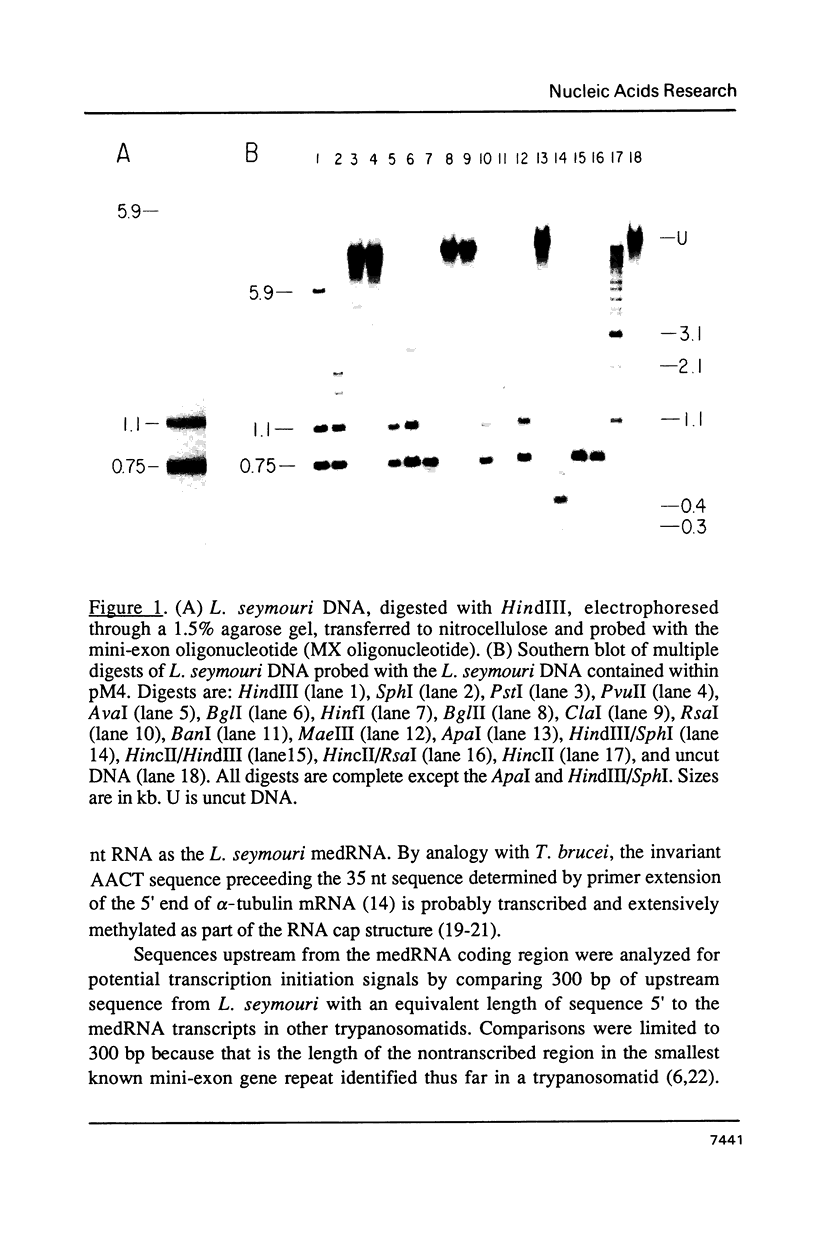
Abstract
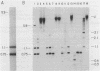
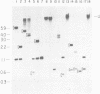
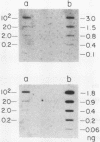
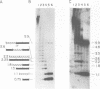
Mature mRNAs of trypanosomatid protozoa result from the joining of at least two exons, which are initially transcribed as separate RNAs. In all trypanosomatids examined to date, the first exon (mini-exon) is encoded by approximately 200 tandemly reiterated genes. In characterizing the mini-exon genes of Leptomonas seymouri, we identified two predominant size classes of repetitive sequences that hybridized strongly to the L. seymouri mini-exon sequence. These two sequences are arranged as interspersed clusters. DNA sequence analysis of a clone representing the smaller size class demonstrated that these sequences have the capacity to encode a mini-exon donor (med)RNA corresponding to the 86 nt component seen in Northern blots of L. seymouri RNA. The larger size class comprises a family of related sequences, some of which contain DNA inserted into the mini-exon portion of the medRNA gene. The specific insert identified here (LINS 1) is exclusively associated with medRNA sequences, and is present in approximately 20% of the larger size class of L. seymouri medRNA genes. Disregarding the insertion, the sequences of the smaller bona fide mini-exon genes and the gene copy containing the insert were almost identical. The insert sequence is transcribed in the same direction as medRNA to yield at least four small non-polyadenylated RNAs, which appeared not to be linked to medRNA sequences.
