Abstract
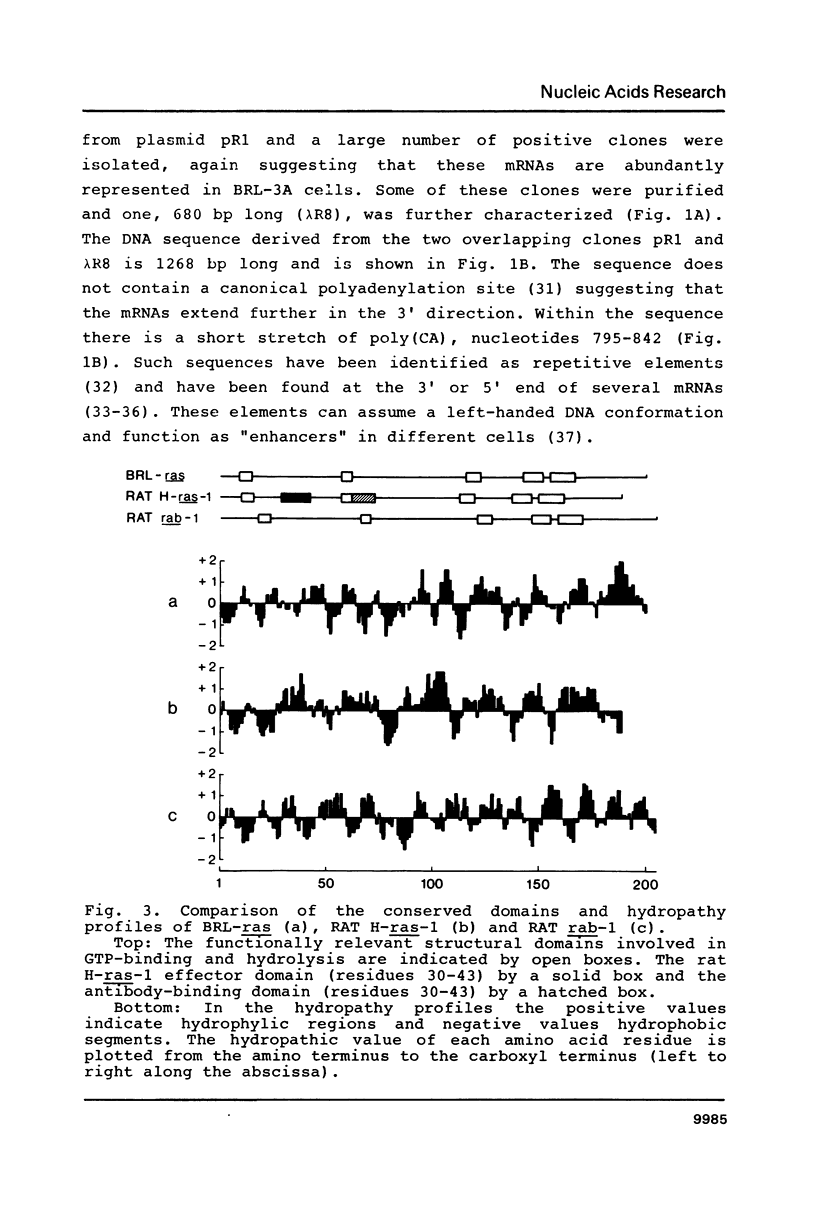
A new member of the ras genes superfamily was isolated from a cDNA library derived from a rat liver cell line (BRL-3A). The predicted 201 amino acids ras-like protein shows 30-35% homology with other members of the ras and ras-related gene products so far described. Conserved features include the GTP-binding and hydrolysis domains and the carboxyl terminal cysteine residues. A protein of the expected size (Mr 23,000) was synthesized in an in vitro transcription-translation system. The BRL-ras gene is present in single copy in the rat genome and is ubiquitously expressed at high levels in all tissues and cell lines examined.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acquaviva A. M., Bruni C. B., Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Cell-free synthesis of rat insulin-like growth factor II. Diabetes. 1982 Jul;31(7):656–658. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.7.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P. S., Lacal J. C. Expression of the Aplysia californica rho gene in Escherichia coli: purification and characterization of its encoded p21 product. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3620–3628. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. L., Graham D. E., Nissley S. P., Hill D. J., Strain A. J., Rechler M. M. Developmental regulation of insulin-like growth factor II mRNA in different rat tissues. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13144–13150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Direct identification of palmitic acid as the lipid attached to p21ras. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):116–122. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calés C., Hancock J. F., Marshall C. J., Hall A. The cytoplasmic protein GAP is implicated as the target for regulation by the ras gene product. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):548–551. doi: 10.1038/332548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardin P., Tavitian A. The ral gene: a new ras related gene isolated by the use of a synthetic probe. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2203–2208. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04485.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Nature of Col E 1 plasmid replication in Escherichia coli in the presence of the chloramphenicol. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):667–676. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.667-676.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFeo-Jones D., Scolnick E. M., Koller R., Dhar R. ras-Related gene sequences identified and isolated from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):707–709. doi: 10.1038/306707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dever T. E., Glynias M. J., Merrick W. C. GTP-binding domain: three consensus sequence elements with distinct spacing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1814–1818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar R., Ellis R. W., Shih T. Y., Oroszlan S., Shapiro B., Maizel J., Lowy D., Scolnick E. Nucleotide sequence of the p21 transforming protein of Harvey murine sarcoma virus. Science. 1982 Sep 3;217(4563):934–936. doi: 10.1126/science.6287572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dull T. J., Gray A., Hayflick J. S., Ullrich A. Insulin-like growth factor II precursor gene organization in relation to insulin gene family. 1984 Aug 30-Sep 5Nature. 310(5980):777–781. doi: 10.1038/310777a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frunzio R., Chiariotti L., Brown A. L., Graham D. E., Rechler M. M., Bruni C. B. Structure and expression of the rat insulin-like growth factor II (rIGF-II) gene. rIGF-II RNAs are transcribed from two promoters. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):17138–17149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Donath C., Sander C. A yeast gene encoding a protein homologous to the human c-has/bas proto-oncogene product. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):704–707. doi: 10.1038/306704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H., Seidman M., Howard B. H., Gorman C. M. Enhanced gene expression by the poly(dT-dG).poly(dC-dA) sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2622–2630. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haubruck H., Disela C., Wagner P., Gallwitz D. The ras-related ypt protein is an ubiquitous eukaryotic protein: isolation and sequence analysis of mouse cDNA clones highly homologous to the yeast YPT1 gene. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4049–4053. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02750.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Grez M., Hauser H., Lindenmaier W., Schütz G. Synthesis of ds-cDNA involving addition of dCMP tails to allow cloning of 5'-terminal m RNA sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:285–292. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00062-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe D. G., Capon D. J., Delwart E., Sakaguchi A. Y., Naylor S. L., Goeddel D. V. Structure of the human and murine R-ras genes, novel genes closely related to ras proto-oncogenes. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90364-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madaule P., Axel R. A novel ras-related gene family. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90058-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Krystal M., Arnheim N. A member of a new repeated sequence family which is conserved throughout eucaryotic evolution is found between the human delta and beta globin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):5931–5947. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.5931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissley S. P., Short P. A., Rechler M. M., Podskalny J. M., Coon H. G. Proliferation of Buffalo rat liver cells in serum-free medium does not depend upon multiplication-stimulating activity (MSA). Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):441–446. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao C. D., Igarashi H., Chiu I. M., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A. Structure and sequence of the human c-sis/platelet-derived growth factor 2 (SIS/PDGF2) transcriptional unit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2392–2396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reymond C. D., Gomer R. H., Mehdy M. C., Firtel R. A. Developmental regulation of a Dictyostelium gene encoding a protein homologous to mammalian ras protein. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90199-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotwein P., Pollock K. M., Didier D. K., Krivi G. G. Organization and sequence of the human insulin-like growth factor I gene. Alternative RNA processing produces two insulin-like growth factor I precursor peptides. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4828–4832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruta M., Wolford R., Dhar R., Defeo-Jones D., Ellis R. W., Scolnick E. M. Nucleotide sequence of the two rat cellular rasH genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1706–1710. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salminen A., Novick P. J. A ras-like protein is required for a post-Golgi event in yeast secretion. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):527–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90455-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt H. D., Puzicha M., Gallwitz D. Study of a temperature-sensitive mutant of the ras-related YPT1 gene product in yeast suggests a role in the regulation of intracellular calcium. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):635–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90579-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt H. D., Wagner P., Pfaff E., Gallwitz D. The ras-related YPT1 gene product in yeast: a GTP-binding protein that might be involved in microtubule organization. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90597-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segev N., Mulholland J., Botstein D. The yeast GTP-binding YPT1 protein and a mammalian counterpart are associated with the secretion machinery. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):915–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90433-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimatsu A., Rotwein P. Mosaic evolution of the insulin-like growth factors. Organization, sequence, and expression of the rat insulin-like growth factor I gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7894–7900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B., D'Alonzo J. S., Scolnick E. M. Identification of effector residues and a neutralizing epitope of Ha-ras-encoded p21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4725–4729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stempien M. M., Fong N. M., Rall L. B., Bell G. I. Sequence of a placental cDNA encoding the mouse insulin-like growth factor II precursor. DNA. 1986 Oct;5(5):357–361. doi: 10.1089/dna.1986.5.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takanami M. RNA polymerase nascent product analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):497–499. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touchot N., Chardin P., Tavitian A. Four additional members of the ras gene superfamily isolated by an oligonucleotide strategy: molecular cloning of YPT-related cDNAs from a rat brain library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8210–8214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., McCormick F. A cytoplasmic protein stimulates normal N-ras p21 GTPase, but does not affect oncogenic mutants. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):542–545. doi: 10.1126/science.2821624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner P., Molenaar C. M., Rauh A. J., Brökel R., Schmitt H. D., Gallwitz D. Biochemical properties of the ras-related YPT protein in yeast: a mutational analysis. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2373–2379. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02514.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield H. J., Bruni C. B., Frunzio R., Terrell J. E., Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Isolation of a cDNA clone encoding rat insulin-like growth factor-II precursor. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):277–280. doi: 10.1038/312277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen B. M., Christensen A., Hubbert N. L., Papageorge A. G., Lowy D. R. The p21 ras C-terminus is required for transformation and membrane association. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):583–586. doi: 10.1038/310583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D. Retention of differentiation potentialities during prolonged cultivation of myogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):477–483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]