Abstract
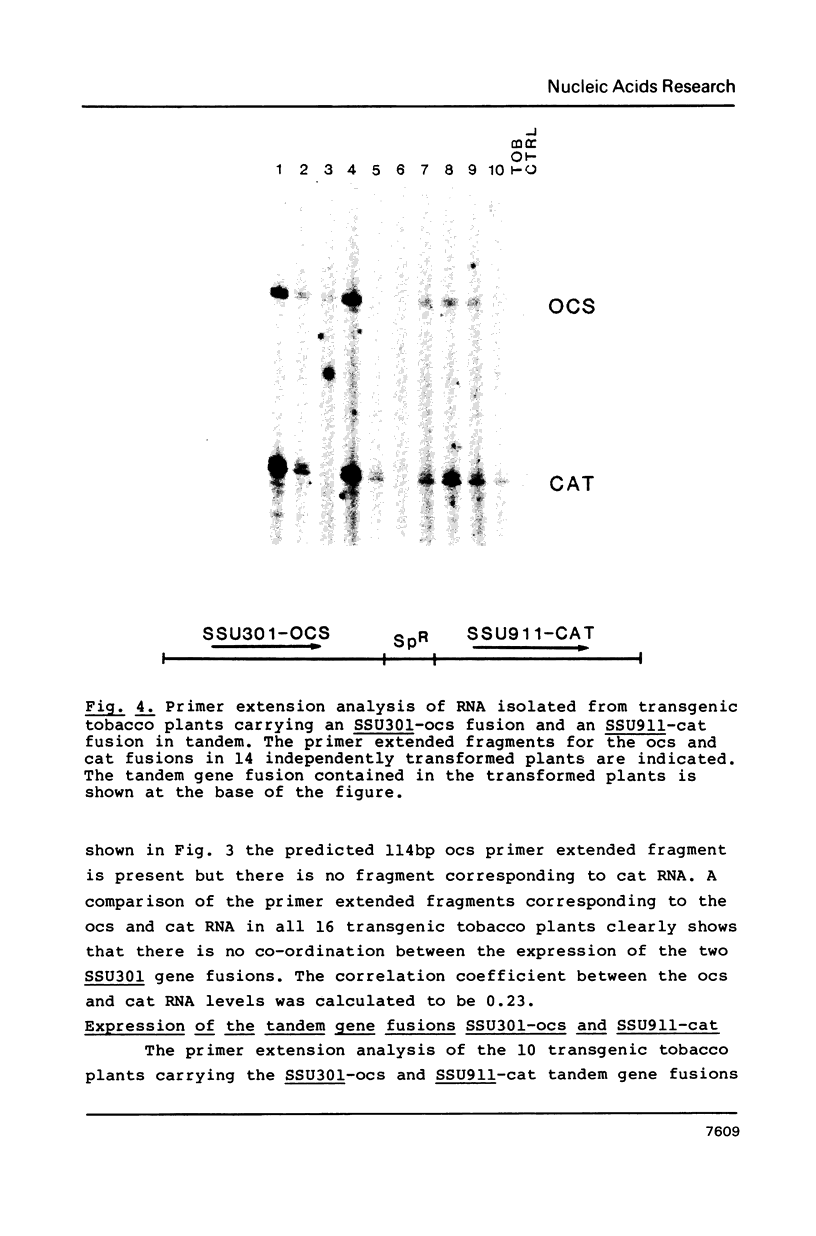
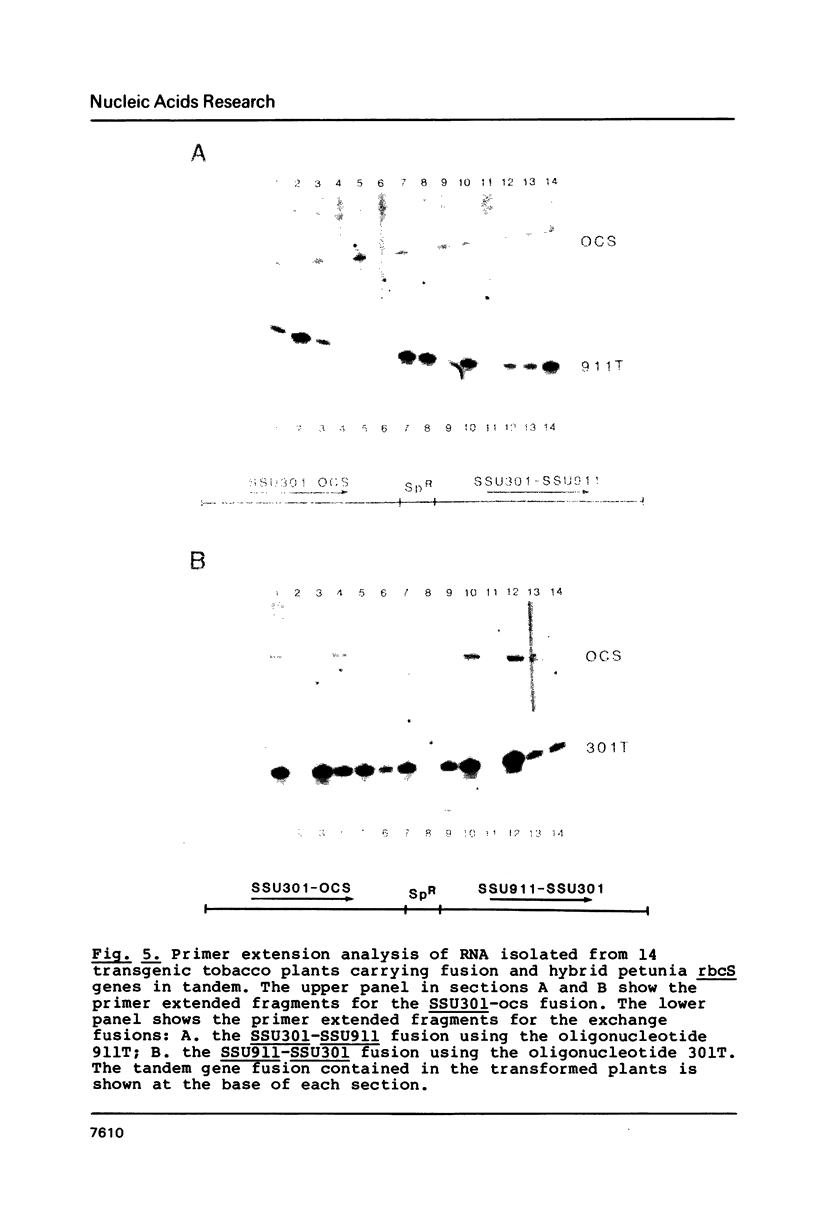
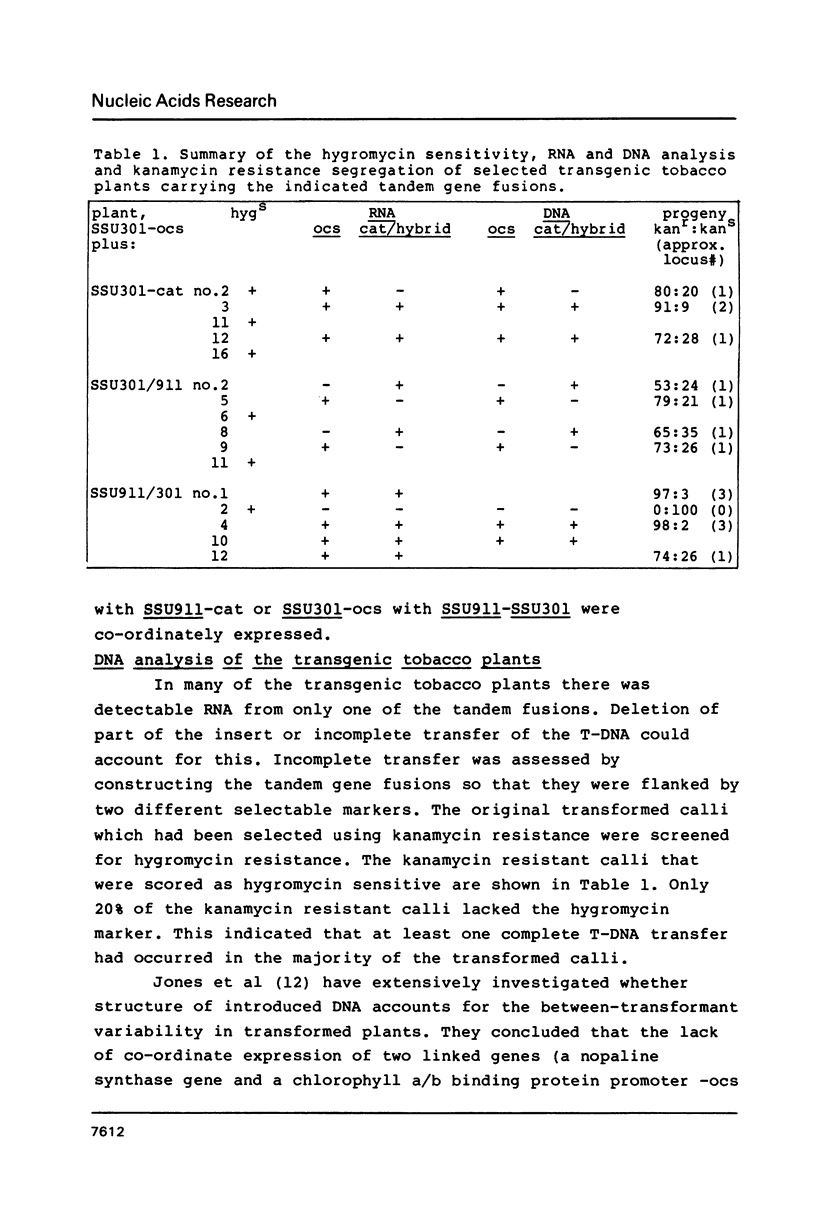
We have studied the expression of four sets of tandem gene fusions in transgenic tobacco plants. This was to determine if the problem of between-transformant variability in expression of introduced genes could be overcome by using a linked reference gene as a co-ordinately expressed control. Tandem gene fusions containing identical 5' flanking regions (SSU301-ocs with either SSU301-cat or SSU301-SSU911) were not co-ordinately expressed in the transgenic tobacco plants whereas the tandem gene fusions containing similar but not identical 5' flanking regions (SSU301-ocs with SSU911-cat or SSU911-SSU301) were co-ordinately expressed. The lack of co-ordinate expression of some of the tandem gene fusions appears to be partially explained by absence of the corresponding genomic DNA segments in the transgenic plants.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alton N. K., Vapnek D. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the chloramphenicol resistance transposon Tn9. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):864–869. doi: 10.1038/282864a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- An G. Development of plant promoter expression vectors and their use for analysis of differential activity of nopaline synthase promoter in transformed tobacco cells. Plant Physiol. 1986 May;81(1):86–91. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck E., Ludwig G., Auerswald E. A., Reiss B., Schaller H. Nucleotide sequence and exact localization of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene from transposon Tn5. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Greve H., Dhaese P., Seurinck J., Lemmers M., Van Montagu M., Schell J. Nucleotide sequence and transcript map of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid-encoded octopine synthase gene. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(6):499–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean C., Elzen P., Tamaki S., Dunsmuir P., Bedbrook J. Differential expression of the eight genes of the petunia ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit multi-gene family. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3055–3061. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04045.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean C., Favreau M., Dunsmuir P., Bedbrook J. Confirmation of the relative expression levels of the Petunia (Mitchell) rbcS genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4655–4668. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean C., Tamaki S., Dunsmuir P., Favreau M., Katayama C., Dooner H., Bedbrook J. mRNA transcripts of several plant genes are polyadenylated at multiple sites in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):2229–2240. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.2229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean C., van den Elzen P., Tamaki S., Dunsmuir P., Bedbrook J. Linkage and homology analysis divides the eight genes for the small subunit of petunia ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase into three gene families. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4964–4968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunsmuir P., Smith S. M., Bedbrook J. The major chlorophyll a/b binding protein of petunia is composed of several polypeptides encoded by a number of distinct nuclear genes. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(3):285–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluhr R., Kuhlemeier C., Nagy F., Chua N. H. Organ-specific and light-induced expression of plant genes. Science. 1986 May 30;232(4754):1106–1112. doi: 10.1126/science.232.4754.1106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. D., Dunsmuir P., Bedbrook J. High level expression of introduced chimaeric genes in regenerated transformed plants. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2411–2418. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03949.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlemeier C., Fluhr R., Green P. J., Chua N. H. Sequences in the pea rbcS-3A gene have homology to constitutive mammalian enhancers but function as negative regulatory elements. Genes Dev. 1987 May;1(3):247–255. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.3.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson J., VAN Montagu M., Herrera-Estrella L. Photosynthesis-associated gene families: differences in response to tissue-specific and environmental factors. Science. 1986 Jul 4;233(4759):34–38. doi: 10.1126/science.233.4759.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. P., Cohen S. N. Structural and functional analysis of cloned DNA segments containing the replication and incompatibility regions of a miniplasmid derived from a copy number mutant of NR1. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):92–104. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.92-104.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velten J., Schell J. Selection-expression plasmid vectors for use in genetic transformation of higher plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):6981–6998. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.6981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]