Abstract
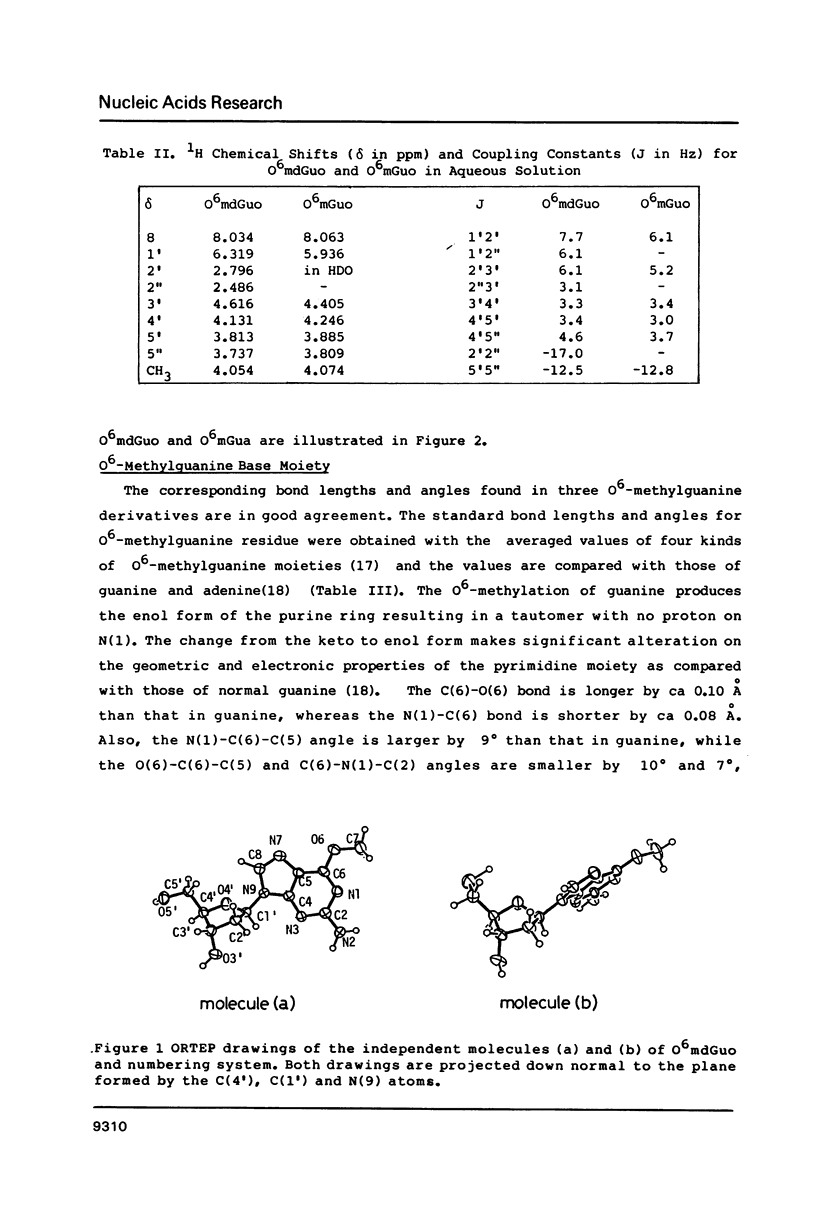
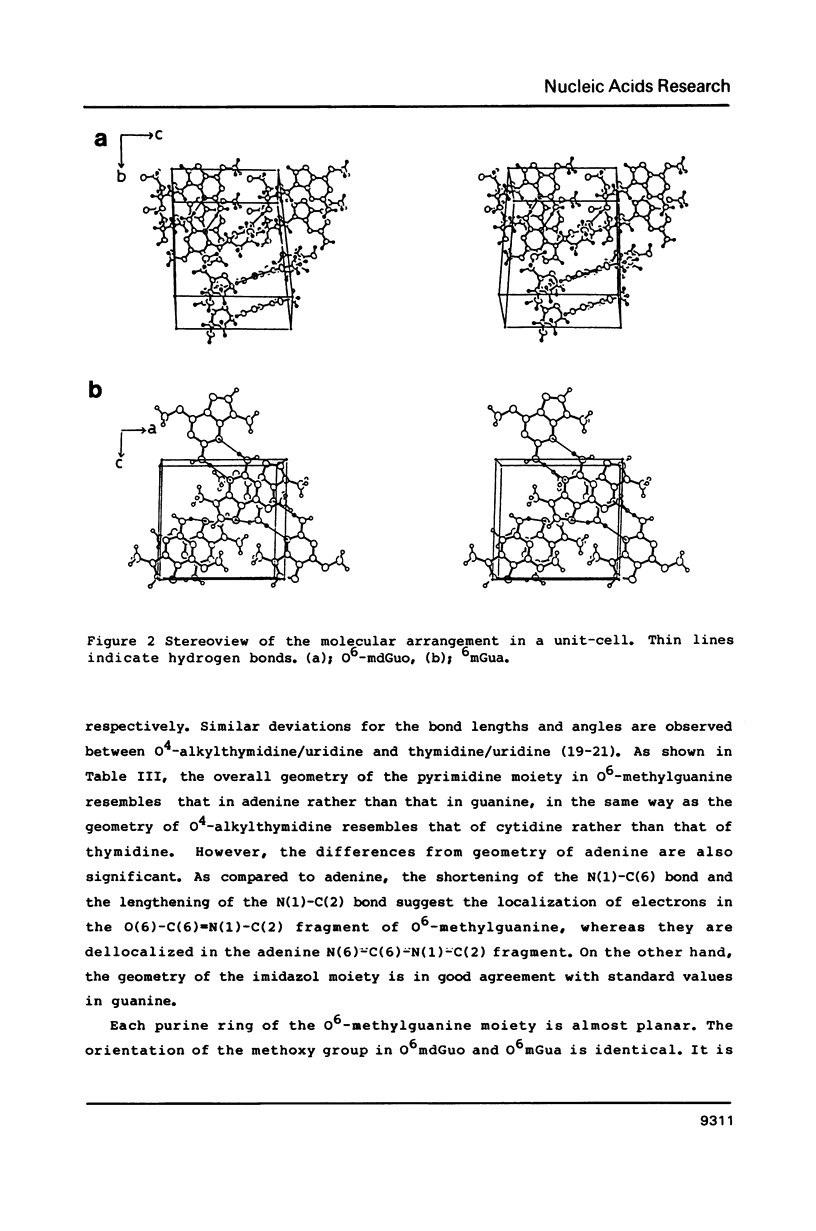
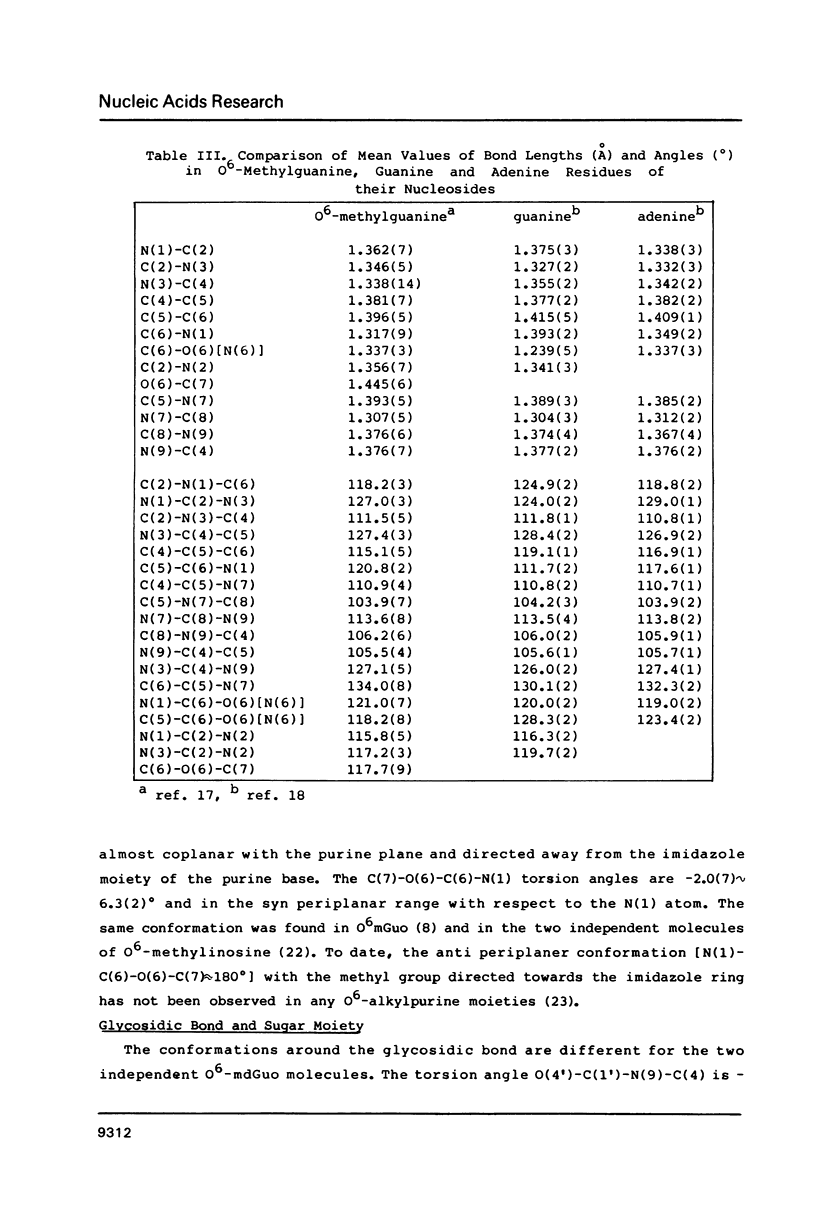
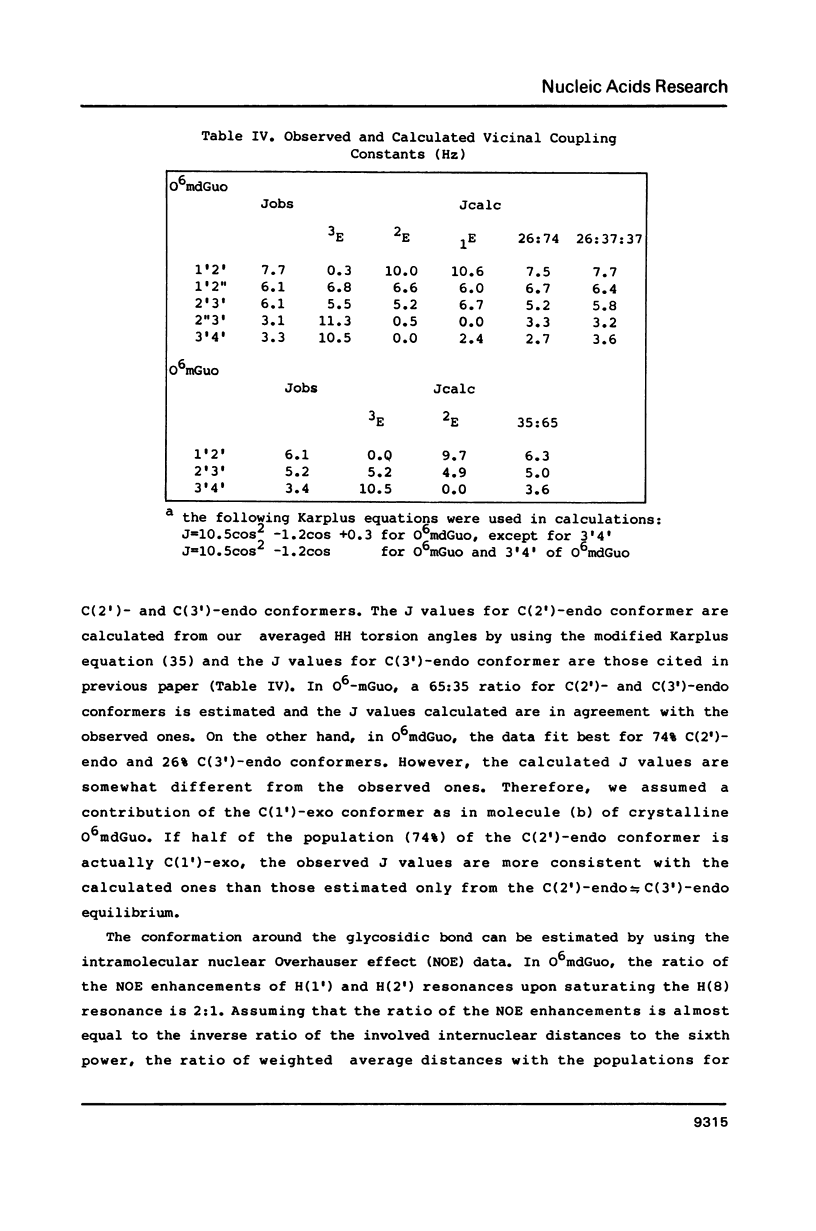
O6-Methylation of guanine residues in DNA can induce mutations by formation of base mispairing due to the deprotonation of N(1). The electronic, geometric and conformational properties of three N(9)-Substituted O6-methylguanine derivatives, O6-methyldeoxyguanosine (O6mdGuo), O6-methylguanosine (O6mGuo) and O6, 9-dimethylguanine (O6mdGua), were investigated by X-ray and/or NMR studies. O6mdGuo crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P2(1) with cell parameters a = 5.267(1), b = 19.109(2), c = 12.330(2) A, beta = 92.45(1) degrees, V = 1239.8(3) A3, z = 4 (two nucleosides per asymmetric unit), and O6mGua in the monoclinic space group P2(1)/n with cell parameters a = 10.729(2), b = 7.640(1) c = 10.216(1) A, beta = 92.17(2) degrees, V = 836.7(2) A3, z = 4. The geometry and conformation of O6-methylguanine moieties observed in both crystals and are very similar. Furthermore, the molecular dimensions of the O6methylguanine residue resemble more closely those of adenine than those of guanine. The methoxy group is coplanar with the purine ring, the methyl group being cis to N(1). The conformation of O6-methylguanine nucleosides is variable. The glycosidic conformation of O6mdGuo is anti for molecule (a) and high-anti for molecule (b) in the crystal, while that of O6mGuo is syn [Parthasarathy, R & Fridey, S. M. (1986) Carcinogenesis 7, 221-227]. The