Abstract
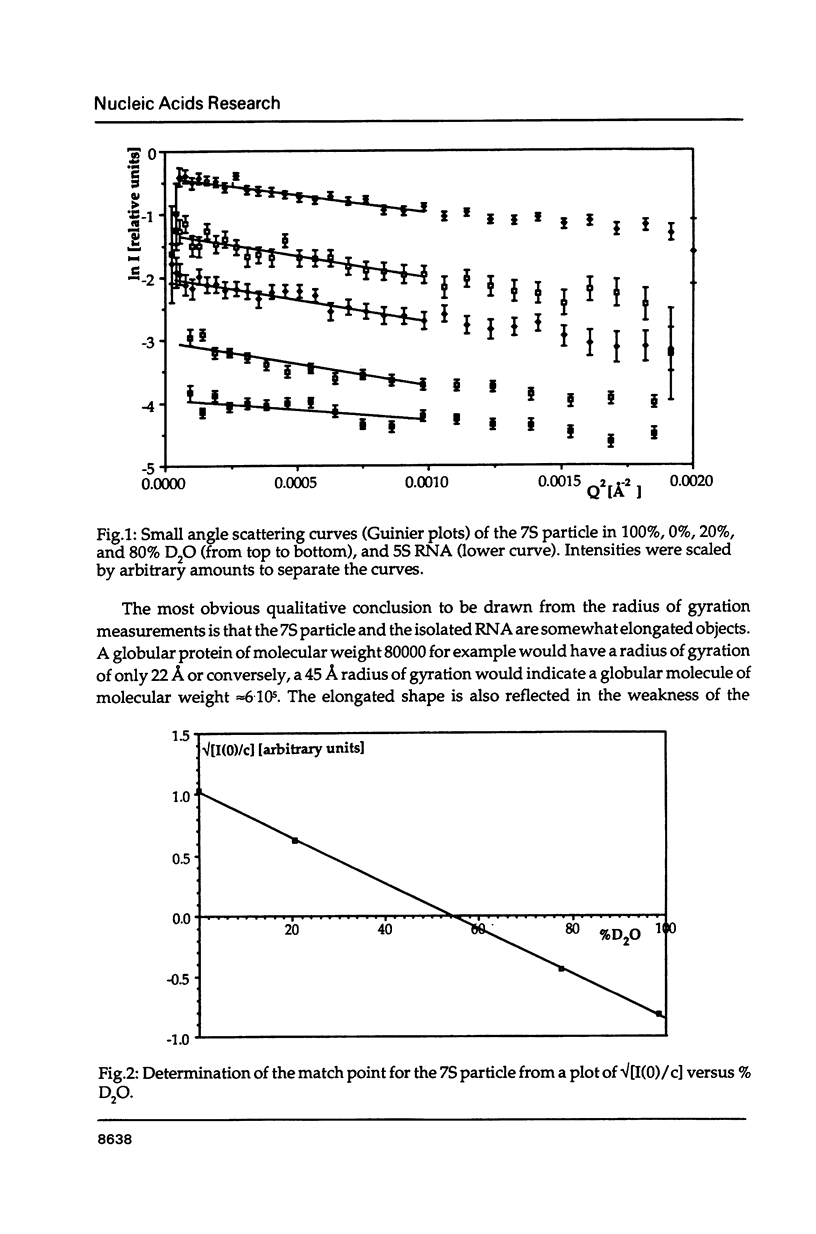
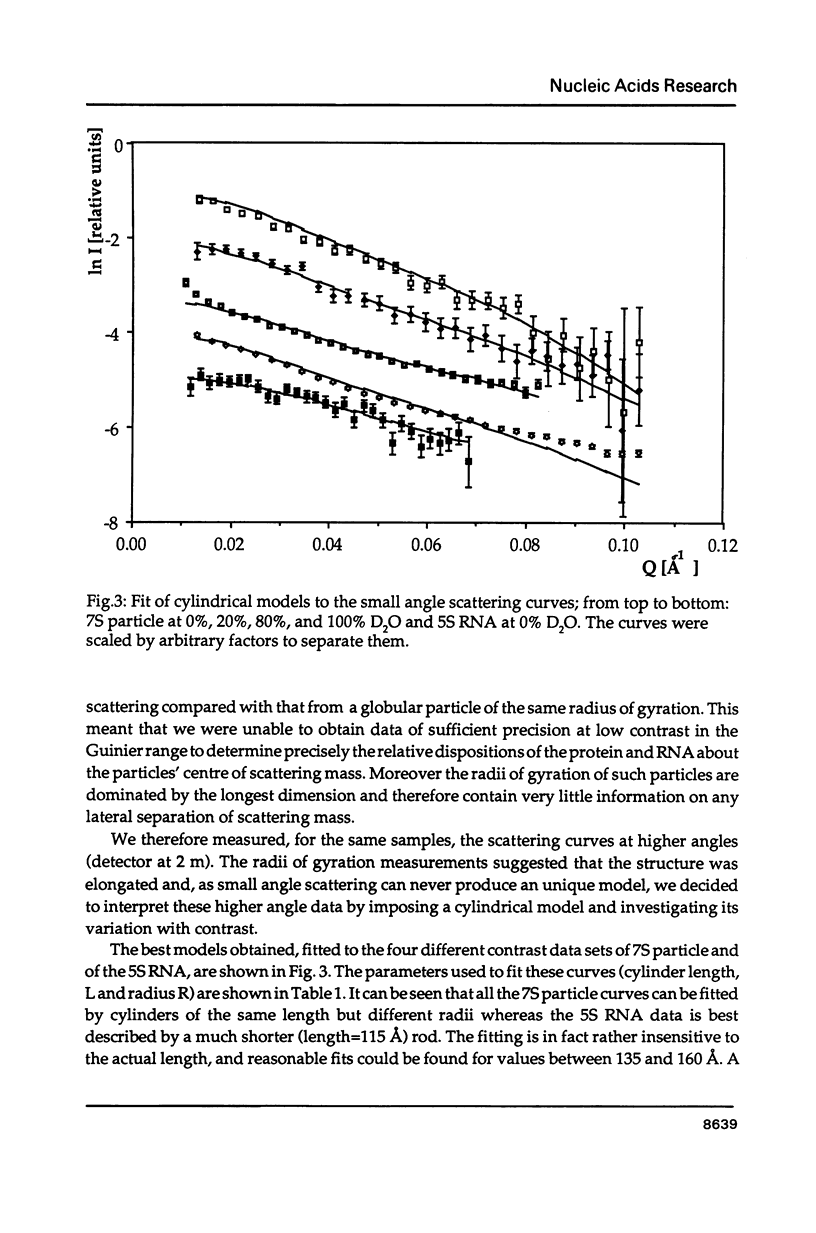
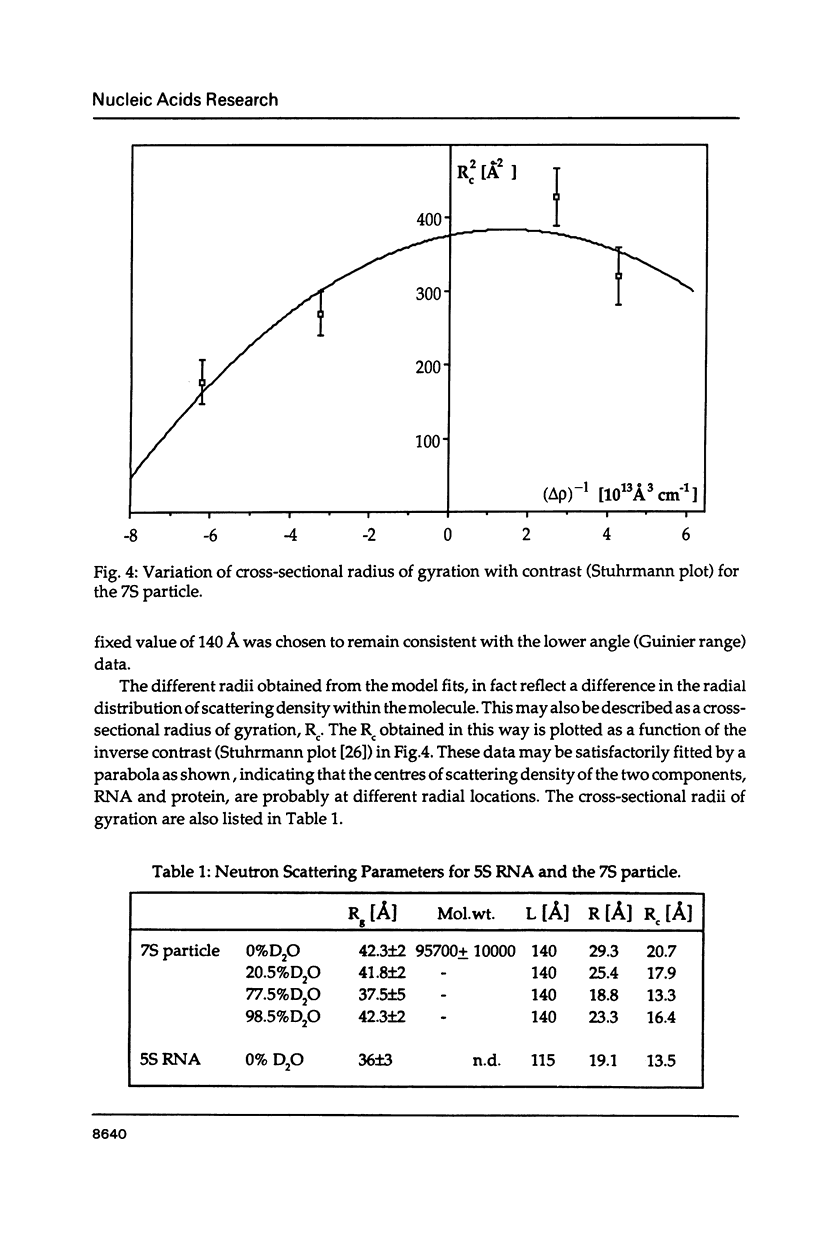
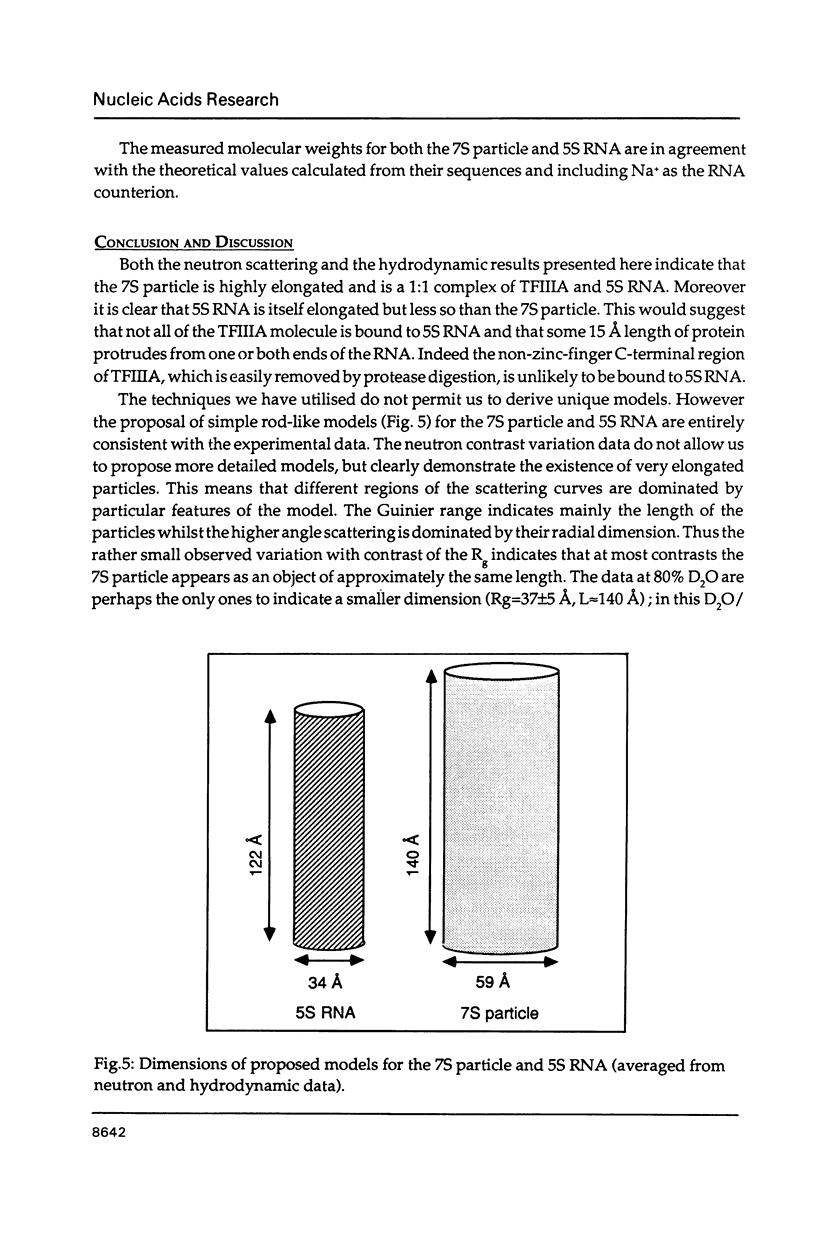
The precise molecular composition of the Xenopus laevis TFIIIA-5S ribosomal RNA complex (7S particle) has been established from small angle neutron and dynamic light scattering. The molecular weight of the particle was found to be 95,700 +/- 10,000 and 86,700 +/- 9000 daltons from these two methods respectively. The observed match point of 54.4% D2O obtained from contrast variation experiments indicates a 1:1 molar ratio. It is concluded that only a single molecule of TFIIIA, a zinc-finger protein, and of 5S RNA are present in this complex. At high neutron scattering contrast radius of gyration of 42.3 +/- 2 A was found for the 7S particle. In addition a diffusion coefficient of 4.4 x 10(-11) [m2 s-1] and a sedimentation coefficient of 6.2S were determined. The hydrodynamic radius obtained for the 7S particle is 48 +/- 5 A. A simple elongated cylindrical model with dimensions of 140 A length and 59 A diameter is compatible with the neutron results. A globular model can be excluded by the shallow nature of the neutron scattering curves. It is proposed that the observed difference of 15 A in length between the 7S particle and isolated 5S RNA most likely indicates that part(s) of the protein protrudes from the end(s) of the RNA molecule. There is no biochemical evidence for any gross alteration in 5S RNA conformation upon binding to TFIIIA.