Abstract
DNA polymerase beta (beta-polymerase) is a housekeeping enzyme involved in DNA repair in vertebrate cells. We used a cDNA probe to study abundance of beta-polymerase mRNA in cultured human cells. The mRNA level in synchronized HeLa cells, representing different stages of the cell-cycle, varied only slightly. Contact inhibited fibroblasts AG-1522 contained the same level of mRNA as growing cells. The steady-state level of mRNA in fibroblasts is equivalent to 6 molecules per cell. The results indicate that the beta-polymerase transcript is "low abundance" and is neither cell-cycle nor growth phase responsive.
Full text
PDF



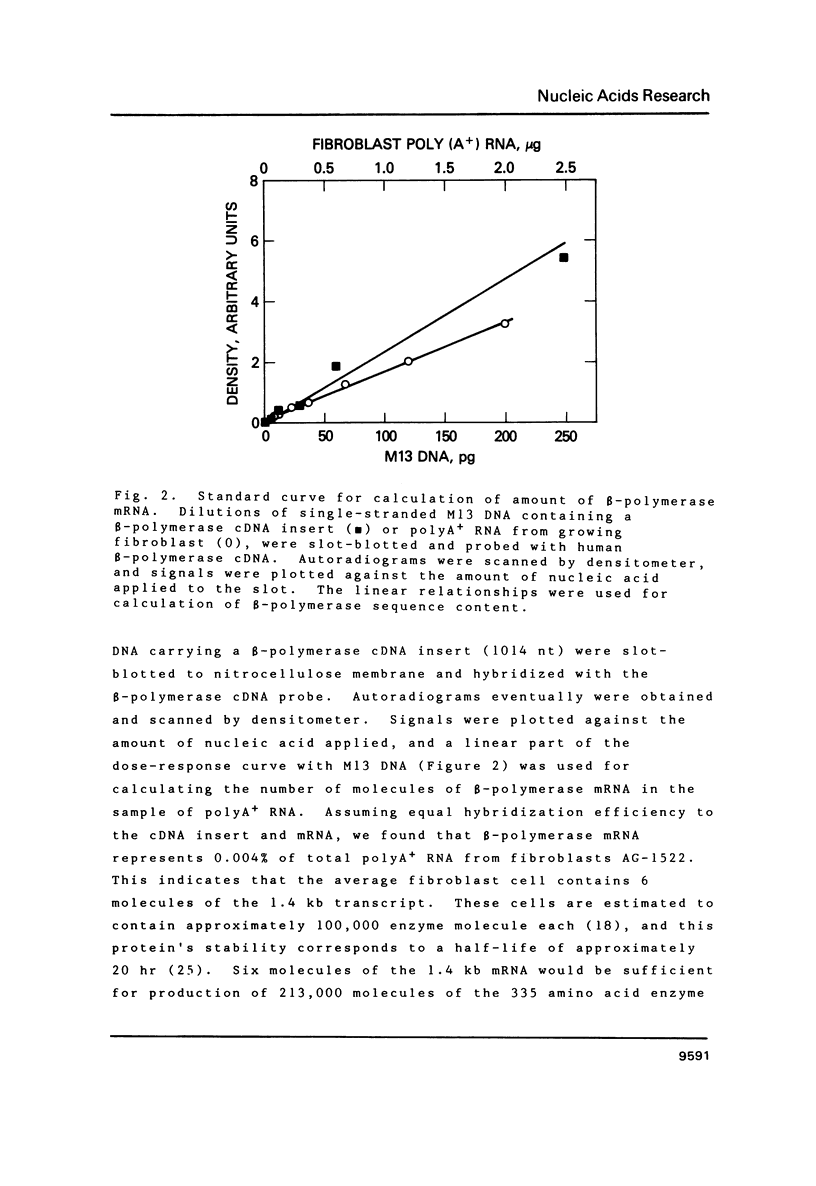
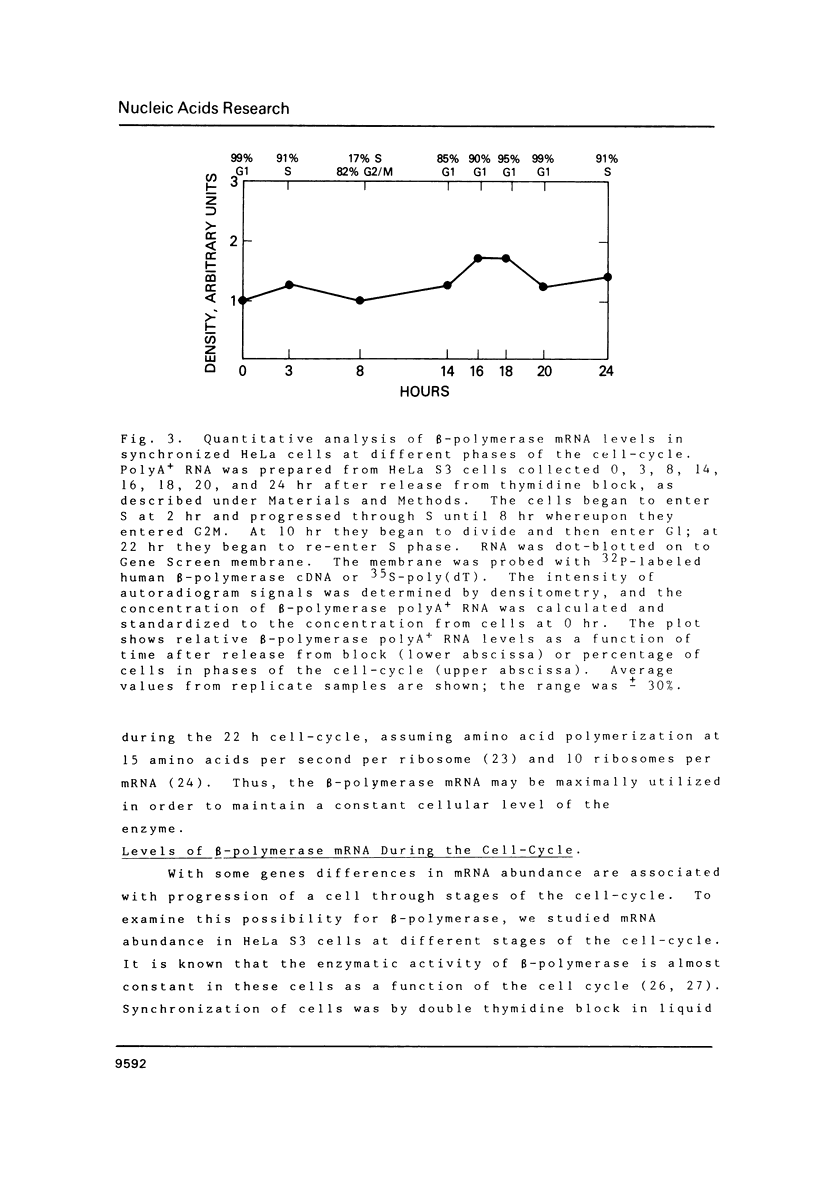
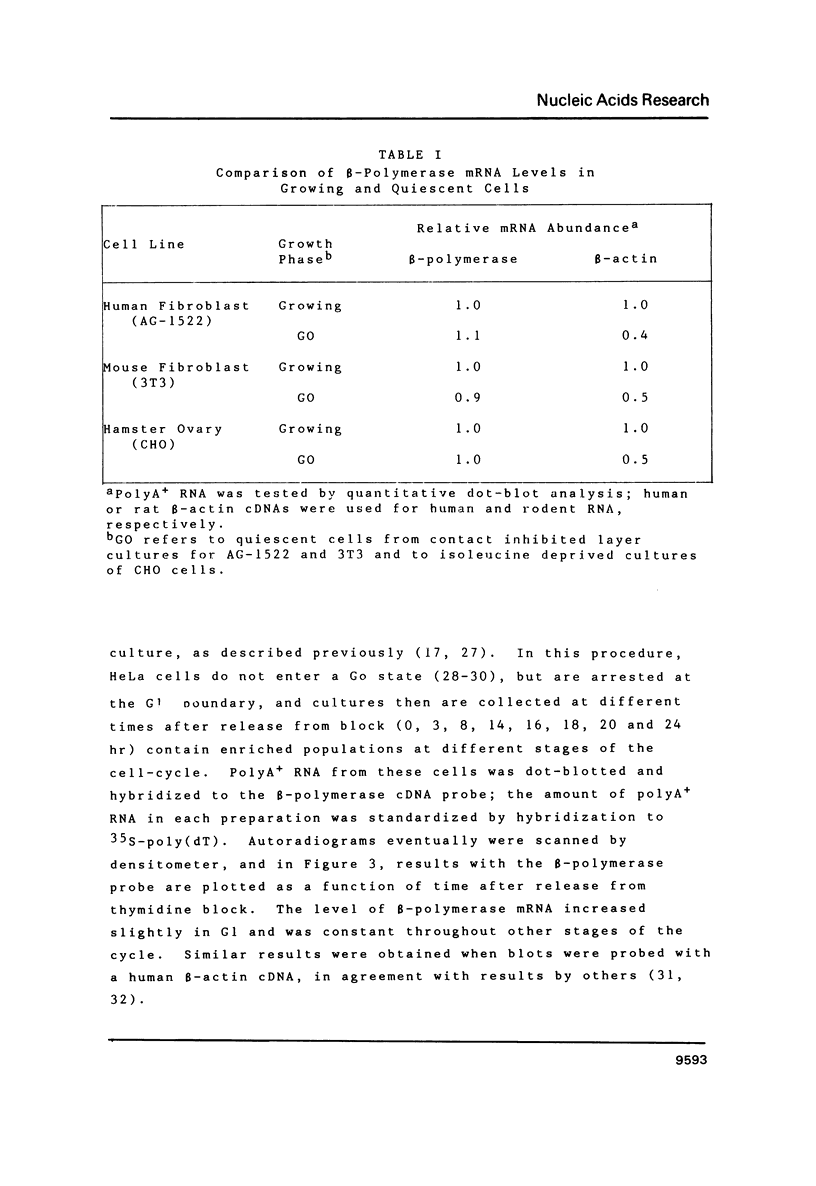



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbotts J., SenGupta D. N., Zmudzka B., Widen S. G., Notario V., Wilson S. H. Expression of human DNA polymerase beta in Escherichia coli and characterization of the recombinant enzyme. Biochemistry. 1988 Feb 9;27(3):901–909. doi: 10.1021/bi00403a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baserga R., Costlow M., Rovera G. Changes in membrane function and chromatin template activity in diploid and transformed cells in culture. Fed Proc. 1973 Nov;32(11):2115–2118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertazzoni U., Scovassi A. I., Brun G. M. Chick-embryo DNA polymerase gamma. Identity of gamma-polymerases purified from nuclei and mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Dec 1;81(2):237–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11945.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Gray H. E., Pardee A. B., Dean M., Sonenshein G. E. Cell-cycle control of c-myc but not c-ras expression is lost following chemical transformation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carneiro M., Schibler U. Accumulation of rare and moderately abundant mRNAs in mouse L-cells is mainly post-transcriptionally regulated. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 5;178(4):869–880. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90316-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. M., Brown M., Bollum F. J. Induction of DNA polymerase in mouse L cells. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 15;74(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90349-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. M. Low molecular weight deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from calf thymus chromatin. I. Preparation of homogeneous enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3789–3795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R. W., Baril E. F. Nuclear DNA polymerases and the HeLa cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7951–7957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E. Structure of repaired sites in human DNA synthesized in the presence of inhibitors of DNA polymerases alpha and beta in human fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Apr 15;739(3):301–311. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(83)90105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Sullivan K. F. Molecular biology and genetics of tubulin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:331–365. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobianchi F., SenGupta D. N., Zmudzka B. Z., Wilson S. H. Structure of rodent helix-destabilizing protein revealed by cDNA cloning. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3536–3543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. M. Rates of DNA synthesis during the S-phase of HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8570–8577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dresler S. L., Lieberman M. W. Identification of DNA polymerases involved in DNA excision repair in diploid human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9990–9994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. R., Wan K. M., Ben-Ze'ev A., Penman S. Regulation of actin mRNA levels and translation responds to changes in cell configuration. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):182–189. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornace A. J., Jr, Mitchell J. B. Induction of B2 RNA polymerase III transcription by heat shock: enrichment for heat shock induced sequences in rodent cells by hybridization subtraction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5793–5811. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster K. A., Collins J. M. The interrelation between DNA synthesis rates and DNA polymerases bound to the nuclear matrix in synchronized HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4229–4235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAJTHA L. G. Problems of bone marrow cell kinetics. Postgrad Med J. 1962 Jan;38:41–47. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.38.435.