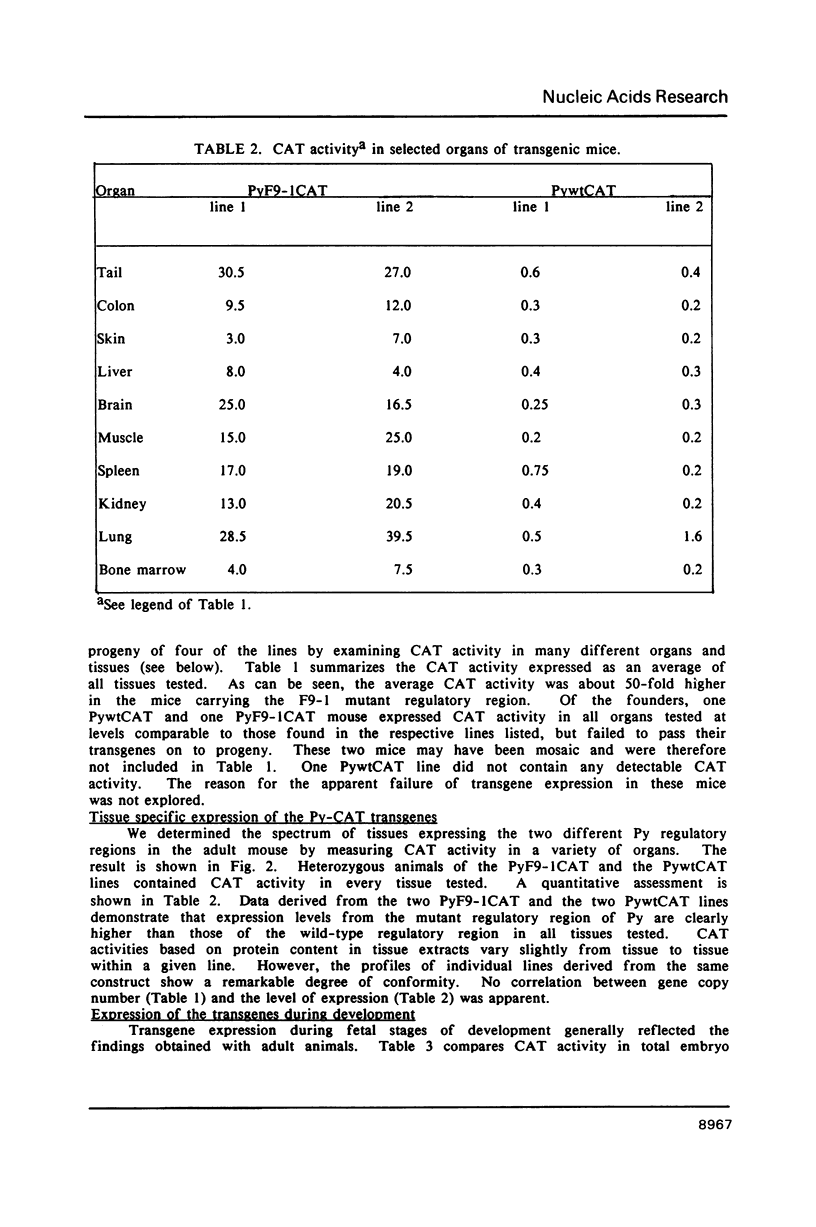
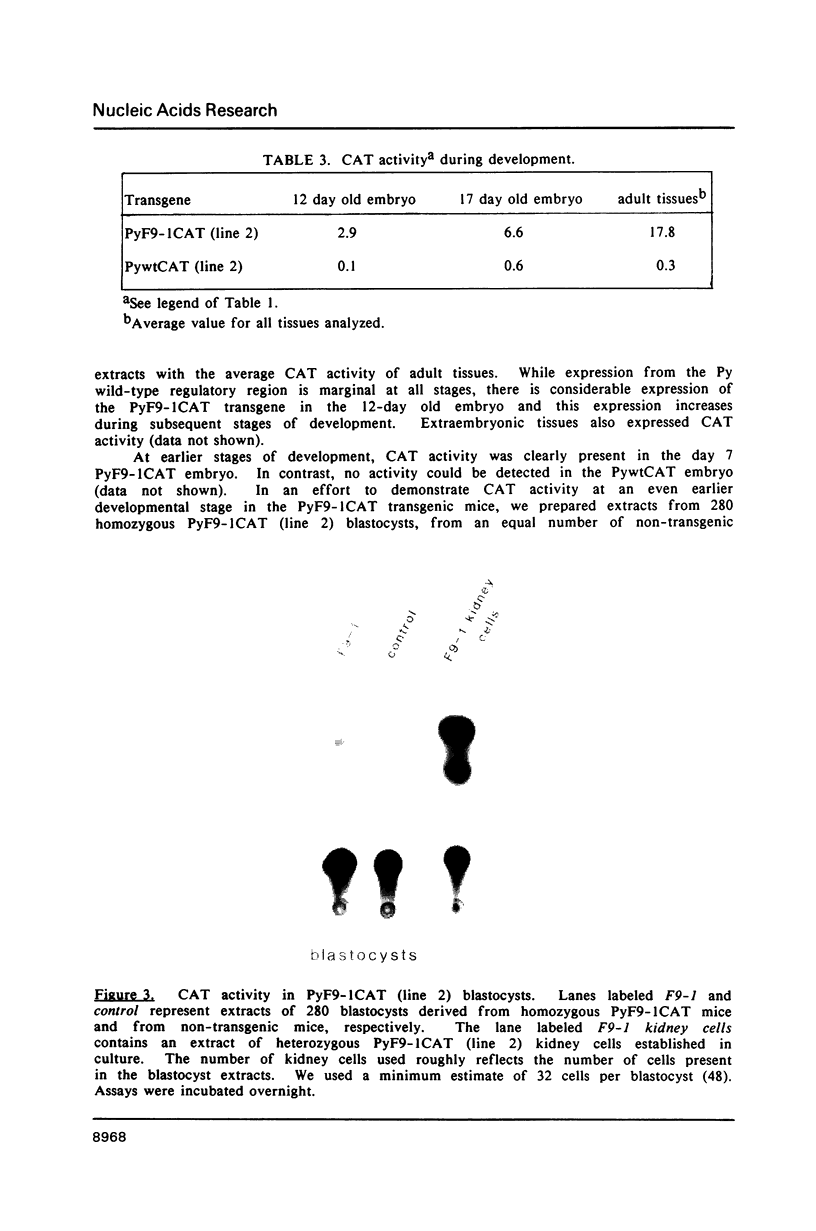
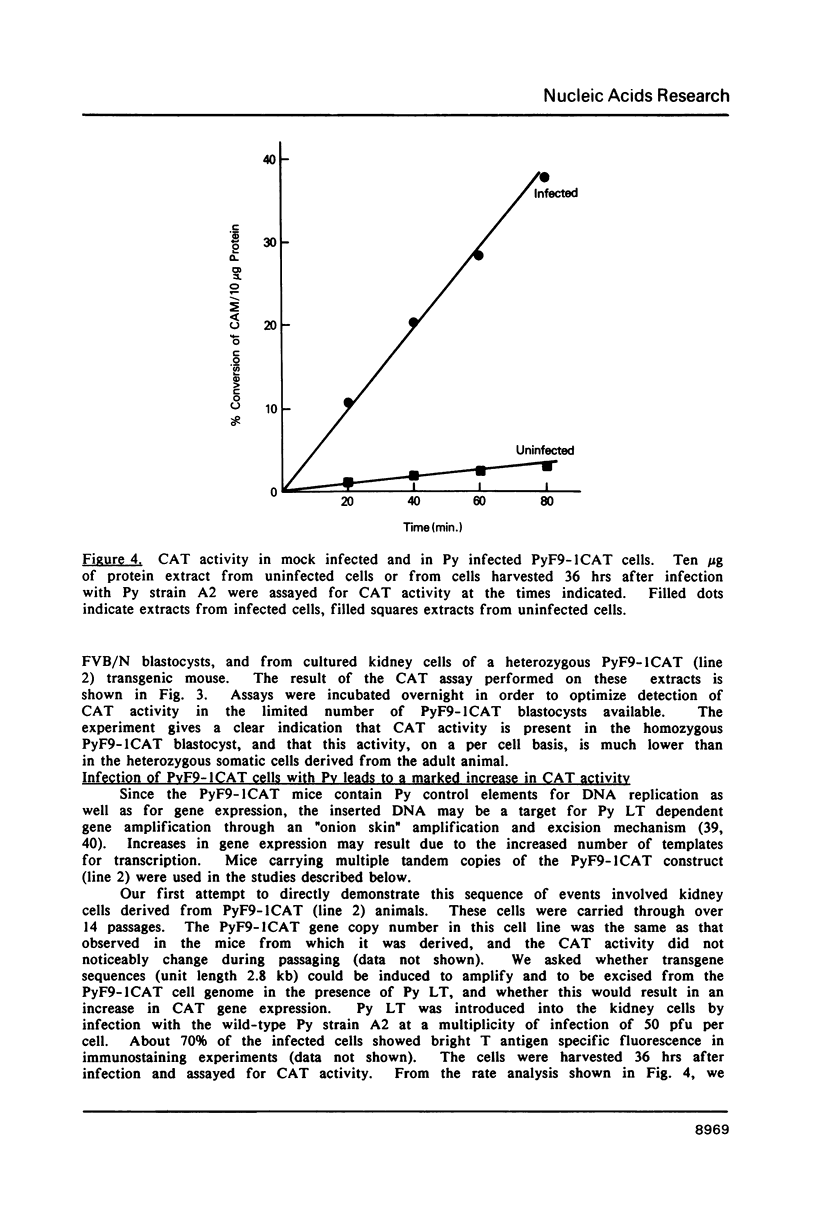
Abstract
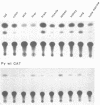
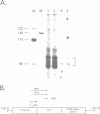
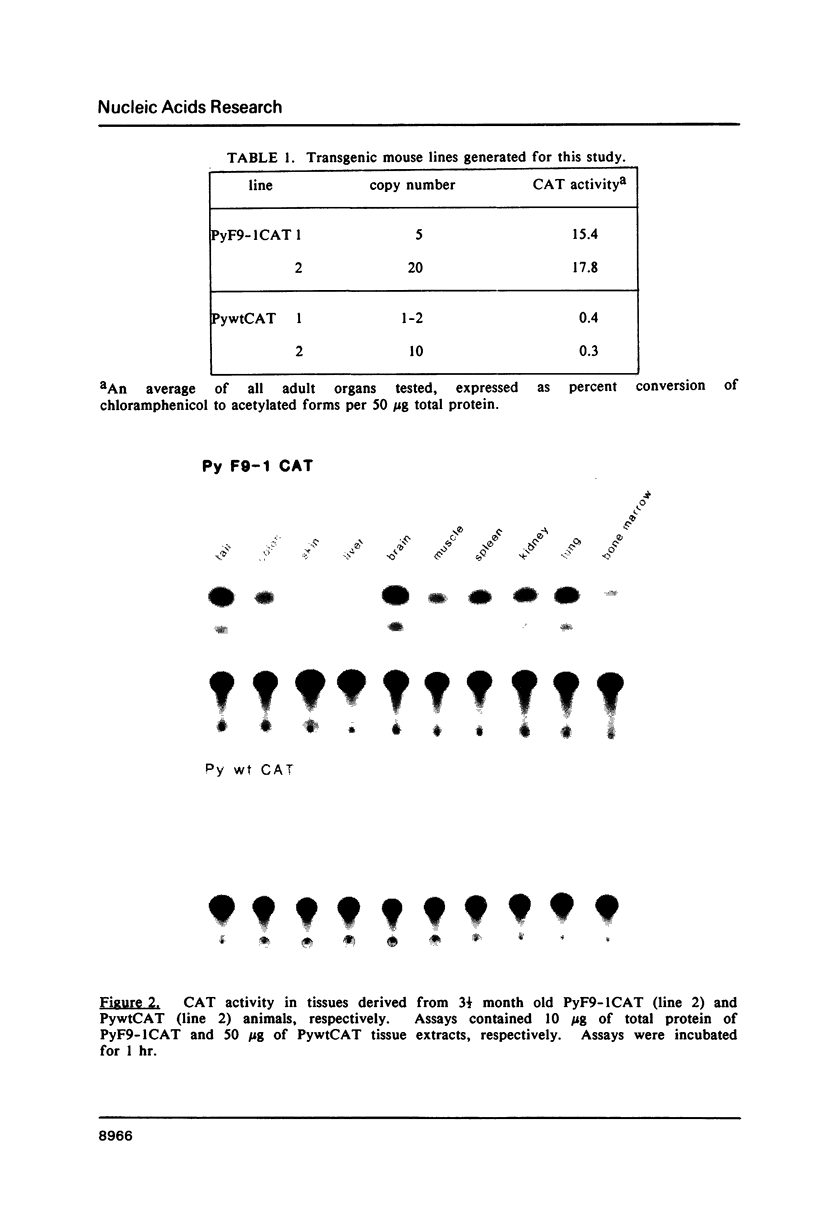
Two hybrid gene constructs consisting of wild-type and mutant polyoma regulatory regions fused to a bacterial reporter gene were inserted in the mouse germline. Both transgenes were expressed in a large number of different organs. However, marker gene expression controlled by the polyoma wild-type regulatory region was not detectable in the early embryo and remained low throughout the life of the animal while expression controlled by the polyoma F9-1 mutation was detectable in blastocysts and was significantly higher at later stages of development. The F9-1 hybrid gene was also amplifiable when large T-antigen was supplied in trans to mice or to kidney cells derived from these transgenic mice. Amplification resulted in the appearance of several hundred copies of episomal transgenes and a marked increase of marker gene RNA and protein. Our results suggest that the F9-1 mutation does not alter the target spectrum of gene expression in vivo but does create a more efficient enhancer element in the polyoma early control region. Transgene amplification based upon use of the polyoma regulatory elements may be a means of increasing expression of genes in transgenic mice.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basilico C., Gattoni S., Zouzias D., Valle G. D. Loss of integrated viral DNA sequences in polyomatransformed cells is associated with an active viral A function. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):645–659. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger H., Wintersberger E. Polyomavirus small T antigen enhances replication of viral genomes in 3T6 mouse fibroblasts. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):768–770. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.768-770.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Topp W., Sambrook J. Studies on simian virus 40 excision from cellular chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):709–719. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhnlein E., Chowdhury K., Gruss P. Functional analysis of the regulatory region of polyoma mutant F9-1 DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4789–4809. