Abstract
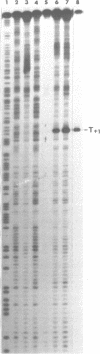
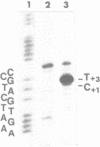
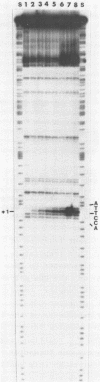
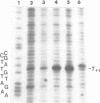
Upon irradiation of the RNA polymerase-lacUV5 or deoP1 promoter complex with short wavelength ultraviolet light (lambda less than or equal to 300 nm) the polymerase is covalently crosslinked at an efficiency of greater than 10% to the first transcribed base of the template DNA strand when this is a thymine. The temperature dependence of this RNA polymerase-T+1 photoreaction strongly indicates a relation to the formation of the open complex. It is suggested that open complex formation is preceded or accompanied by a specific contact between the RNA polymerase and the first transcribed base of the DNA template.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker M. M., Wang J. C. Use of light for footprinting DNA in vivo. Nature. 1984 Jun 21;309(5970):682–687. doi: 10.1038/309682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Jendrisak J. J. A procedure for the rapid, large-scall purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4634–4638. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterji D., Wu F. Y. Direct coordination of nucleotide with the intrinsic metal in Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. A nuclear magnetic resonance study with cobalt-substituted enzyme. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 14;21(19):4657–4664. doi: 10.1021/bi00262a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenchick A., Beabealashvilli R., Mirzabekov A. Topography of interaction of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase subunits with lac UV5 promoter. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 1;128(1):46–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour D. S., Lis J. T. In vivo interactions of RNA polymerase II with genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2009–2018. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison C. A., Turner D. H., Hinkle D. C. Laser crosslinking of E. coli RNA polymerase and T7 DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 10;10(7):2399–2414. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.7.2399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heil A., Zillig W. Reconstitution of bacterial DNA-dependent RNA-polymerase from isolated subunits as a tool for the elucidation of the role of the subunits in transcription. FEBS Lett. 1970 Dec;11(3):165–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80519-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeppesen C., Buchardt O., Henriksen U., Nielsen P. E. Photocleavage of DNA and photofootprinting of E. coli RNA polymerase bound to promoter DNA by azido-9-acridinylamines. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):5755–5770. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.5755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkegaard K., Buc H., Spassky A., Wang J. C. Mapping of single-stranded regions in duplex DNA at the sequence level: single-strand-specific cytosine methylation in RNA polymerase-promoter complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2544–2548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruger K., Grabowski P. J., Zaug A. J., Sands J., Gottschling D. E., Cech T. R. Self-splicing RNA: autoexcision and autocyclization of the ribosomal RNA intervening sequence of Tetrahymena. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):147–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90414-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. E., Jeppesen C., Egholm M., Buchardt O. Adenosine-guanosine preferential photocleavage of DNA by azido-benzoyl- and diazocyclopenta-dienylcarbonyloxy derivatives of 9-aminoacridine. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):3877–3888. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.3877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selleck S. B., Majors J. Photofootprinting in vivo detects transcription-dependent changes in yeast TATA boxes. Nature. 1987 Jan 8;325(7000):173–177. doi: 10.1038/325173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. B. The molecular topography of RNA polymerase-promoter interaction. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer P., Wu C. W. Promoter search by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase on a circular DNA template. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14178–14189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spassky A., Kirkegaard K., Buc H. Changes in the DNA structure of the lac UV5 promoter during formation of an open complex with Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1985 May 21;24(11):2723–2731. doi: 10.1021/bi00332a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. The study of histone--histone associations by chemical cross-linking. Methods Cell Biol. 1978;18:429–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentin-Hansen P., Aiba H., Schümperli D. The structure of tandem regulatory regions in the deo operon of Escherichia coli K12. EMBO J. 1982;1(3):317–322. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01167.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu F. Y., Wu C. W. Fluorescent affinity labeling of initiation site on ribonucleic acid polymerase of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2562–2566. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]