sugar ring pucker of O6mdGuo is C(2')-endo for molecule (a) and C(1')-exo for molecule (b). The C(4')-C(5') exocyclic bond conformation in O6mdGuo is gauche- for molecule (a) but trans for molecule (b), in contrast with gauche+ for O6mGuo. The hydrogen bonds exhibited by O6-methylguanine derivatives differ from those in guanine derivatives; the amino N(2) and ring N(3) and N(7) atoms of O6-methylguanine residues are involved in hydrogen bonding. 1H-NMR data for O6mdGuo and O6mdGuo reveal the predominance of a C(2')-endo type sugar puckering. In O6mdGuo, however, a contribution of a C(1')-exo sugar puckering is significant. The NOE data also indicate that O6mdGuo molecules exist with nearly equal population for anti (including high anti) and syn glycosidic conformations. These observations and their biological implications are discussed.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altona C., Sundaralingam M. Conformational analysis of the sugar ring in nucleosides and nucleotides. Improved method for the interpretation of proton magnetic resonance coupling constants. J Am Chem Soc. 1973 Apr 4;95(7):2333–2344. doi: 10.1021/ja00788a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan R. G., Pyzalska D., Blonski W. J., Hruska F. E., Sundaralingam M. Crystal structure of the promutagen O4-methylthymidine: importance of the anti conformation of the O(4) methoxy group and possible mispairing of O4-methylthymidine with guanine. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 11;25(5):1181–1185. doi: 10.1021/bi00353a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugg C. E., Thomas J. M., Sundaralingam M., Rao S. T. Stereochemistry of nucleic acids and their constituents. X. Solid-state base-stacking patterns in nucleic acid constituents and polynucleotides. Biopolymers. 1971;10(1):175–219. doi: 10.1002/bip.360100113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell J. W., Kollman P. A. The effect of methylation of the 6 oxygen of guanine on the structure and stability of double helical DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1985 Aug;3(1):57–66. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1985.10508398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruse W. B., Egert E., Kennard O., Sala G. B., Salisbury S. A., Viswamitra M. A. Self base pairing in a complementary deoxydinucleoside monophosphate duplex: crystal and molecular structure of deoxycytidylyl-(3'-5')-deoxyguanosine. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 12;22(8):1833–1839. doi: 10.1021/bi00277a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Sedgwick B., Robins P., Totty N., Waterfield M. D., Lindahl T. Active site and complete sequence of the suicidal methyltransferase that counters alkylation mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2688–2692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake J. W., Baltz R. H. The biochemistry of mutagenesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:11–37. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.000303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer P. B., Foster A. B., Jarman M., Tisdale M. J. The alkylation of 2'-deoxyguanosine and of thymidine with diazoalkanes. Some observations on o-alkylation. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;135(1):203–213. doi: 10.1042/bj1350203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney B. L., Marky L. A., Jones R. A. Synthesis and characterization of a set of four dodecadeoxyribonucleoside undecaphosphates containing O6-methylguanine opposite adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5686–5691. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerchman L. L., Dombrowski J., Ludlum D. B. Synthesis and polymerization of O 6 -methylguanosine 5'-diphosphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 31;272(4):672–675. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90527-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter W. N., Brown T., Anand N. N., Kennard O. Structure of an adenine-cytosine base pair in DNA and its implications for mismatch repair. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):552–555. doi: 10.1038/320552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loveless A. Possible relevance of O-6 alkylation of deoxyguanosine to the mutagenicity and carcinogenicity of nitrosamines and nitrosamides. Nature. 1969 Jul 12;223(5202):206–207. doi: 10.1038/223206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta J. R., Ludlum D. B. Synthesis and properties of O6-methyldeoxyguanylic acid and its copolymers with deoxycytidylic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 21;521(2):770–778. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90316-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Kondo H., Kawabata S., Iwanaga S., Sekiguchi M. Purification and structure of the intact Ada regulatory protein of Escherichia coli K12, O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7281–7288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson M., Lindahl T. Repair of alkylated DNA in Escherichia coli. Methyl group transfer from O6-methylguanine to a protein cysteine residue. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10569–10571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parthasarathy R., Fridey S. M. Conformation of O6-alkylguanosines: molecular mechanism of mutagenesis. Carcinogenesis. 1986 Feb;7(2):221–227. doi: 10.1093/carcin/7.2.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer B., Kuśmierek J. T. Chemical mutagenesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:655–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow E. T., Foote R. S., Mitra S. Base-pairing properties of O6-methylguanine in template DNA during in vitro DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8095–8100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata Y., Fukumoto S., Hamada K., Fujiwara T., Tomita K. A novel guanine-guanine base pairing: crystal structure of a complex between 7-methylguanosine and its iodide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6475–6486. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


