Abstract
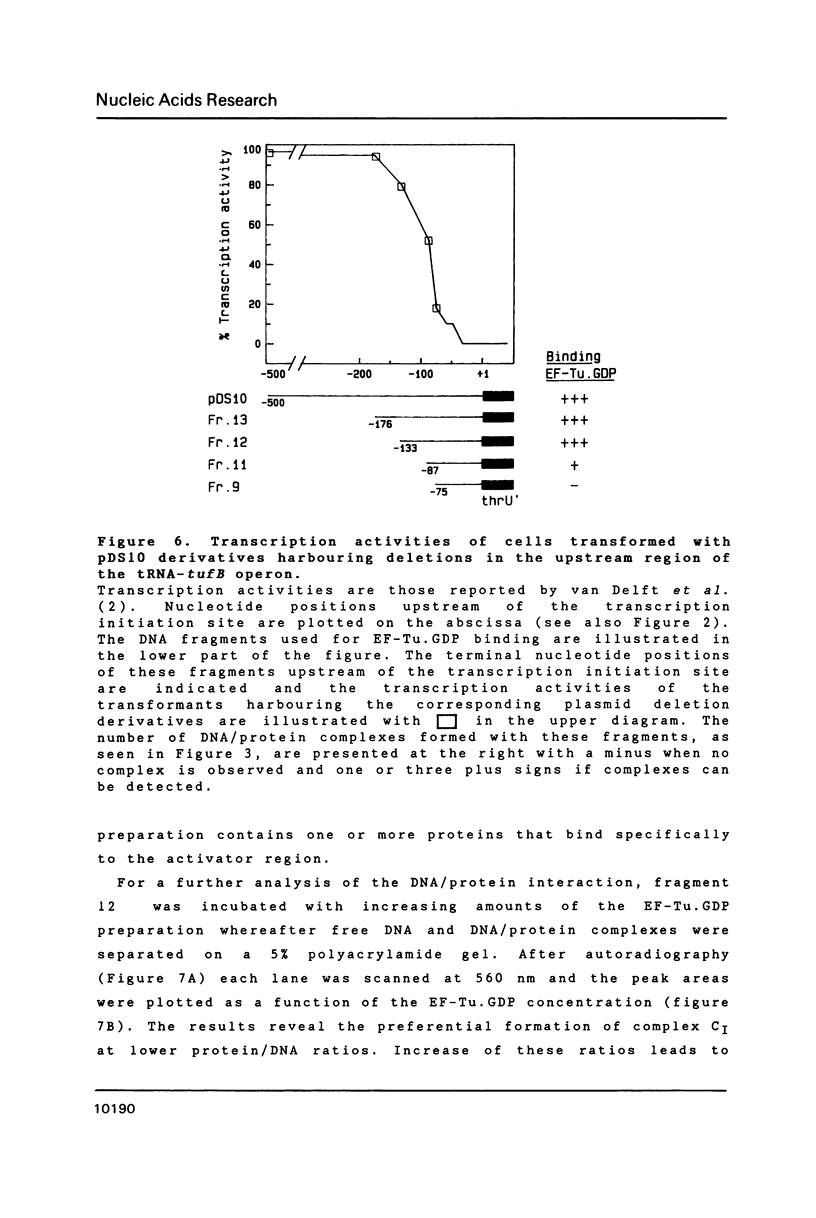
The polypeptide chain elongation factor EF-Tu of Escherichia coli is encoded by two genes, tufA and tufB, located in two different operons. Experiments in which either tufA or tufB was inactivated demonstrated that expression of the tRNA-tufB operon is dependent on a functioning tufA and thus on EF-Tu (1, to be published). In order to study a possible role of EF-Tu as trans-activator of the tRNA-tufB operon, we have investigated in vitro binding of an EF-Tu. GDP preparation to various DNA fragments of the operon. We demonstrate that specific binding occurs to a cis-acting region delimited from position -134 to the promoter, previously shown to enhance tufB transcription. Electrophoretic retardation assays reveal the formation of maximally three protein/DNA complexes, indicating that more than one protein molecule can bind to the DNA. The EF-Tu preparation used was obtained by affinity chromatography and appeared to be 95% pure. It lost its DNA binding activity upon further purification. That EF-Tu is nonetheless involved in the DNA binding is suggested by the observation that none of the three complexes is formed in the presence of kirromycin, an antibiotic that binds EF-Tu with high specificity. If so, EF-Tu.GDP most likely binds to the activator region of the tRNA-tufB operon in combination with another non-identified protein or component.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- An G., Friesen J. D. The nucleotide sequence of tufB and four nearby tRNA structural genes of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(1-2):33–39. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer B. F., Kar E. G., Elford R. M., Holmes W. M. Sequence determinants for promoter strength in the leuV operon of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1988;63(1):123–134. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90551-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch L., Kraal B., Van der Meide P. H., Duisterwinkel F. J., Van Noort J. M. The elongation factor EF-Tu and its two encoding genes. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1983;30:91–126. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60684-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossi L., Smith D. M. Conformational change in the DNA associated with an unusual promoter mutation in a tRNA operon of Salmonella. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):643–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90471-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinali G., Wolf H., Parmeggiani A. Effect of kirromycin on elongation factor Tu. Location of the catalytic center for ribosome-elongation-factor-Tu GTPase activity on the elongation factor. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):55–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11503.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gausing K. Construction and characterization of a tufA-lacZ fusion coding for an E. coli EF-Tu-beta-galactosidase chimeric protein. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(2):265–271. doi: 10.1007/BF00272915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gausing K. Rates of growth, ribosome synthesis and elongation factor synthesis in a tufA defective strain of E. coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(2):272–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00272916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L., de Boer H. A., Nomura M. DNA determinants of rRNA synthesis in E. coli: growth rate dependent regulation, feedback inhibition, upstream activation, antitermination. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90498-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson G. R., Rosenbusch J. P. Affinity purification of elongation factors Tu and Ts. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 1;79(1):8–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80338-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I., Travers A. A. Requirement for an upstream element for optimal transcription of a bacterial tRNA gene. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):248–250. doi: 10.1038/305248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., An G., Friesen J. D., Fill N. P. Location of the tufB promoter of E. coli: cotranscription of tufB with four transfer RNA genes. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):251–258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90250-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl L., Post L., Zengel J., Gilbert S. F., Strycharz W. A., Nomura M. Mapping of ribosomal protein genes by in vitro protein synthesis using DNA fragments of lambdafus3 transducing phage DNA as templates. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7365–7383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi T., Itoh S. Enhancement of transcriptional activity of the Escherichia coli trp promoter by upstream A + T-rich regions. Gene. 1986;44(1):29–36. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Delft J. H., Schmidt D. S., Bosch L. The tRNA-tufB operon transcription termination and processing upstream from tufB. J Mol Biol. 1987 Oct 20;197(4):647–657. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90471-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Delft J. H., Talens A., De Jong P. J., Schmidt D. S., Bosch L. Control of the tRNA-tufB operon in Escherichia coli. 2. Mechanisms of the feedback inhibition of tufB expression studied in vivo and in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 1;175(2):363–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14205.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijgenboom E., Bosch L. Transfer of plasmid-borne tuf mutations to the chromosome as a genetic tool for studying the functioning of EF-TuA and EF-TuB in the E. coli cell. Biochimie. 1987 Oct;69(10):1021–1030. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H., Chinali G., Parmeggiani A. Kirromycin, an inhibitor of protein biosynthesis that acts on elongation factor Tu. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4910–4914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H., Chinali G., Parmeggiani A. Mechanism of the inhibition of protein synthesis by kirromycin. Role of elongation factor Tu and ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):67–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11504.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Sugisaki H., Takanami M., Kaziro Y. The nucleotide sequence of the cloned tufA gene of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(1-2):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Delft J. H., Mariñon B., Schmidt D. S., Bosch L. Transcription of the tRNA-tufB operon of Escherichia coli: activation, termination and antitermination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9515–9530. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meide P. H., Vijgenboom E., Dicke M., Bosch L. Regulation of the expression of tufA and tufB, the two genes coding for the elongation factor EF-Tu in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1982 Mar 22;139(2):325–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80881-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meide P. H., Vijgenboom E., Talens A., Bosch L. The role of EF-Tu in the expression of tufA and tufB genes. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Feb 1;130(2):397–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]