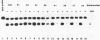Abstract
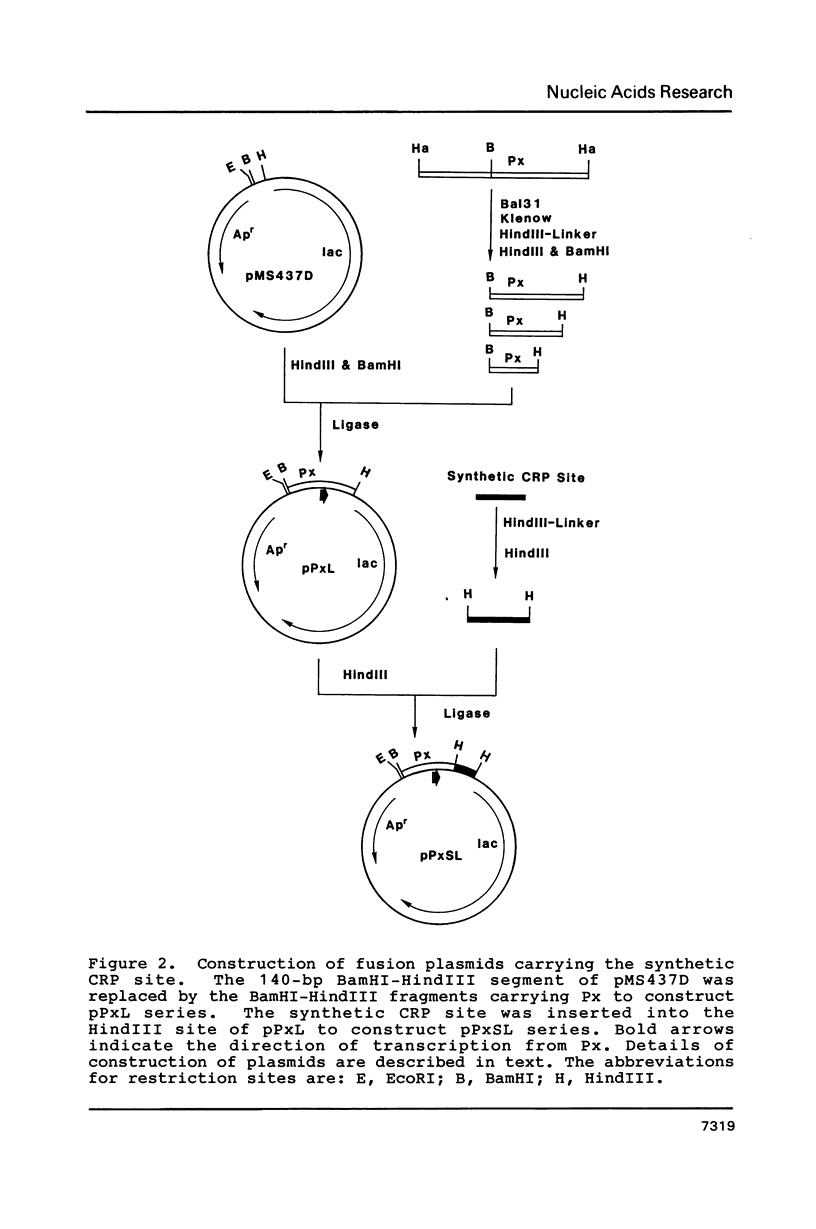
A series of plasmids were constructed in which a promoter was introduced into a lac-based operon fusion vector. A perfectly symmetrical oligonucleotide of 22-bp corresponding to an idealized binding site for cAMP receptor protein (CRP) of E. coli was chemically synthesized. The synthetic CRP site was placed between the promoter and the lacZ structural gene with varying distances from the promoter. Specific binding of cAMP-CRP complex to the synthetic CRP site was shown by a gel retardation and a DNase I footprinting assays. Plasmid constructs were transformed into crp+ and crp- cells carrying a chromosomal deletion of the lac genes. The regulatory effect of the inserted CRP site was examined by comparing the beta-galactosidase activity and the levels of RNA transcript in two cells harboring the plasmids. We found a strong inhibitory effect of the CRP site in the presence of cAMP and CRP when it was placed close to the promoter. When the CRP site was placed far downstream of the promoter, a moderate repression of transcription was observed.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba H., Adhya S., de Crombrugghe B. Evidence for two functional gal promoters in intact Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11905–11910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiba H. Autoregulation of the Escherichia coli crp gene: CRP is a transcriptional repressor for its own gene. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):141–149. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90504-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiba H., Fujimoto S., Ozaki N. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequencing of the gene for E. coli cAMP receptor protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 25;10(4):1345–1361. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.4.1345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiba H. Transcription of the Escherichia coli adenylate cyclase gene is negatively regulated by cAMP-cAMP receptor protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):3063–3070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg O. G., von Hippel P. H. Selection of DNA binding sites by regulatory proteins. II. The binding specificity of cyclic AMP receptor protein to recognition sites. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 20;200(4):709–723. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90482-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besse M., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. Synthetic lac operator mediates repression through lac repressor when introduced upstream and downstream from lac promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1377–1381. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04370.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., Figge J., Hansen U., Wright C., Jeang K. T., Khoury G., Livingston D. M., Roberts T. M. lac repressor can regulate expression from a hybrid SV40 early promoter containing a lac operator in animal cells. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):603–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90536-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J. Transposition and fusion of the lac genes to selected promoters in Escherichia coli using bacteriophage lambda and Mu. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):541–555. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossart P., Gicquel-Sanzey B. Cloning and sequence of the crp gene of Escherichia coli K 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 25;10(4):1363–1378. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.4.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossart P., Gicquel-Sanzey B. Regulation of expression of the crp gene of Escherichia coli K-12: in vivo study. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):454–457. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.454-457.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuschle U., Gentz R., Bujard H. lac Repressor blocks transcribing RNA polymerase and terminates transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4134–4137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilen E., Pampeno C., Krakow J. S. Production and properties of the alpha core derived from the cyclic adenosine monophosphate receptor protein of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 27;17(13):2469–2473. doi: 10.1021/bi00606a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figge J., Wright C., Collins C. J., Roberts T. M., Livingston D. M. Stringent regulation of stably integrated chloramphenicol acetyl transferase genes by E. coli lac repressor in monkey cells. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):713–722. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90409-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrin G. L., Jr, Bennett G. N. Role of DNA regions flanking the tryptophan promoter of Escherichia coli. II. Insertion of lac operator fragments. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):349–356. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano M., Shigesada K., Imai M. Construction and characterization of plasmid and lambda phage vector systems for study of transcriptional control in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(1):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz H., Platt T. Regulation of transcription from tandem and convergent promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 25;10(18):5447–5465. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.18.5447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu M. C., Davidson N. The inducible lac operator-repressor system is functional in mammalian cells. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):555–566. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90234-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen C., Gronenborn A. M., Clore G. M. The binding of the cyclic AMP receptor protein to synthetic DNA sites containing permutations in the consensus sequence TGTGA. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 15;246(1):227–232. doi: 10.1042/bj2460227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovanovich S. B. Regulation of a cya-lac fusion by cyclic AMP in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):641–649. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.641-649.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Carner K. R., Masiarz F. R., Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamukai M., Kishimoto J., Utsumi R., Himeno M., Komano T., Aiba H. Negative regulation of adenylate cyclase gene (cya) expression by cyclic AMP-cyclic AMP receptor protein in Escherichia coli: studies with cya-lac protein and operon fusion plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):872–877. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.872-877.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb A., Busby S., Herbert M., Kotlarz D., Buc H. Comparison of the binding sites for the Escherichia coli cAMP receptor protein at the lactose and galactose promoters. EMBO J. 1983;2(2):217–222. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01408.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb A., Spassky A., Chapon C., Blazy B., Buc H. On the different binding affinities of CRP at the lac, gal and malT promoter regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7833–7852. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakow J. S., Pastan I. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate receptor: loss of cAMP-dependent DNA binding activity after proteolysis in the presence of cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2529–2533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallick U., Herrlich P. Regulation of synthesis of a major outer membrane protein: cyclic AMP represses Escherichia coli protein III synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5520–5523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori K., Aiba H. Evidence for negative control of cya transcription by cAMP and cAMP receptor protein in intact Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14838–14843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musso R. E., Di Lauro R., Adhya S., de Crombrugghe B. Dual control for transcription of the galactose operon by cyclic AMP and its receptor protein at two interspersed promoters. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):847–854. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulmier N., Yaniv M., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. gal4 transcription activator protein of yeast can function as a repressor in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3539–3542. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02680.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler J. R., Sasmor H., Betz J. L. A perfectly symmetric lac operator binds the lac repressor very tightly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6785–6789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawai T., Takahashi I., Yamagishi S. Iodometric assay method for beta-lactamase with various beta-lactam antibiotics as substrates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jun;13(6):910–913. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.6.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellitti M. A., Pavco P. A., Steege D. A. lac repressor blocks in vivo transcription of lac control region DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3199–3203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha N. D., Biernat J., McManus J., Köster H. Polymer support oligonucleotide synthesis XVIII: use of beta-cyanoethyl-N,N-dialkylamino-/N-morpholino phosphoramidite of deoxynucleosides for the synthesis of DNA fragments simplifying deprotection and isolation of the final product. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4539–4557. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. D., Jordan P. M. Nucleotide sequence of the hemC locus encoding porphobilinogen deaminase of Escherichia coli K12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6215–6226. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Crombrugghe B., Busby S., Buc H. Cyclic AMP receptor protein: role in transcription activation. Science. 1984 May 25;224(4651):831–838. doi: 10.1126/science.6372090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]