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride O. W., Zmudzka B. Z., Wilson S. H. Chromosomal location of the human gene for DNA polymerase beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):503–507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. R., Chinault D. N. The roles of DNA polymerases alpha, beta, and gamma in DNA repair synthesis induced in hamster and human cells by different DNA damaging agents. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10204–10209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. B., Karawya E., Kinsella T. J., Wilson S. H. Measurement of DNA polymerase beta in skin fibroblast cell lines from patients with ataxia telangiectasia. Mutat Res. 1985 Nov;146(3):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(85)90071-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Planck S. R., Tanabe K., Wilson S. H. Distinction between mouse DNA polymerases alpha and beta by tryptic peptide mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 25;8(12):2771–2782. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.12.2771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SenGupta D. N., Zmudzka B. Z., Kumar P., Cobianchi F., Skowronski J., Wilson S. H. Sequence of human DNA polymerase beta mRNA obtained through cDNA cloning. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):341–347. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90916-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T. S., Eichler D. C., Korn D. Effect of Mn2+ on the in vitro activity of human deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase beta. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 1;16(22):4927–4934. doi: 10.1021/bi00641a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S., Abbotts J., Widen S. Progress toward molecular biology of DNA polymerase beta. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 28;949(2):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K., Hanaoka F., Yamada M. Effects of aphidicolin and/or 2',3'-dideoxythymidine on DNA repair induced in HeLa cells by four types of DNA-damaging agents. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10412–10417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zmudzka B. Z., SenGupta D., Matsukage A., Cobianchi F., Kumar P., Wilson S. H. Structure of rat DNA polymerase beta revealed by partial amino acid sequencing and cDNA cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5106–5110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]