of ribosomes induced by centrifugation: evidence for doubting conformational changes in ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 12;246(1):81–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenicke R. Enzymes under extremes of physical conditions. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1981;10:1–67. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.10.060181.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephs R., Harrington W. F. An unusual pressure dependence for a reversibly associating protein system; sedimentation studies on myosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1587–1594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kegeles G., Rhodes L., Bethune J. L. Sedimentation behavior of chemically reacting systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):45–51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljas A. Structural studies of ribosomes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1982;40(3):161–228. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(82)90013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minton A. P. The effect of volume occupancy upon the thermodynamic activity of proteins: some biochemical consequences. Mol Cell Biochem. 1983;55(2):119–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00673707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minton A. P., Wilf J. Effect of macromolecular crowding upon the structure and function of an enzyme: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 18;20(17):4821–4826. doi: 10.1021/bi00520a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miskin R., Zamir A., Elson D. Inactivation and reactivation of ribosomal subunits: the peptidyl transferase activity of the 50 s subunit of Escherihia coli. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 14;54(2):355–378. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90435-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M., Hapke B., Noll H. Structural dynamics of bacterial ribosomes. II. Preparation and characterization of ribosomes and subunits active in the translation of natural messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 5;80(3):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90419-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M., Noll H. Structural dynamics of bacterial ribosomes. V. Magnesium-dependent dissociation of tight couples into subunits: measurements of dissociation constants and exchange rates. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 25;105(1):111–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Structure of ribosomal RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:119–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross P. D., Minton A. P. Analysis of non-ideal behavior in concentrated hemoglobin solutions. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):437–452. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80191-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross P. D., Minton A. P. The effect of non-aggregating proteins upon the gelation of sickle cell hemoglobin: model calculations and data analysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jun 27;88(4):1308–1314. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91123-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitnik-Elson P., Elson D. Studies on the ribosome and its components. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1976;17:77–98. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60066-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TISSIERES A., WATSON J. D. Ribonucleoprotein particles from Escherichia coli. Nature. 1958 Sep 20;182(4638):778–780. doi: 10.1038/182778b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teneyck L. F., Kauzmann W. Pressure and hydration effects on chemically reacting systems in the ultracentrifuge. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):888–894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber G., Drickamer H. G. The effect of high pressure upon proteins and other biomolecules. Q Rev Biophys. 1983 Feb;16(1):89–112. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500004935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamir A., Miskin R., Elson D. Inactivation and reactivation of ribosomal subunits: amino acyl-transfer RNA binding activity of the 30 s subunit of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1971 Sep 14;60(2):347–364. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90299-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman S. B., Harrison B. Macromolecular crowding increases binding of DNA polymerase to DNA: an adaptive effect. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1871–1875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman S. B., Pheiffer B. H. Macromolecular crowding allows blunt-end ligation by DNA ligases from rat liver or Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5852–5856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zitomer R. S., Flaks J. G. Magnesium dependence and equilibrium of the Escherichia coli ribosomal subunit association. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 14;71(2):263–279. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90350-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Diggelen O. P., Oostrom H., Bosch L. Association products of native and derived ribosomal subunits of E. coli and their stability during centrifugation. FEBS Lett. 1971 Dec 1;19(2):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80492-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duin J., VAN Dieijen G., Dieijen G., van Knippenberg P. H., Bosch L. Different species of 70S ribosomes of Escherichia coli and their dissociation into subunits. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Dec;17(3):433–440. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