Full text
PDF


















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aksoy S., Lalor T. M., Martin J., Van der Ploeg L. H., Richards F. F. Multiple copies of a retroposon interrupt spliced leader RNA genes in the African trypanosome, Trypanosoma gambiense. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3819–3826. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02718.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONE G. J., STEINERT M. Isotopes incorporated in the nucleic acids of Trypanosoma mega. Nature. 1956 Aug 11;178(4528):308–309. doi: 10.1038/178308a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington M., Roditi I., Williams R. O. The structure and transcription of an element interspersed between tandem arrays of mini-exon donor RNA genes in Trypanosoma brucei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10179–10198. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook G. A., Donelson J. E. Mini-exon gene repeats of Trypanosoma (Nannomonas) congolense have internal repeats of 190 base pairs. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Aug;25(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cully D. F., Ip H. S., Cross G. A. Coordinate transcription of variant surface glycoprotein genes and an expression site associated gene family in Trypanosoma brucei. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):173–182. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80113-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lange T., Berkvens T. M., Veerman H. J., Frasch A. C., Barry J. D., Borst P. Comparison of the genes coding for the common 5' terminal sequence of messenger RNAs in three trypanosome species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4431–4443. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lange T., Liu A. Y., Van der Ploeg L. H., Borst P., Tromp M. C., Van Boom J. H. Tandem repetition of the 5' mini-exon of variant surface glycoprotein genes: a multiple promoter for VSG gene transcription? Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):891–900. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90546-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorfman D. M., Donelson J. E. Characterization of the 1.35 kilobase DNA repeat unit containing the conserved 35 nucleotides at the 5'-termini of variable surface glycoprotein mRNAs in Trypanosoma brucei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 25;12(12):4907–4920. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.12.4907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freistadt M. S., Cross G. A., Branch A. D., Robertson H. D. Direct analysis of the mini-exon donor RNA of Trypanosoma brucei: detection of a novel cap structure also present in messenger RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9861–9879. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel A., Sisodia S. S., Cleveland D. W. Evidence of discontinuous transcription in the trypanosomatid Crithidia fasciculata. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16192–16199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasan G., Turner M. J., Cordingley J. S. Complete nucleotide sequence of an unusual mobile element from trypanosoma brucei. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):333–341. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90329-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasan G., Turner M. J., Cordingley J. S. Ribosomal RNA genes of Trypanosoma brucei: mapping the regions specifying the six small ribosomal RNAs. Gene. 1984 Jan;27(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90240-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel B. E., ole-MoiYoi O. K., Young J. R. Ingi, a 5.2-kb dispersed sequence element from Trypanosoma brucei that carries half of a smaller mobile element at either end and has homology with mammalian LINEs. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1465–1475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kooter J. M., De Lange T., Borst P. Discontinuous synthesis of mRNA in trypanosomes. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2387–2392. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02144.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause M., Hirsh D. A trans-spliced leader sequence on actin mRNA in C. elegans. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):753–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90613-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird P. W., Zomerdijk J. C., de Korte D., Borst P. In vivo labelling of intermediates in the discontinuous synthesis of mRNAs in Trypanosoma brucei. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1055–1062. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04858.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Dorfman D. M., Reddy L. V., Donelson J. E. Characterization of the Trypanosoma brucei 5S ribosomal RNA gene and transcript: the 5S rRNA is a spliced-leader-independent species. Gene. 1985;35(1-2):131–141. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90165-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milhausen M., Nelson R. G., Sather S., Selkirk M., Agabian N. Identification of a small RNA containing the trypanosome spliced leader: a donor of shared 5' sequences of trypanosomatid mRNAs? Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):721–729. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90267-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. I., Landfear S. M., Wirth D. F. Cloning and characterization of a Leishmania gene encoding a RNA spliced leader sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 25;14(18):7341–7360. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.18.7341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhich M. L., Hughes D. E., Simpson A. M., Simpson L. The monogenetic kinetoplastid protozoan, Crithidia fasciculata, contains a transcriptionally active, multicopy mini-exon sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):3141–3153. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.3141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy N. B., Pays A., Tebabi P., Coquelet H., Guyaux M., Steinert M., Pays E. Trypanosoma brucei repeated element with unusual structural and transcriptional properties. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):855–871. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90490-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. G., Parsons M., Barr P. J., Stuart K., Selkirk M., Agabian N. Sequences homologous to the variant antigen mRNA spliced leader are located in tandem repeats and variable orphons in trypanosoma brucei. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):901–909. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90547-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pays E., Murphy N. B. DNA-binding fingers encoded by a trypanosome retroposon. J Mol Biol. 1987 Sep 5;197(1):147–148. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90617-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry K. L., Watkins K. P., Agabian N. Trypanosome mRNAs have unusual "cap 4" structures acquired by addition of a spliced leader. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8190–8194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Brown D. D. Contact points between a positive transcription factor and the Xenopus 5S RNA gene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):395–405. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Cornelissen A. W., Michels P. A., Borst P. Chromosome rearrangements in Trypanosoma brucei. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90207-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]