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg J. M. Proposed structure for the zinc-binding domains from transcription factor IIIA and related proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):99–102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieker J. J., Roeder R. G. Physical properties and DNA-binding stoichiometry of a 5 S gene-specific transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6158–6164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D. The role of stable complexes that repress and activate eucaryotic genes. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90366-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. S., Argos P. Fingers and helices. Nature. 1986 Nov 20;324(6094):215–215. doi: 10.1038/324215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. S., Ferguson C., Kingswell A., Winkler F. K., Leonard K. R. Electron microscopic study of crystals of the Xenopus laevis transcription factor IIIA-5S ribosomal RNA complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3802–3804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. S., Sander C., Argos P. The primary structure of transcription factor TFIIIA has 12 consecutive repeats. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 8;186(2):271–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80723-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen J., Brown R. S., Sproat B. S., Garrett R. A. Xenopus transcription factor IIIA binds primarily at junctions between double helical stems and internal loops in oocyte 5S RNA. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):453–460. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04775.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diakun G. P., Fairall L., Klug A. EXAFS study of the zinc-binding sites in the protein transcription factor IIIA. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):698–699. doi: 10.1038/324698a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairall L., Rhodes D., Klug A. Mapping of the sites of protection on a 5 S RNA gene by the Xenopus transcription factor IIIA. A model for the interaction. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 5;192(3):577–591. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90278-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Berg J. M., Pabo C. O. Metal-dependent folding of a single zinc finger from transcription factor IIIA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4841–4845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibel K. Comparison of neutron and X-ray scattering of dilute myoglobin solutions. J Mol Biol. 1975 Apr 5;93(2):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90131-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Coppard N. J., Brown R. S., Clark B. F., De Robertis E. M. 42S p48--the most abundant protein in previtellogenic Xenopus oocytes--resembles elongation factor 1 alpha structurally and functionally. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2409–2413. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02519.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller J. J., Zalkova T. N., Zirwer D., Misselwitz R., Gast K., Serdyuk I. N., Welfle H., Damaschun G. Comparison of the structure of ribosomal 5S RNA from E. coli and from rat liver using X-ray scattering and dynamic light scattering. Eur Biophys J. 1986;13(5):301–307. doi: 10.1007/BF00254212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Brown D. D. A specific transcription factor that can bind either the 5S RNA gene or 5S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard B., Wegnez M. Isolation of a 7S particle from Xenopus laevis oocytes: a 5S RNA-protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):241–245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provencher S. W. A Fourier method for the analysis of exponential decay curves. Biophys J. 1976 Jan;16(1):27–41. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85660-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Jackson I. J., Brown D. D. Domains of the positive transcription factor specific for the Xenopus 5S RNA gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90396-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmins P. A., Zaccai G. Low resolution structures of biological complexes studied by neutron scattering. Eur Biophys J. 1988;15(5):257–268. doi: 10.1007/BF00256476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamyatnin A. A. Protein volume in solution. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1972;24:107–123. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(72)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