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhnlein E., Gruss P. Interaction of distinct nuclear proteins with sequences controlling the expression of polyomavirus early genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1401–1411. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowie A., Jat P., Kamen R. Determination of sequences at the capped 5' ends of polyoma virus early region transcripts synthesized in vivo and in vitro demonstrates an unusual microheterogeneity. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 5;159(2):225–255. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90494-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey L., Basilico C. Sequences in the polyomavirus DNA regulatory region involved in viral DNA replication and early gene expression. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):739–749. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.739-749.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilworth S. M., Cowie A., Kamen R. I., Griffin B. E. DNA binding activity of polyoma virus large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1941–1945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmerie W. G., Folk W. R. Regulation of polyomavirus transcription by large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6919–6923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton R. G., Basilico C. Regulation of polyoma virus early transcription in transformed cells by large T-antigen. Virology. 1982 Sep;121(2):384–392. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke B., Eckhart W. Polyoma gene function required for viral DNA synthesis. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):127–135. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann T., LaPorte P., Esty A. Nucleotide sequence studies of polyoma DNA. The Hpa II 3/5 junction to the Hpa II 4/Hae III 18 junction, encoding the origin of DNA replication and the 5' end of the early region. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6561–6567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura F. K., Deininger P. L., Friedmann T., Linney E. Mutation near the polyoma DNA replication origin permits productive infection of F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):809–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90445-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudray P., Tyndall C., Kamen R., Cuzin F. The high affinity binding site on polyoma virus DNA for the viral large-T protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5697–5710. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor R. B., Tsukamoto A., Montell C., Berk A. J. Enhanced expression of adenovirus transforming proteins. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):276–285. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.276-285.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Two distinct enhancers with different cell specificities coexist in the regulatory region of polyoma. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katinka M., Vasseur M., Montreau N., Yaniv M., Blangy D. Polyoma DNA sequences involved in control of viral gene expression in murine embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1981 Apr 23;290(5808):720–722. doi: 10.1038/290720a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern F. G., Pellegrini S., Cowie A., Basilico C. Regulation of polyomavirus late promoter activity by viral early proteins. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):275–285. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.275-285.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khillan J. S., Schmidt A., Overbeek P. A., de Crombrugghe B., Westphal H. Developmental and tissue-specific expression directed by the alpha 2 type I collagen promoter in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):725–729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Satake M., Furukawa K., Reichel R., Ito Y., Nevins J. R. A factor discriminating between the wild-type and a mutant polyomavirus enhancer. Nature. 1987 Jul 2;328(6125):87–89. doi: 10.1038/328087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krippl B., Ferguson B., Rosenberg M., Westphal H. Functions of purified E1A protein microinjected into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6988–6992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kryszke M. H., Piette J., Yaniv M. Induction of a factor that binds to the polyoma virus A enhancer on differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):254–256. doi: 10.1038/328254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostapchuk P., Diffley J. F., Bruder J. T., Stillman B., Levine A. J., Hearing P. Interaction of a nuclear factor with the polyomavirus enhancer region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8550–8554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbeek P. A., Chepelinsky A. B., Khillan J. S., Piatigorsky J., Westphal H. Lens-specific expression and developmental regulation of the bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene driven by the murine alpha A-crystallin promoter in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7815–7819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Germ-line transformation of mice. