Abstract
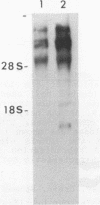
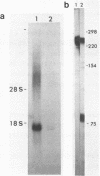
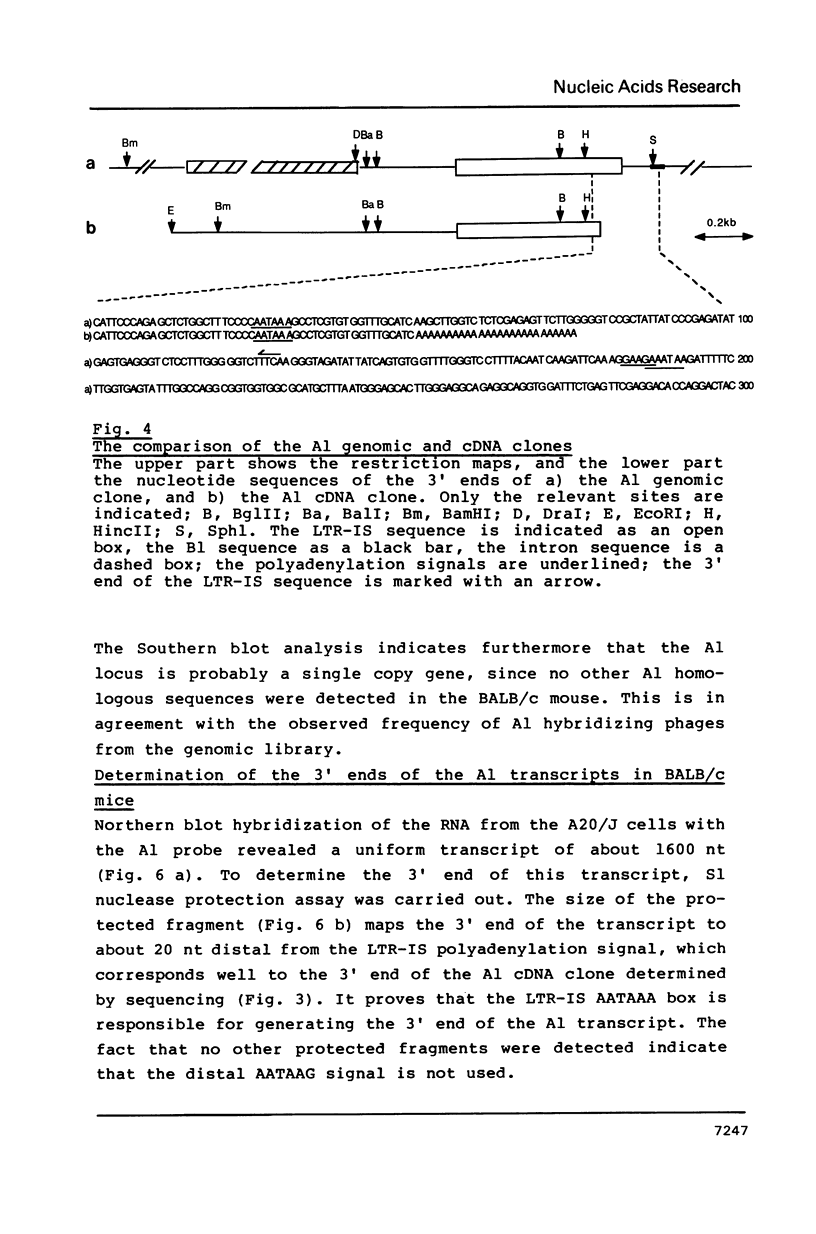
A site of genomic insertion of the mouse retrotransposon LTR-IS/MuRRS was analysed. The comparison of the genomic and the cDNA clones indicates the insertion of the LTR-IS element into the 3' untranslated region of a mouse gene. The fact that the isolated cDNA clone ends with a poly A tail 20 nucleotides downstream from the LTR-IS AATAAA box and the result of the S1-nuclease mapping provides evidence that the 3' end of the mouse gene transcript was generated under the control of the LTR-IS polyadenylation signal.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aho S., Tate V., Boedtker H. Multiple 3' ends of the chicken pro alpha 2(I) collagen gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5443–5450. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amara S. G., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide transcription unit: tissue-specific expression involves selective use of alternative polyadenylation sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2151–2160. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campuzano S., Balcells L., Villares R., Carramolino L., García-Alonso L., Modolell J. Excess function hairy-wing mutations caused by gypsy and copia insertions within structural genes of the achaete-scute locus of Drosophila. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90764-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil A., Proudfoot N. J. A sequence downstream of AAUAAA is required for rabbit beta-globin mRNA 3'-end formation. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):473–474. doi: 10.1038/312473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Wellauer P. K., Cribbs D. L., Schibler U. Termination of transcription in the mouse alpha-amylase gene Amy-2a occurs at multiple sites downstream of the polyadenylation site. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):737–744. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90269-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Sloan J. S., Kelly J. D. A Drosophila metabolic gene transcript is alternatively processed. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):405–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90374-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs D. R., Goodbourn S. E., Lamb J., Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J., Proudfoot N. J. Alpha-thalassaemia caused by a polyadenylation signal mutation. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):398–400. doi: 10.1038/306398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd S., Lockett T. J., Young M. W. The Notch locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):421–433. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhrer K., Grummt I., Horak I. Functional RNA polymerase II promoters in solitary retroviral long terminal repeats (LTR-IS elements). Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2631–2645. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., O'Hare K., Rubin G. M. Effects of transposable element insertions on RNA encoded by the white gene of Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):471–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90502-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt M. A., Imperiale M. J., Ali H., Nevins J. R. Requirement of a downstream sequence for generation of a poly(A) addition site. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):993–999. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90433-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M., Glöggler K., Wirth T., Horak I. Evidence that a major class of mouse endogenous long terminal repeats (LTRs) resulted from recombination between exogenous retroviral LTRs and similar LTR-like elements (LTR-IS). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6696–6700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M., Wirth T., Kröger B., Horak I. Structure and genomic organization of a new family of murine retrovirus-related DNA sequences (MuRRS). Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 24;13(10):3461–3470. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.10.3461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth T., Glöggler K., Baumruker T., Schmidt M., Horak I. Family of middle repetitive DNA sequences in the mouse genome with structural features of solitary retroviral long terminal repeats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3327–3330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth T., Schmidt M., Baumruker T., Horak I. Evidence for mobility of a new family of mouse middle repetitive DNA elements (LTR-IS). Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3603–3610. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]