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:465–499. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini S., Basilico C. Amplification and expression of foreign genes in cells producing polyoma virus large T-antigen. Oncogene Res. 1987 Jun;1(1):23–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini S., Dailey L., Basilico C. Amplification and excision of integrated polyoma DNA sequences require a functional origin of replication. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):943–949. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps W. C., Howley P. M. Transcriptional trans-activation by the human papillomavirus type 16 E2 gene product. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1630–1638. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1630-1638.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Kryszke M. H., Yaniv M. Specific interaction of cellular factors with the B enhancer of polyoma virus. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2675–2685. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03987.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz B. J., Mueller C. R., Hassell J. A. Polyomavirus large T antigen binds independently to multiple, unique regions on the viral genome. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):600–610. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.600-610.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekikawa K., Levine A. J. Isolation and characterization of polyoma host range mutants that replicate in nullipotential embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1100–1104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R., McLaren A. Factors affecting the time of formation of the mouse blastocoele. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1977 Oct;41:79–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeda E., Arrand J. R., Smolar N., Walsh J. E., Griffin B. E. Coding potential and regulatory signals of the polyoma virus genome. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):445–453. doi: 10.1038/283445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeda E., Kimura G., Miura K. Similarity of nucleotide sequences around the origin of DNA replication in mouse polyoma virus and simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):162–166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang W. J., Berger S. L., Triezenberg S. J., Folk W. R. Nucleotides in the polyomavirus enhancer that control viral transcription and DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1681–1690. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyndall C., La Mantia G., Thacker C. M., Favaloro J., Kamen R. A region of the polyoma virus genome between the replication origin and late protein coding sequences is required in cis for both early gene expression and viral DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6231–6250. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasseur M., Katinka M., Herbomel P., Yaniv M., Blangy D. Physical and biological features of polyoma virus mutants able to infect embryonal carcinoma cell lines. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):800–808. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.800-808.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Lupton S., Kamen R. Polyomavirus enhancer contains multiple redundant sequence elements that activate both DNA replication and gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):649–658. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westphal H., Overbeek P. A., Khillan J. S., Chepelinsky A. B., Schmidt A., Mahon K. A., Bernstein K. E., Piatigorsky J., de Crombrugghe B. Promoter sequences of murine alpha A crystallin, murine alpha 2(I) collagen or of avian sarcoma virus genes linked to the bacterial chloramphenicol acetyl transferase gene direct tissue-specific patterns of chloramphenicol acetyl transferase expression in transgenic mice. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:411–416. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittingham D. G. Culture of mouse ova. J Reprod Fertil Suppl. 1971 Jun;14:7–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Schaffner W. A small segment of polyoma virus DNA enhances the expression of a cloned beta-globin gene over a distance of 1400 base pairs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6251–6264. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Schaffner W., Tyndall C., Lupton S., Kamen R. Polyoma virus DNA replication requires an enhancer. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):242–246. doi: 10.1038/312242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]